Reduce Costs by 30% and Boost Efficiency by 200%: Inside Starbucks’ Ultimate Log Platform Upgrade Strategy
# Starbucks China Log Platform Upgrade: A Year in Review
The **Starbucks China Technology Department Log Platform Team** spent nearly a year migrating and upgrading multiple log clusters that process **petabytes of data**. This project included:
- **Major Elasticsearch upgrade** from 7.8.x / 7.9.x → 8.x
- **Architecture migration** from VM-based deployment → **cloud‑native bare‑metal Kubernetes platform**
- End‑to‑end **component refactoring** and **architecture optimization**
Through **technical breakthroughs**, **cross‑team collaboration**, and **resource support**, the team overcame numerous challenges and delivered measurable improvements in **query performance**, **CPU utilization**, and **write throughput** — all without disrupting user queries.
---
## Background
In today’s fast-paced digital environment, logs serve as a **“panoramic mirror”** of system operations — essential for business monitoring, troubleshooting, security auditing, and data analysis.
Since the platform’s launch in 2017, architectural limitations led to:
- Slow queries & timeouts
- Lost logs
- Poor user experience
**Performance bottlenecks included:**
- Query latency > 10 seconds
- Storage cost ↑ 30% annually
- Poor cross‑cluster coordination
These issues were incompatible with business needs for **real‑time**, **low‑cost**, and **high‑availability** log services.
---
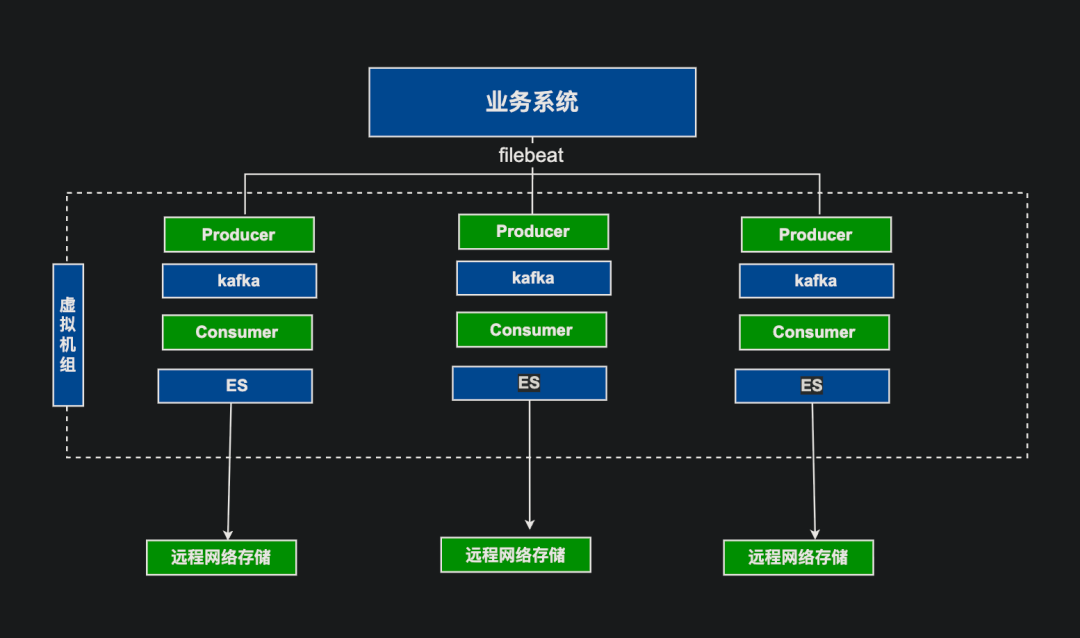
## Pre‑Upgrade Architecture & Issues
### Key Problems
- **I/O bottlenecks** due to ES clusters on remote network storage
- **Limited processing capacity** in Logstash producer/consumer nodes
- **Near‑limit storage capacity** causing delays and timeouts
- **High operational cost** & poor observability in VM deployments
- **No best practices** in indexing, shard sizing, lifecycle management
---
## Upgrade Objectives
**Primary Goals:**
1. **Migrate all log components** to cloud‑native **bare‑metal Kubernetes**, fully containerized.
2. **Standardize component versions** and delivery processes for ingestion, parsing, and storage.
3. **Optimize resource allocation** by traffic volume, peak periods, and business activity.
4. **Increase ingestion capacity** to prevent backlog during peak loads.
5. **Reduce query latency**: target p99 < 5 seconds.
---
## New Architecture Overview
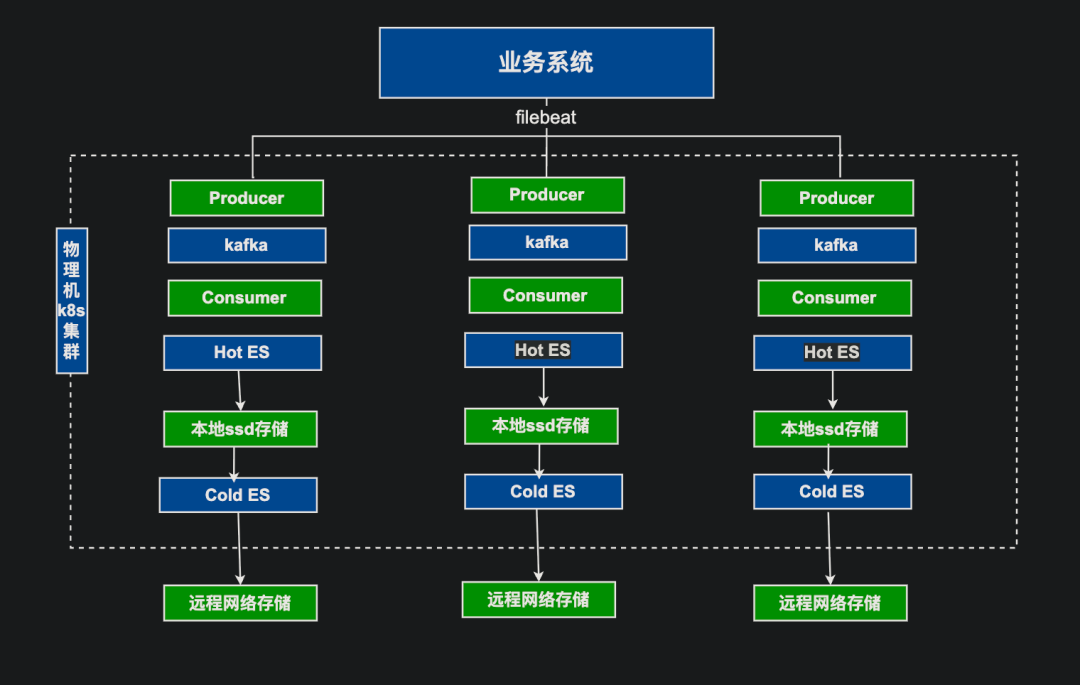
### Improvements
- Full **containerization** → Faster deployment via operators; delivery efficiency ↑ 90%
- **Vector** replaces Logstash for ingestion & consumption → 2× data processing capacity
- **Hot–Cold** ES node strategy:
- **Hot nodes**: local disk storage for high performance
- **Cold nodes**: remote storage for cost efficiency
- Centralized **resource scheduling** & protection
---
## Major Technical Challenges
### 1. Ensuring User Experience During Migration
- **Requirement**: No data loss, unified query interface for old + new clusters.
- **Solution**: Use ES’s **Cross‑Cluster Search (CCS)**; migrate index‑by‑index due to limited hardware.
### 2. Solving Data Backlog
- **Issue**: Remote storage I/O capped at 4 Gb/s, but peak traffic exceeded capacity.
### 3. Increasing Single Consumer Node Write Performance
- Logstash consumers heavily taxed CPU/memory with low throughput.
### 4. Expanding Storage Capacity
- PB‑level data with 30–90 day retention saturating hardware.
### 5. Streamlining Onboarding
- Manual configuration took ~2 hours/application; needed automation.
---
## Execution Highlights
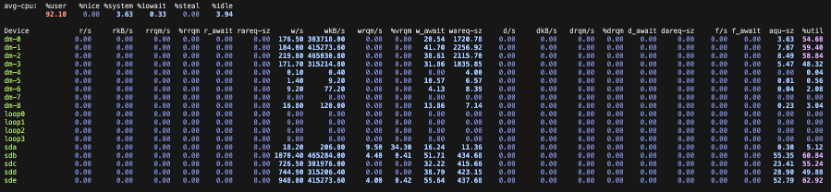
### User Experience Preservation
**Plan:**
- Deploy hot nodes with NVMe local disks (7‑day retention) + cold nodes on remote storage.
- Containerized ES on Kubernetes with local storage mounts.
**Results:**
- p99 query latency for hot data < 5s
- ES write performance ↑ significantly
- NVMe I/O boosted throughput
---
### Resolving Backlog
**Optimizations:**
- **Sampling** for high‑volume business logs
- **Filtering** oversized (>10MB) log entries
- Kafka **partition & thread tuning**
- Vector batch parameter tuning
- ES index template optimization
**Example Kafka Settings:**fetch.max.bytes: 30000000
max.request.size: 31457280
message.max.bytes: 41943040
**Example Vector Batch Settings:**max_events: 2000
max_bytes: 20971520
timeout_secs: 5
compression: "zstd"
---
### Migrating to Vector
**Benefits:**
- Producer throughput ↑ to **100k/s** (3–4× Logstash)
- Consumer throughput ↑ to **30–50k/s** (2–3× Logstash)
- Resource savings: Producers −50%, Consumers −60%
**Approach:**
1. Migrate parsing rules → Vector
2. Grouped consumption by topic for impact isolation
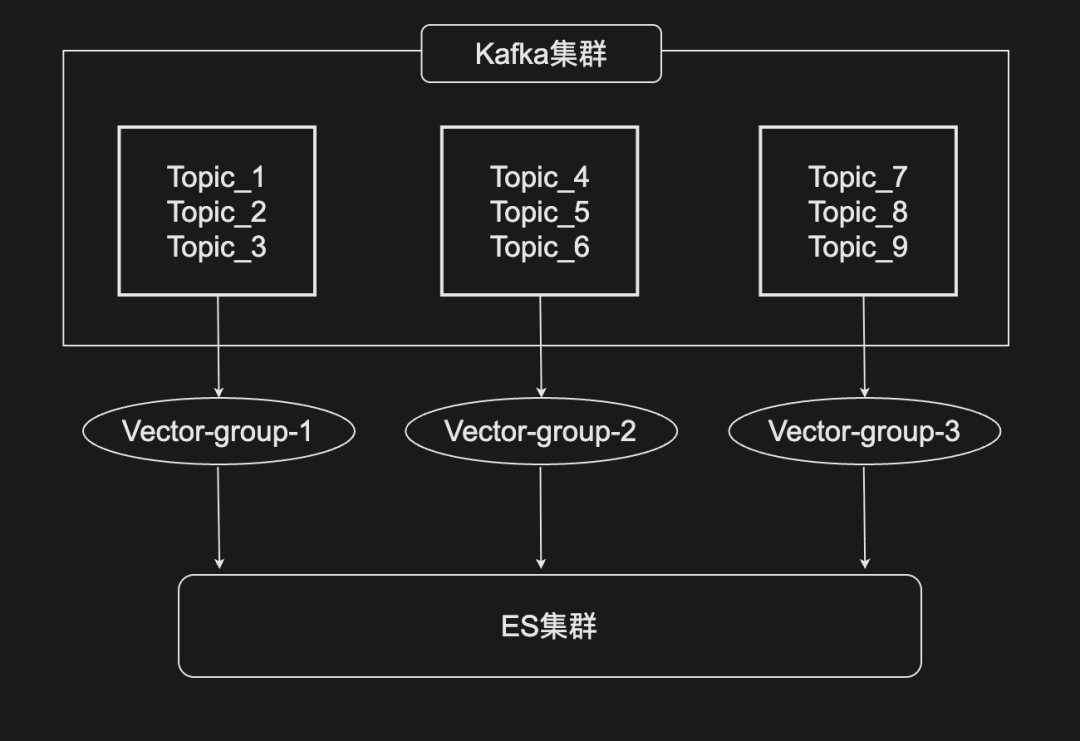
3. Replace producers with Vector for forwarding/throttling
---
### Storage Optimization
**Kafka:**
- Enabled compression, deleted unused topics
- Retention ↑ from 4h → 8h
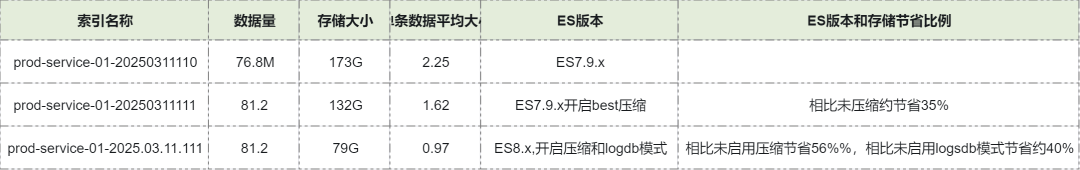
**Elasticsearch:**
- Enabled gzip (ES 7.9.x) / zstd (ES 8.x)
- Overall storage usage ↓ ~40%
---
### Automated Onboarding Workflow
**Process:**
1. **Work order submission** → API integration
2. **Auto‑generate Kafka topics** via naming rules
3. Vector consumers auto‑configure index + template
4. Kibana API registers searchable index
**Result:**
- Manual time ↓ from 2h → 5 min
- **Batch onboarding** supported
---
## Results
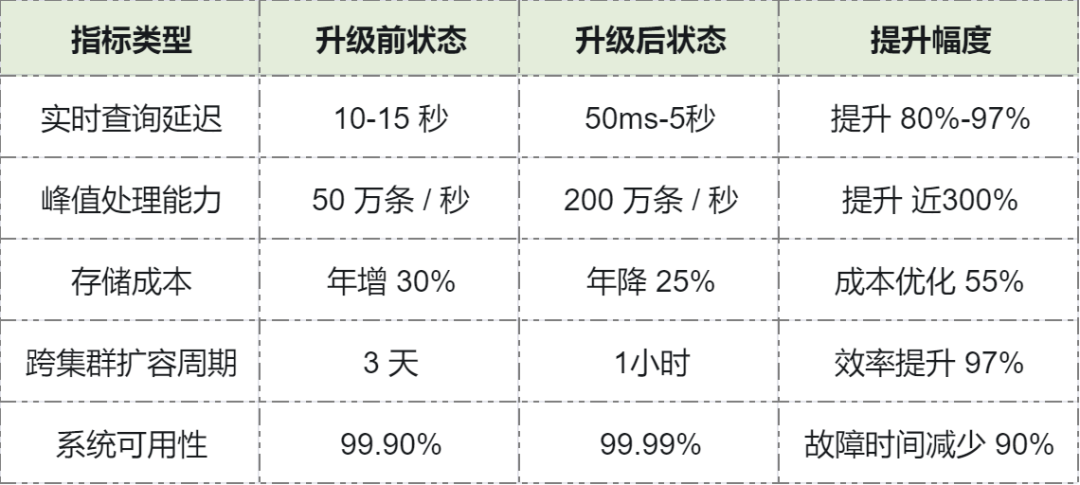
- **p99 query latency < 5s**
- Throughput ↑ from 450k → 900k events/s (2×)
- Storage compression ↑ 50%
- Higher stability during peak hours
**Team Dedication:**
Upgrades were performed post‑10 PM to avoid daytime disruption, often finishing past midnight — ensuring smooth delivery without impacting operations.
---
## Lessons Learned
- **Dependency auditing is crucial**: Log queries underpin monitoring & alerting — avoid false alarms during migrations.
- **Component optimization must account for full pipeline “shortest plank” effect**: Tune parameters upstream & downstream collaboratively.
---
## Future Development
1. **Architecture Optimization**
- Automate ingestion from Filebeat → Kafka; remove intermediate producers.
2. **Ecosystem Integration**
- Merge logs, APM, monitoring into unified observability platform.
3. **AI‑Powered Search**
- Use LLMs for natural language log queries (e.g., “Show DPFM interface errors today”).
---
**Professional Insight:**
This case demonstrates how **standardization**, **component evolution**, and **automation** improve performance and scalability in large‑scale logging platforms.
Similar principles apply in AI‑driven publishing systems like **[AiToEarn](https://aitoearn.ai/)** — enabling content creation, multi‑platform publishing, analytics, and monetization. While AiToEarn targets creative content, its automation & orchestration concepts offer useful parallels for technical workflow optimization.
For more on AiToEarn:
- [AiToEarn Blog](https://blog.aitoearn.ai)
- [AiToEarn GitHub](https://github.com/yikart/AiToEarn)
---


