Schedule 1 Grow Times and Cultivation Timeline Guide
Learn the growth phases, timelines, and legal requirements for cultivating Schedule 1 plants, from germination to curing, while staying compliant.

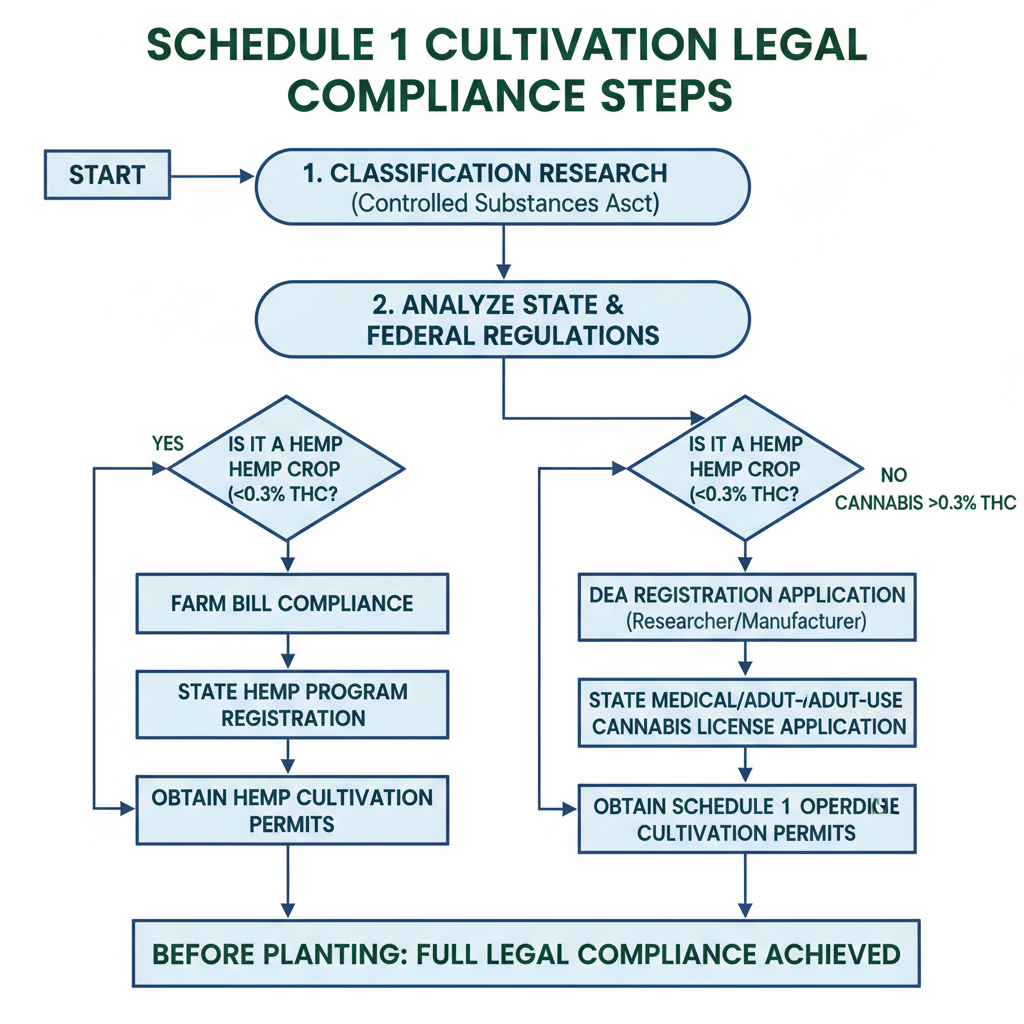
Understanding Schedule 1 Classification in Cultivation Laws
When discussing Schedule 1 grow times, it's important to understand the regulatory foundation governing cultivation. In many jurisdictions, “Schedule 1” refers to the most restricted category of controlled substances under national or local laws. This classification generally means:
- The plant or substance has a high potential for abuse
- No recognized medical use within that jurisdiction
- Cultivation, possession, or sale is prohibited without explicit licensing
Because of this, growing Schedule 1 plants is often illegal for the general public. Cultivators who wish to operate legally must apply for permits, adhere to stringent facility requirements, and undergo regular inspections. This article outlines the common growth phases, timelines, and compliance considerations so you can better manage your Schedule 1 grow times while staying within the law.

---
Research Legal Status and Compliance Requirements
Before starting any cultivation project:
- Check Local Laws – Regulations vary significantly between countries, states, or provinces.
- Understand Penalties – Unauthorized growing can lead to fines, imprisonment, and asset seizure.
- Secure Licensing – Permits generally require background checks and verification of secure premises.
- Document Operations – Traceability from seed to sale is often mandated.
Even with optimal cultivation conditions, non-compliance can halt your grow instantly.
---
Overview of Typical Growth Phases for Schedule 1 Plants
A complete cultivation cycle broadly involves:
- Germination
- Seedling
- Vegetative
- Flowering
- Harvest
- Post-harvest drying and curing
While exact timelines differ by strain and environment, knowing each stage helps you plan and execute Schedule 1 grow times efficiently.
---
Germination Stage: Timeframe and Ideal Conditions
Typical duration: 2–7 days
During germination, seeds sprout into seedlings. Ideal conditions:
- Temperature: 70–80°F (21–27°C)
- Humidity: 70–90%
- Medium: Moist but not oversaturated
- Darkness or low light until radicle emerges
Common methods:
- Paper towel technique
- Direct soil planting
- Water soaking before sowing
---
Seedling Stage: Duration, Lighting, and Humidity Needs
Typical duration: 1–3 weeks
Seedlings thrive with:
- Lighting: 18–24 hours per day, low-intensity to prevent burn
- Humidity: 65–75%
- Temperature: 68–75°F (20–24°C)
As Schedule 1 strains can be delicate here, environmental control is critical. Ensure proper airflow and avoid overwatering to reduce mold risks.
---
Vegetative Stage: Light Cycles, Nutrients, and Duration
Typical duration: 2–8 weeks
Goals:
- Build plant structure and foliage
- Strengthen root systems
- Prepare for flowering
Requirements:
- Lighting: 18–20 hours daily
- Nutrients: Higher nitrogen proportion
- Temperature: 70–85°F (21–29°C)
- Humidity: 40–60%

---
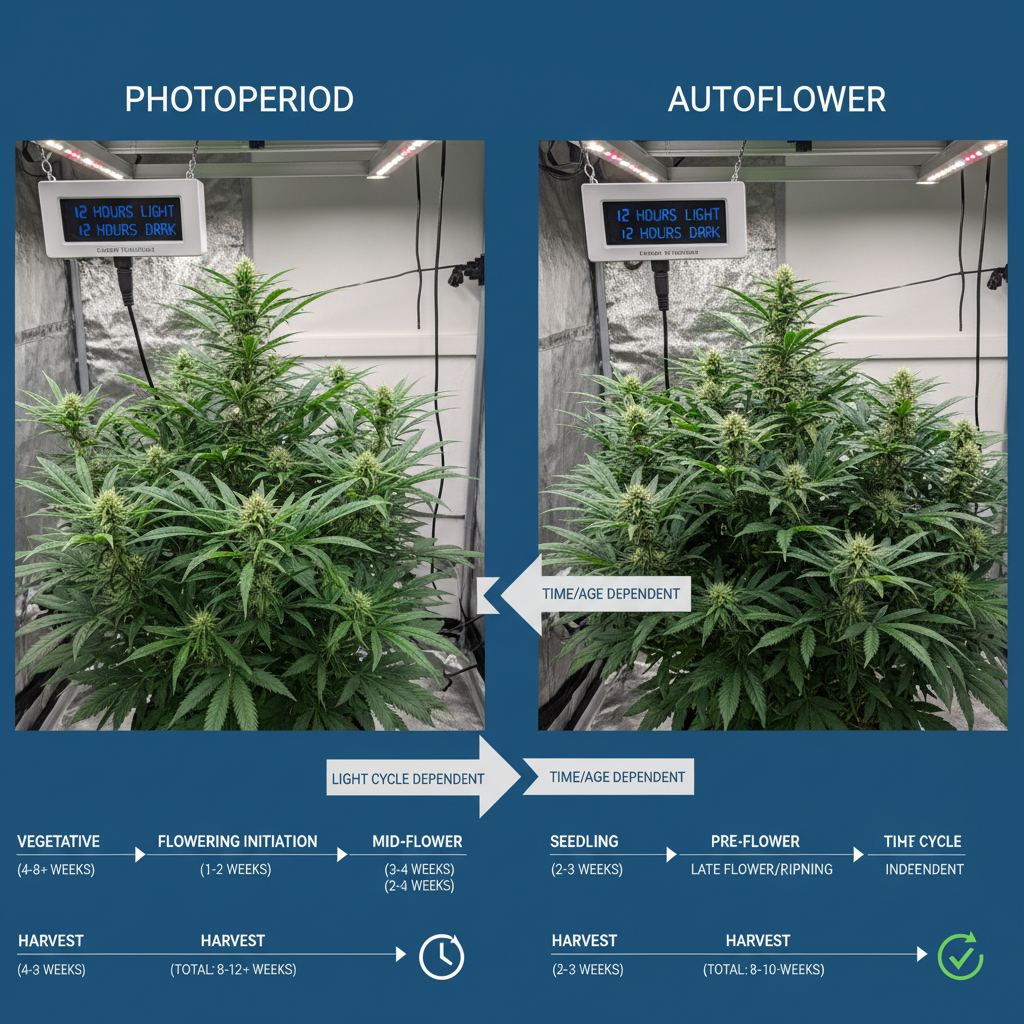
Flowering Stage: Timelines for Photoperiod vs. Autoflower
Photoperiod strains:
- Triggered by 12/12 light cycle change
- Duration: 6–14 weeks, strain-dependent
Autoflower strains:
- Transition automatically after 3–5 weeks vegetative growth
- Duration: Around 7–11 weeks total
Environmental focus:
- Humidity: 40–50%
- Nutrients: Increased potassium and phosphorus balance
---
Drying and Curing Timelines Post-Harvest
Drying phase:
- Duration: 5–14 days
- Temperature: 60–70°F (15–21°C), humidity 50–60%
- Hanging plants or rack drying
Curing phase:
- Duration: Minimum 2 weeks, often longer
- Storage: Airtight containers
- Burping periodically to release moisture
Proper curing enhances flavor and potency, critical for high-quality output.
---
How Strain Genetics Impact Total Grow Time
Genetics play a pivotal role in determining Schedule 1 grow times:
| Strain Type | Average Total Grow Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Indica Photoperiod | 8–12 weeks flowering | Typically shorter flowering cycle |
| Sativa Photoperiod | 10–14 weeks flowering | Usually taller plants, longer flowering |
| Autoflower Hybrid | 7–11 weeks total | No light schedule change required |
---
Indoor vs. Outdoor Growth Duration Comparisons
Indoor cultivation:
- Controlled environments yield predictable timelines
- Allows potential year-round production
Outdoor cultivation:
- Relies on natural light cycles and seasonal shifts
- Subject to longer timelines from variable conditions
---
Environmental Factors Affecting Grow Cycles
Variables that may extend or reduce Schedule 1 grow times include:
- Temperature variation
- Humidity instability
- Pests or pathogens
- Nutrient mismanagement
- Light cycle inconsistency
Even minor changes can alter harvest schedules by weeks.
---
Tracking and Documenting Grow Times for Consistency
Professional growers keep:
- Stage-by-stage logs with dates
- Temp, humidity, and light readings
- Nutrient schedules
- Plant health observations
This data aids in identifying bottlenecks and boosting efficiency.
---
Common Mistakes That Delay Harvest and Prevention Tips
Avoid delays by preventing:
- Over/underwatering
- Irregular lighting schedules
- Improper pruning
- Nutrient imbalances
- Ignoring early pest signs
Following strict routines and monitoring plants daily greatly reduces issues.
---
Planning Year-Round Grows and Multiple Harvests
For continuous production:
- Schedule staggered planting cycles
- Use separate spaces for each growth stage
- Leverage autoflowers for quick turnover
- Diversify strains to balance workloads
---
Final Thoughts: Balancing Speed and Quality in Schedule 1 Cultivation
While faster grows can boost profit margins, rushing risks reducing potency, flavor, and yield. Balancing speed with quality is the hallmark of expert cultivation.
Mastering environmental controls, respecting strain characteristics, and adhering to legal frameworks will help ensure your Schedule 1 grow times result in compliant, high-quality harvests.
Summary: By understanding each growth stage, monitoring conditions closely, and following local laws, you can achieve consistent and efficient Schedule 1 cultivation. Start documenting your cycles today to refine timing and improve output.