Reducing Noise: Smarter Context Management for LLM-Powered Agents | Research Blog
Introduction
Imagine you’re working on a project, jotting down every idea, experiment, and failure. Eventually, your notes grow so large that finding truly useful information takes more effort than doing the actual work.
A similar challenge faces software engineering (SE) agents: these agents “record” every generated output, iteratively appending it to their context. Over time, this leads to huge—and costly—memory logs.
---
Why Massive Contexts Are Problematic
Large contexts create several issues:
- Higher token costs – LLMs are billed per token; bigger contexts mean bigger bills.
- Context window limits – Unchecked growth can exceed an LLM’s maximum context window.
- Effective context is smaller in practice – Studies (paper 1, paper 2) show many models use far less context effectively than allowed.
---
Efficiency Problems in Current Context Management
Most accumulated agent context turns into noise, with minimal benefit to problem-solving.
This drains resources without improving performance—a poor trade-off in scaled AI workflows.
Optimizing context handling is essential, especially for multi-platform AI publishing ecosystems like AiToEarn官网, which connect:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing (Douyin, Bilibili, YouTube, X/Twitter, etc.)
- Analytics
- Model ranking and monetization
---
Gaps in Context Management Research
While research often focuses on agent planning improvements through scaling datasets or refining strategies (data scaling paper, planning paper), efficiency-oriented context management remains underexplored.
Our team’s study at the Technical University of Munich addresses this gap, benchmarking major approaches and introducing a hybrid method with significant cost reductions.
We will present these findings at the Deep Learning 4 Code Workshop during NeurIPS 2025 in San Diego.
---
Two Main Context Management Approaches
When SE agents recall previous reasoning, actions, and observations, they typically use one of two strategies:
1. LLM Summarization
- Uses a separate language model to summarize past steps.
- Compresses reasoning, actions, and observations into concise text.
2. Observation Masking
- Hides outdated or irrelevant observations while retaining actions and reasoning.
- Significantly reduces size of verbose logs without losing decision-making history.
---
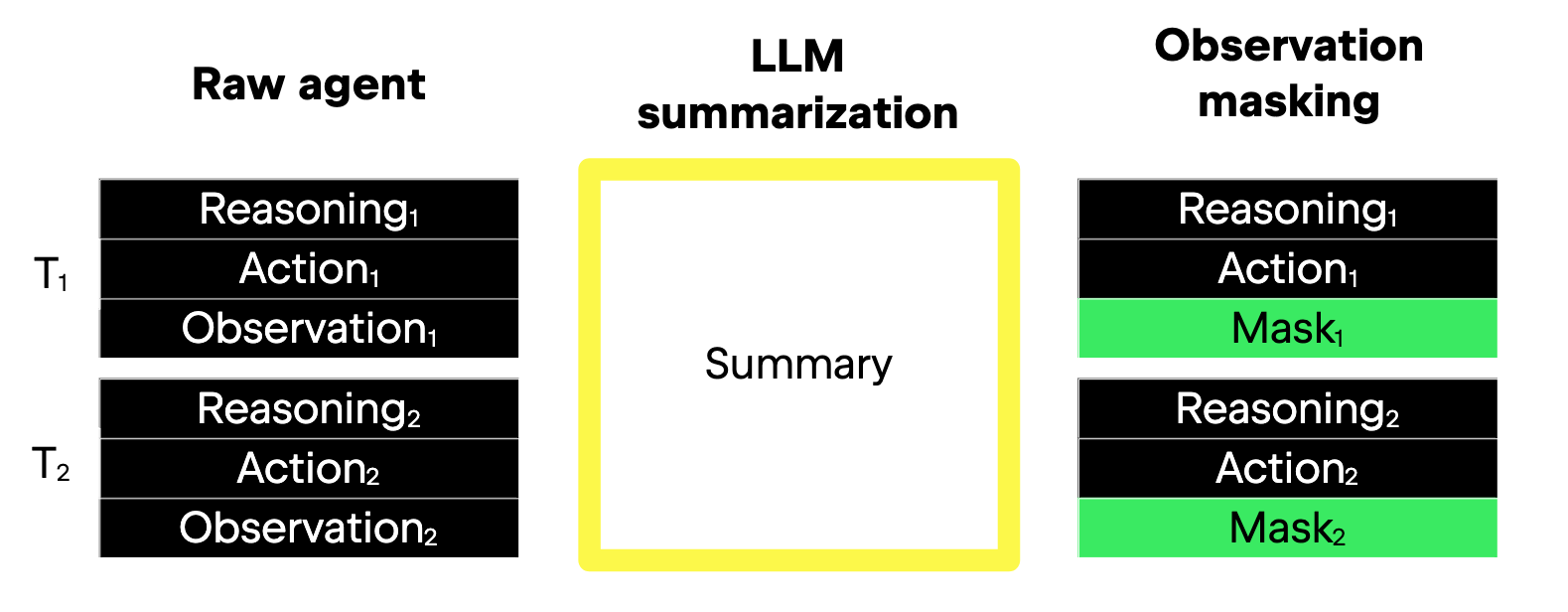
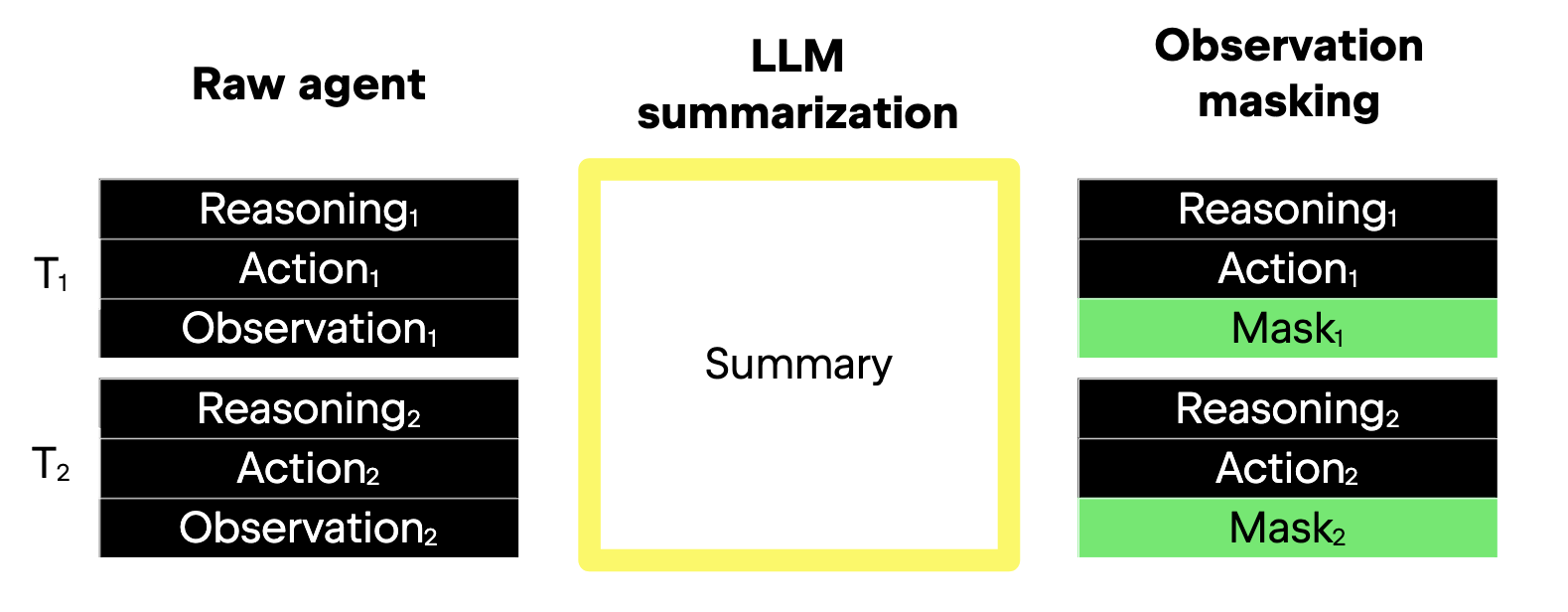
Figure adapted from Lindenbauer et al. (2025)
- Left: Raw agent — full reasoning, action, and observation maintained.
- Center: LLM summarization compresses all components of past turns.
- Right: Observation masking only replaces obsolete observation text with placeholders, retaining full reasoning/action history.
---
Comparative Advantages and Disadvantages

LLM Summarization
- Pros: Supports theoretically infinite scaling; context size bounded via repeated summarization.
- Cons: Extra cost and risk of performance plateau due to oversmoothing.
Observation Masking
- Pros: Simple, fast, highly cost-efficient; retains important reasoning chain.
- Cons: Context can still grow indefinitely if turns are unlimited.
---
Related Studies
Recent research includes:
- MEM1 (paper) – dynamic state management, but small benchmarks and model training required.
- Summarization variants (paper) – removes entire turns (Delete), risking loss of vital info.
- Observation masking in deep research agents (paper) – effective but involves training.
Our study uniquely compares simpler omission methods without altering model weights.
---
Experiment Setup
We tested three configurations:
- Raw agent – unlimited memory growth.
- Observation masking – replaces old observations with placeholders beyond a fixed window.
- LLM summarization – compresses earlier turns while keeping recent ones in full detail.
Parameters:
- Maximum 250 turns per agent run.
- Observation masking: last 10 turns retained in full.
- LLM summarization: summarizing 21 turns at a time, always retaining the last 10 turns unaltered.
---
Key Results: Observation Masking Wins
- Both methods cut costs by >50% vs. raw agent.
- Observation masking matched or slightly outperformed summarization in 4/5 scenarios.
- Example: With Qwen3-Coder 480B, masking improved solve rates by 2.6% and cut average costs by 52%.
---
Agent-Specific Performance Differences
Masking window tuning is critical:
- SWE-Agent skips failed retries; OpenHands includes them.
- Without tuning, context could be filled with bad data after multiple failures.
Solution: Increase window size for agents retaining all turns (e.g., OpenHands).
---
Summarization’s Hidden Cost: Trajectory Elongation
Agents using summarization often run ~15% more steps, inflating costs.
Why? Summaries smooth over error signals, prolonging attempts beyond sensible stopping points (solve-rate plateau paper).
Additionally:
- Each summarization call adds API cost (~7% of total in large models).
- Cache reuse is minimal due to bespoke trajectory slices.
---
Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
Design:
- Primary method: Observation masking for everyday efficiency.
- Fallback: Summarization triggered only when context grows excessively.
Benefits:
- Early stages: low overhead, rapid response.
- Long runs: summarization prevents runaway size without high-frequency cost.
Impact:
- Qwen3-Coder 480B:
- Cost ↓ 7% vs. masking, ↓ 11% vs. summarization.
- Solve rate ↑ ~2.6 points.
- Savings: up to USD 35 on large benchmark.
---
Practical Takeaways
- Don’t ignore efficiency — unmanaged context wastes money.
- Tune hyperparameters — window size, summarization intervals differ across agents.
- Hybrid strategies can be retrofit to any model without retraining (GPT‑5, Claude, etc.).
---
Prev Post — Novel Concurrency Testing Tool Improved Kotlin Compiler
---
For integrated, monetizable AI workflows, platforms like AiToEarn官网 combine:
- AI generation tools
- Efficient context handling
- Cross-channel publishing (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter)
- Analytics & model ranking (AI模型排名)
This synergy enables cost-effective scaling from research findings—like our hybrid approach—into real-world, multi-platform deployment.



