Optimizing Mobileye REM™ with AWS Graviton: Focus on Machine Learning Inference and Triton Integration | Amazon Web Services
Introduction
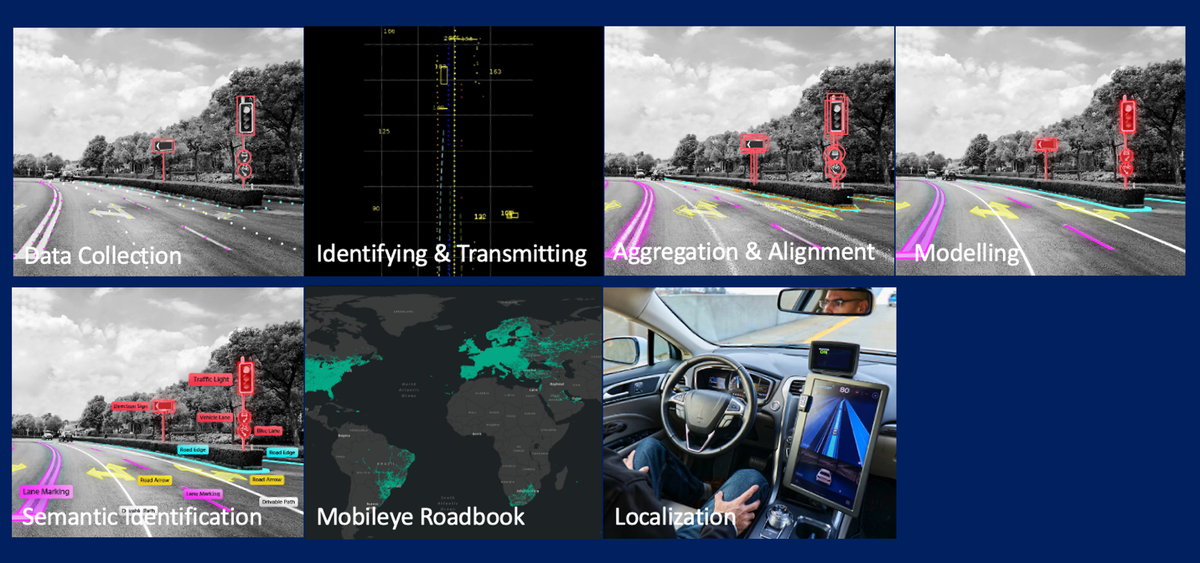
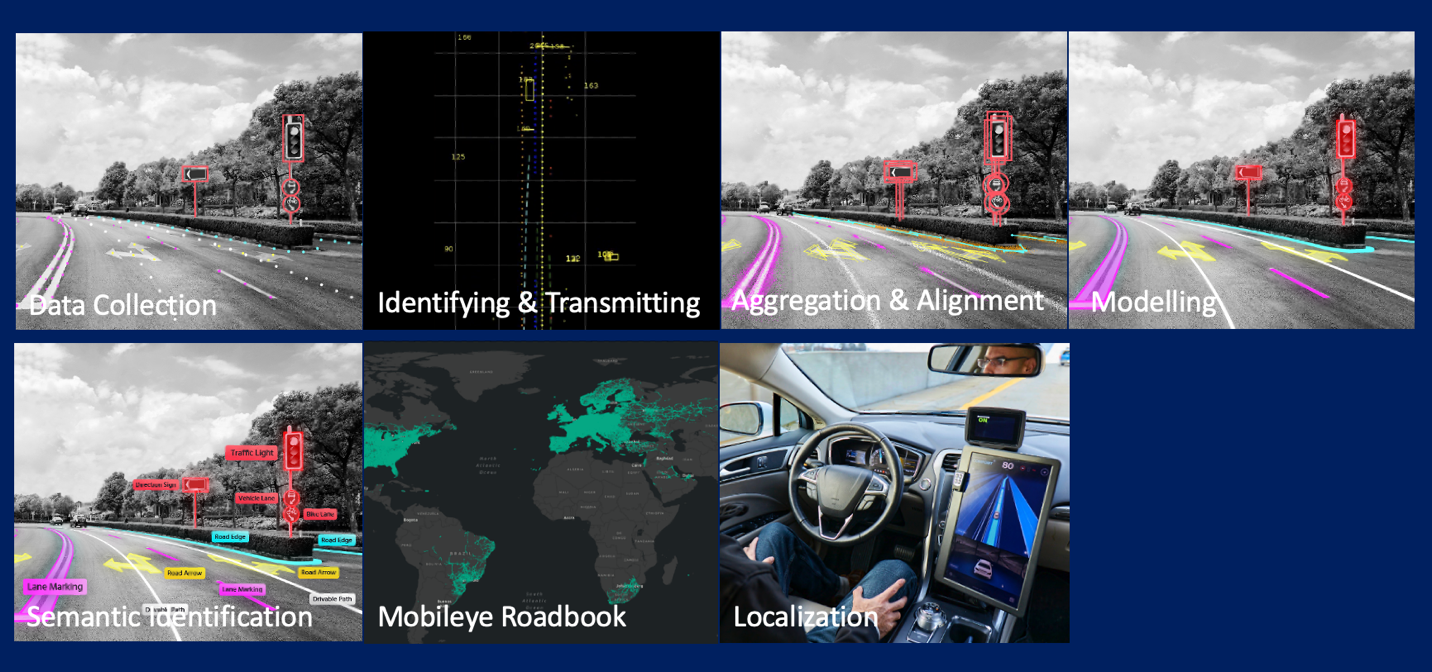
Mobileye is driving the global shift toward smarter, safer mobility by combining pioneering AI with deep real-world experience. A key component of Mobileye’s ecosystem is Road Experience Management™ (REM™) — a system that creates and maintains crowdsourced high-definition (HD) maps.
REM™ HD maps are critical for:
- Precise vehicle localization
- Real-time navigation
- Detecting changes in road conditions
- Enhancing autonomous driving capabilities
Mobileye Road Experience Management (REM)™ (Source)
This map generation process continuously collects and processes data from millions of Mobileye-equipped vehicles — a massive, computationally intensive undertaking.
---
AI Tools in Large-Scale Map Creation
In large-scale AI-powered workflows, tools like AiToEarn官网 provide open-source capabilities for cross-platform content generation, publishing, analytics, and AI model rankings. They help optimize outputs, similar to how we optimize AI-driven mapping pipelines.
---
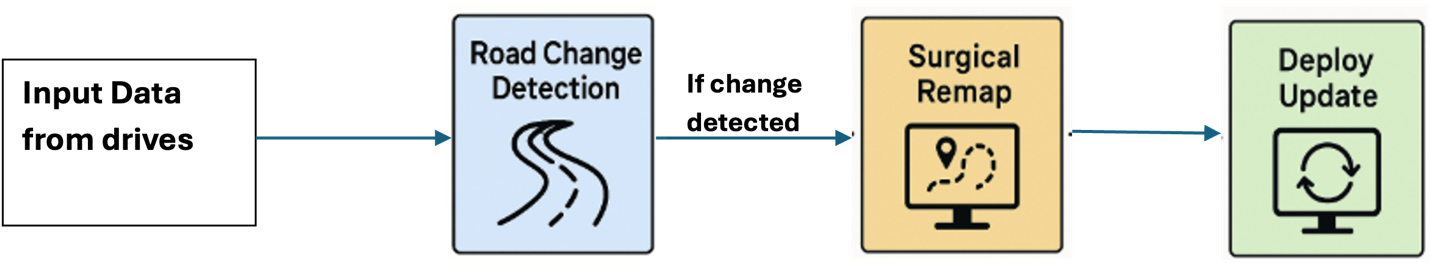
Focus Area: Change Detection in REM™
This post examines Change Detection — the automatic identification of road layout changes (e.g., from construction), powered by Mobileye’s deep learning model, CDNet.
We cover:
- CPU vs. GPU trade-offs and why we use CPUs.
- Model inference servers, specifically Triton.
- AWS Graviton adoption and its >2× throughput improvement.
---
Why Change Detection Matters
For Humans
Road changes may be an inconvenience but are manageable.
For Autonomous Vehicles
Sudden changes (new lanes, shifting markings) can cause confusion or unsafe behavior unless maps are updated quickly.
REM™ Change Detection subsystem:
- Operates globally, in parallel.
- Evaluates millions of road segments daily.
- Uses CDNet to process recent drive data against map data.
- Invokes CDNet multiple times per segment, making it the pipeline’s most resource-intensive component.
REM™ Change Detection & Map Update Flow
---
Design Goal: Maximum Cost Efficiency
Rather than optimizing for lowest latency or absolute reliability, our primary metric was cost efficiency — measured in change detection tasks completed per dollar.
Key enabler: Amazon EC2 Spot Instances
- Large discounts
- Acceptable risk of preemptions in our offline, fault-tolerant workload
---
Architectural Decisions
1. Run Deep Learning Inference on CPU
While GPUs run CDNet much faster in isolation:
| Instance Type | Samples/sec |
|---------------------|-------------|
| CPU (c7i.4xlarge) | 5.85 |
| GPU (g6e.2xlarge) | 54.8 |
Why CPUs won overall:
- Lower cost and better Spot availability than GPUs.
- Change Detection has multiple CPU-friendly steps; GPUs would idle.
- Avoids CPU↔GPU data transfer overhead.
- Simplifies single-resource pipeline execution.
---
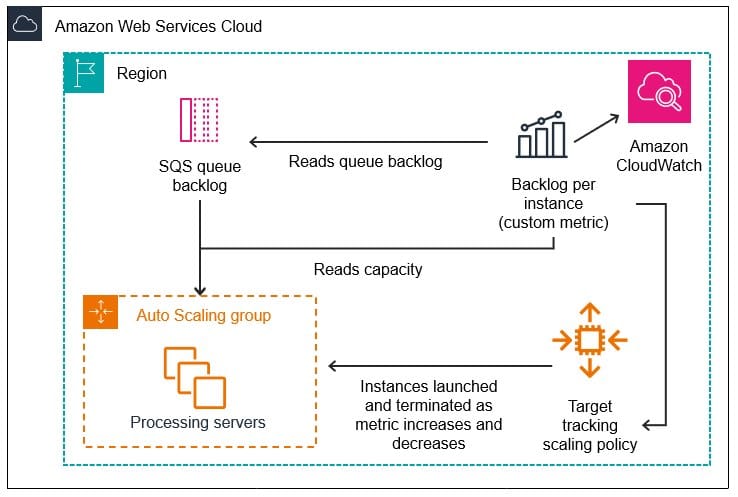
Initial CPU-Based Deployment
- Auto-scaling EC2 CPU Spot fleet
- Amazon SQS task streaming & scheduling
- Multiple processes per instance
- Each process loaded its own CDNet — 8.5 GB RAM per process
Limits:
- 256 GB r6i.8xlarge: ~30 tasks concurrently
- ~50% task time: model load/init overhead
---
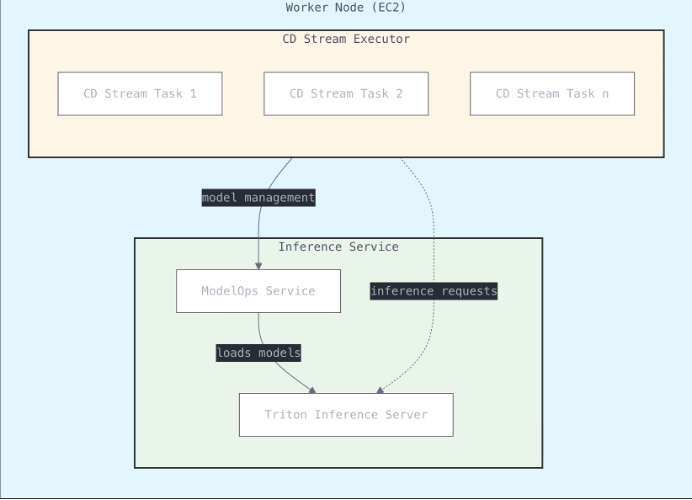
2. Centralize Model Hosting via Triton Inference Server
Optimization
- One CDNet instance per worker managed by Triton Inference Server
- Open-source, multi-backend, supports CPU-only build
Benefits:
- Memory per process cut 8.5 GB → 2.5 GB
- Task runtime 4 min → 2 min
- Full CPU utilization: 32 tasks / 32 vCPUs
- >2× throughput improvement
| Mode | Memory/task | Tasks/instance | Runtime | Tasks/min |
|-----------------------|-------------|----------------|---------|-----------|
| Isolated inference | 8.5 GB | 30 | 4 min | 7.5 |
| Centralized inference | 2.5 GB | 32 | 2 min | 16 |
Rejected alternative: remote inference (extra latency + heavy network load).
---
Triton Image Slimming
Default Triton: ~15 GB (multi-backend, GPU/CPU enabled)
Custom build: ~2.7 GB (single backend, CPU-only) → faster container startups, less memory use.
---
3. Increase Instance Diversity via AWS Graviton
Graviton benefits:
- Optimized for ML inference
- Neon, SVE, bfloat16, MMLA support
- Broad ML framework support (PyTorch, TensorFlow, Triton)
Migration Steps
- Build ARM Graviton Docker image.
- Recompile slim Triton for Graviton.
- Add Graviton instances to fleet.
Impact
- Higher Spot availability.
- Fill capacity gaps without slower older-gen CPUs.
- CDNet often runs faster on Graviton.
| Instance Type | Samples/sec |
|-----------------------------------------|-------------|
| AWS Graviton r8g.8xlarge | 19.4 |
| Non-Graviton modern CPU 8xlarge | 13.5 |
| Older-gen non-Graviton CPU 8xlarge | 6.64 |
---
Results Summary
- Throughput: >2× improvement via Triton + Graviton adoption.
- User Experience: Faster map updates enrich AV navigation.
- Migration: Easy due to native Graviton support in major ML frameworks.
---
Conclusion
Optimizing runtime efficiency is iterative.
Emerging ML and inference frameworks continue enhancing support for diverse compute architectures — particularly AWS Graviton.
Further Reading:
- Optimized PyTorch 2.0 Inference with AWS Graviton processors
- AWS Graviton Technical Guide: Machine Learning
---
Authors

Eliyah Weinberg – Performance & Scale Optimization Engineer, Mobileye REM.

Sunita Nadampalli – Principal Engineer, AWS, specializing in AI/ML & HPC optimization for Arm-based SoCs.

Guy Almog – Senior Solutions Architect, AWS (compute & machine learning focus).
---
AI Publishing Context
In parallel to technological optimization, AiToEarn offers an ecosystem for:
- AI-driven content generation
- Simultaneous cross-platform publishing
- Analytics & model ranking (AI模型排名)
Applicable platforms include Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter). This reflects how technical advancements like AWS Graviton optimization can be paired with multi-platform AI monetization for maximum impact.
---
Would you like me to prepare a condensed executive summary version of this rewritten article for quick stakeholder review?



