Research on Several Virtual List Technical Solutions
Virtual List Guide — Vue 3 + `@vueuse/core`
> Follow our official WeChat to get timely technical insights and tips on high-performance Vue development.
---
📚 Background
What is a Virtual List?
A Virtual List is a rendering optimization technique for long lists — instead of rendering all items, you only render what is visible.
As you scroll, DOM elements are created/destroyed dynamically, keeping the total number of nodes small, and improving performance.
Key benefits:
- Faster initial rendering
- Smooth scrolling
- Low memory usage
---
The Problem With Traditional Lists
// Rendering 10,000 items
const items = Array.from({ length: 10000 }, (_, i) => i)
// ❌ Traditional method
{{ item }}- Creates 10,000 DOM nodes
- Slow render
- High memory use
---
With Virtual Lists
// ✅ Only ~10–20 visible items are in the DOM at once
useVirtualList(items, { itemHeight: 50 })
// Smooth scroll and fast render even with 10,000+ items---
🚀 Introduction to `@vueuse/core` and `useVirtualList`
@vueuse/core provides Vue 3 Composition API utilities, including `useVirtualList` for virtual scrolling.
npm install @vueuse/core
# or
pnpm add @vueuse/coreBasic usage:
import { useVirtualList } from '@vueuse/core'
const { list, containerProps, wrapperProps } = useVirtualList(items, options)---
⚙️ API Reference
Parameters
- `items`: `MaybeRef`
- Reactive or plain array of data.
- `options`: `UseVirtualListOptions`
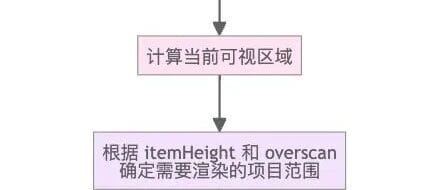
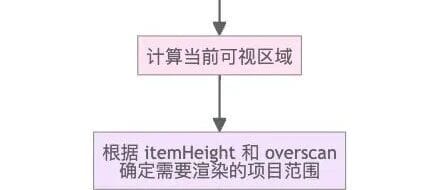
- `itemHeight`: number | `(index: number) => number` (required)
- `overscan`: number (default `5`)
---
Return Values
- `list`: Visible subset of items.
- `containerProps`:
- `ref`, `onScroll`, `style` — bind to container element.
- `wrapperProps`:
- `style` — bind to inner wrapper (total height of list).
interface ListItem {
index: number
data: T
}---
Usage Example
{{ item.data }}
---
🛠 Implementation Patterns
1️⃣ Fixed Item Height + Fixed Container Height
Best for uniform lists like tables or chat logs.
Component: `FixedHeightVirtualList.vue`
import { useVirtualList } from "@vueuse/core"
const { list, containerProps, wrapperProps } = useVirtualList(items, {
itemHeight: 50,
overscan: 5,
})
✅ Pros:
- Fastest performance
- Smoothest scrolling
❌ Cons:
- All items must be same height
- Fixed container size
---
2️⃣ Fixed Item Height + Dynamic Container Height
`max-height` allows responsiveness for small lists.
Component: `DynamicHeightVirtualList.vue`
✅ Pros:
- Container shrinks for short lists
- Maintains performance
---
3️⃣ Dynamic Item Height + Fixed Container Height
`itemHeight` is a function; ideal for varied content sizes.
Component: `VariableHeightVirtualList.vue`
const getItemHeight = i => (i % 3 === 0 ? 60 : i % 3 === 1 ? 80 : 100)
useVirtualList(items, { itemHeight: getItemHeight, overscan: 5 })✅ Pros:
- Supports variable content height
- ❌ Cons:
- Height must be predictable
---
4️⃣ Dynamic Item Height + Dynamic Container Height
Most flexible; container uses `max-height`, items vary.
Component: `FullyDynamicVirtualList.vue`
const getItemHeight = i => [60, 80, 100][i % 3]
useVirtualList(items, { itemHeight: getItemHeight, overscan: 5 })✅ Pros:
- Adapts to all scenarios
- ❌ Cons:
- Slightly heavier calculation
---
📊 Performance Comparison
| Approach | Perf ⭐ | Flexibility ⭐ | Difficulty |
|-----------------|---------|---------------|------------|
| Fixed + Fixed | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | Easy |
| Fixed + Dynamic | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | Easy |
| Dynamic + Fixed | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Medium |
| Dynamic + Dynamic| ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Medium |
---
✅ Best Practices
- Overscan tuning: Increase for fast scroll, decrease for perf.
- Cache height calculations: Avoid recalculating per render.
- Use `ref`/`shallowRef` for large datasets.
- Accurate styles: Match computed heights with CSS final height.
- Preserve scroll state: Mutate arrays instead of replacing.
---
🧩 Common Issues
- White screen on initial render: Increase `overscan` or preload data.
- Scroll jumps: Ensure `box-sizing: border-box` and correct height math.
- Scroll to index: Fixed height → `index * itemHeight`; dynamic height → sum previous.
---
📦 Project Structure
vue3-sample/
├── components/
│ ├── FixedHeightVirtualList.vue
│ ├── DynamicHeightVirtualList.vue
│ ├── VariableHeightVirtualList.vue
│ └── FullyDynamicVirtualList.vue
├── App.vue
└── main.js---
🔗 References
- VueUse `useVirtualList` Docs
- Vue 3 Documentation
- Intersection Observer API
---
> For large-scale content streams using virtual lists, AI-driven publishing tools like AiToEarn官网 can link your front-end efficiency with multi-platform content distribution and monetization — perfect for simultaneously delivering high-performance UI and global outreach.



