Social Media Feed Meaning and How Feeds Work
Learn what a social media feed is, how algorithms curate posts, and the differences between chronological and algorithmic feeds for users.
Social Media Feed Meaning and How Feeds Work
Social media feeds are the central hub of our online interactions, serving as personalized streams of posts, images, videos, and shared links. In today’s digital landscape, understanding the social media feed meaning and how feeds operate is essential for both casual users and marketers aiming to optimize content visibility. This guide will break down how feeds function, how platforms design them, the algorithms driving them, and their implications for privacy, engagement, and the future.
---
What Is a Social Media Feed?
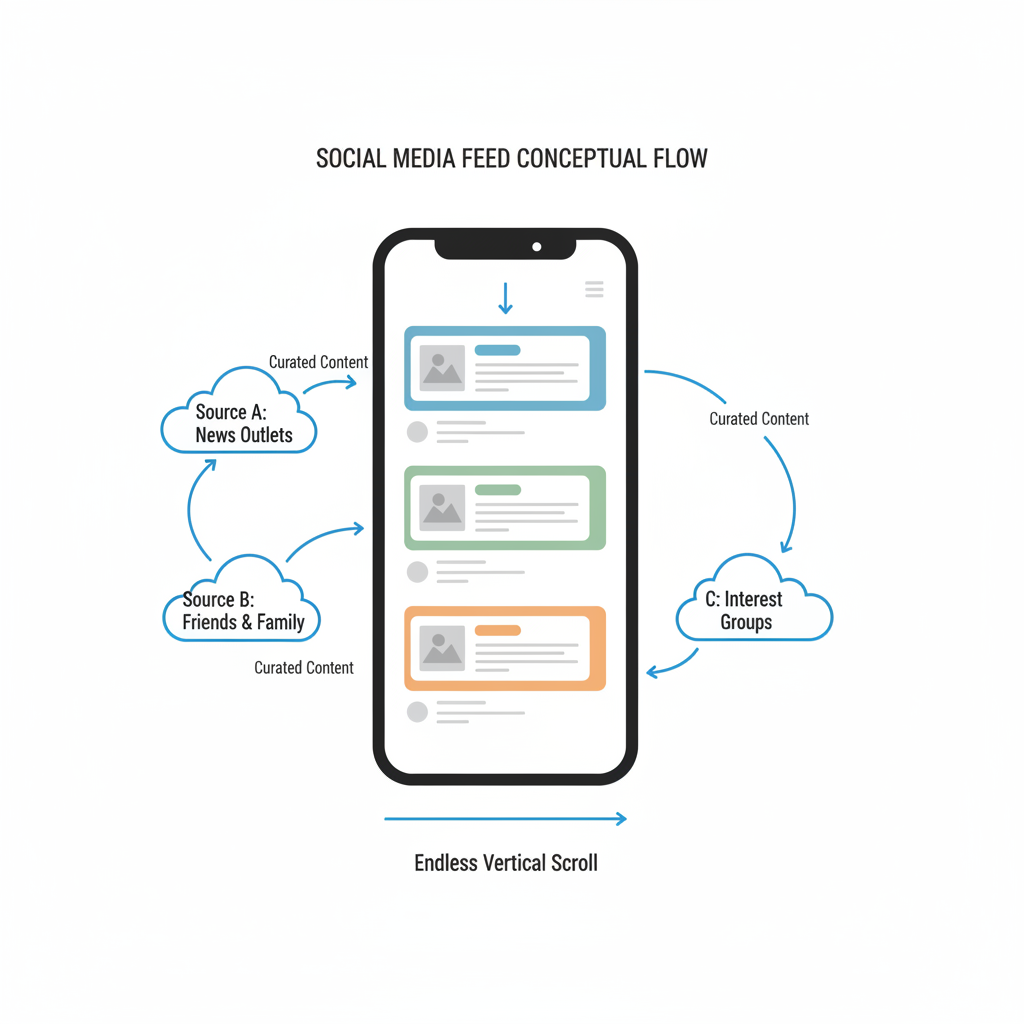
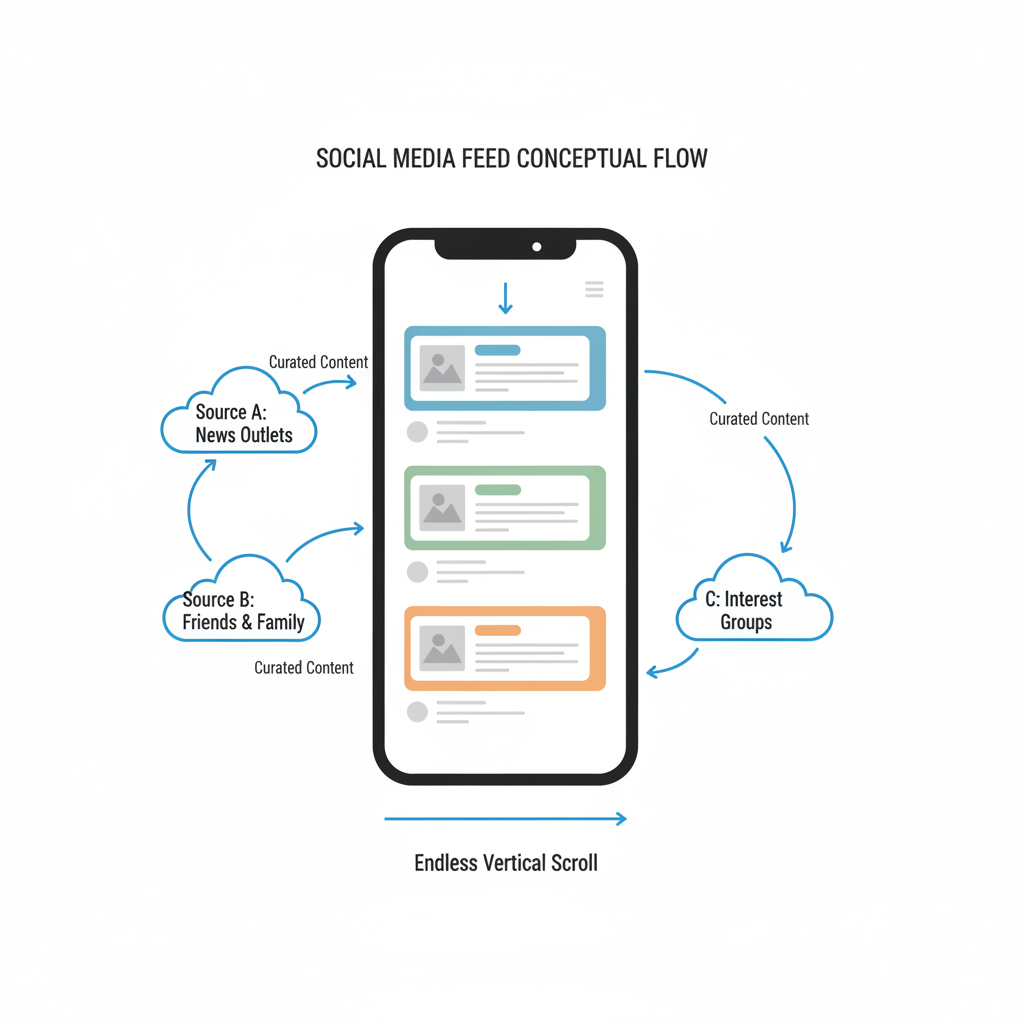
A social media feed is the continuously updating section of a social networking app or website where new content appears in a scrollable list.
- It collects updates from accounts, pages, and topics you follow.
- It may also insert recommended posts from creators you don’t follow.
- Platforms design feeds to keep you engaged with relevant or entertaining media.
In essence, it is your personalized homepage each time you open a platform, shaped by both your network and the algorithms that curate content.
---
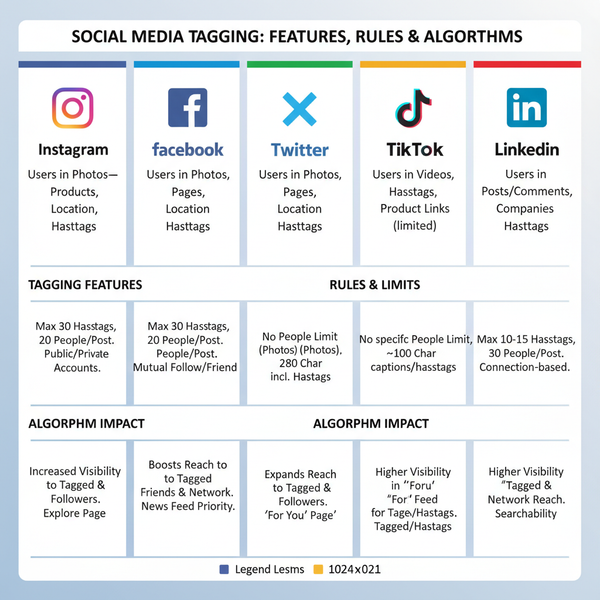
Feeds Across Different Platforms
While almost all social platforms feature feeds, the style and curation vary significantly.
| Platform | Feed Style | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithmic News Feed | Mix of posts from friends, pages, groups, and ads; “Top Stories” prioritized | |
| Algorithmic main feed + Stories feed | Content from followed accounts, Reels, recommendations; chronological Stories at top | |
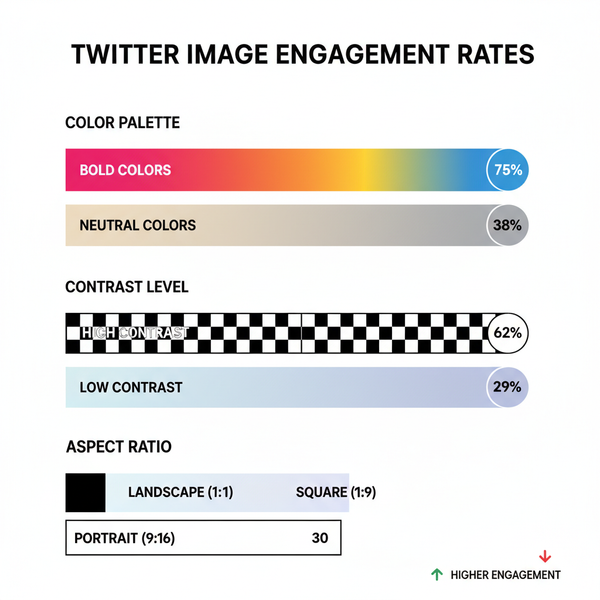
| Twitter/X | Hybrid (For You / Following) | “For You” is algorithmic; “Following” shows a chronological timeline |
| TikTok | For You Page (FYP) | Highly personalized, fully algorithm-driven video feed |
| Algorithmic professional feed | Prioritizes professional updates, industry news, job postings, and networking content |
---
How Feed Algorithms Work
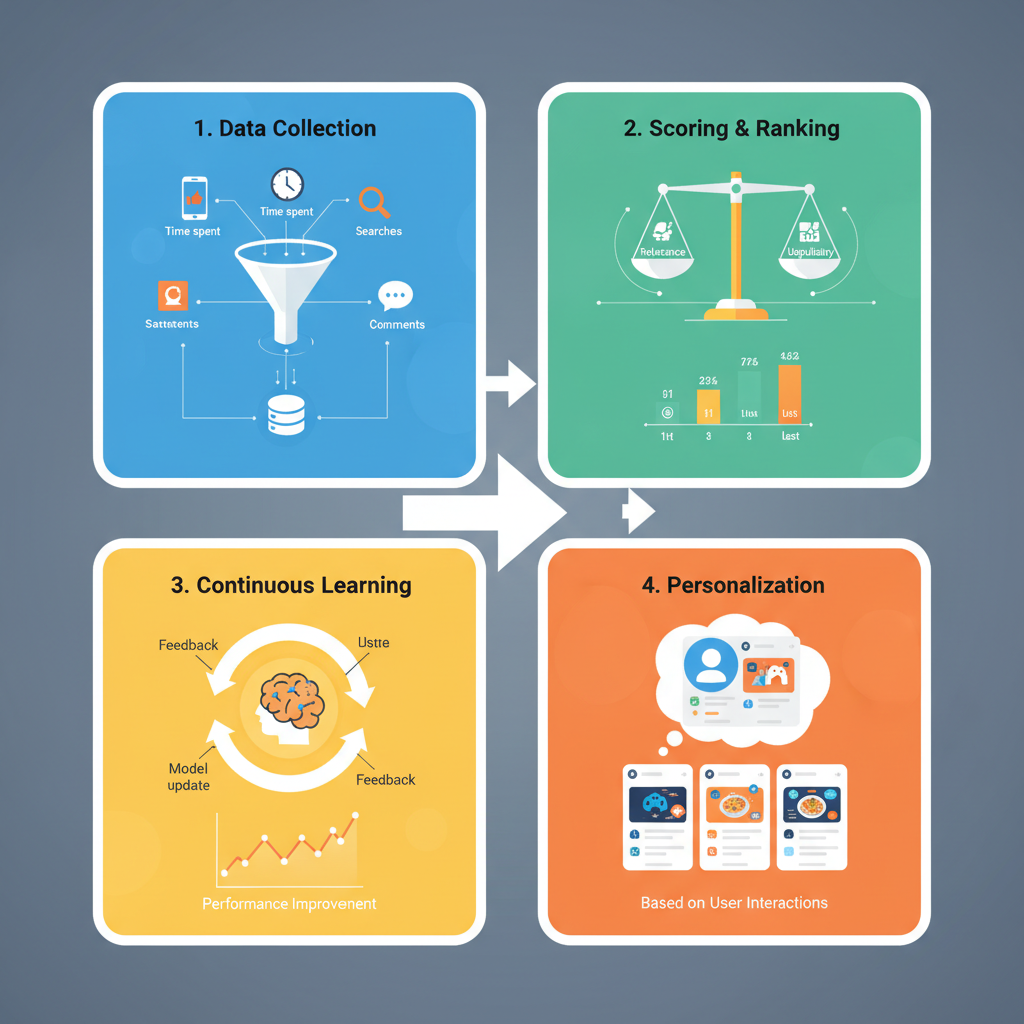
Every feed is powered by algorithms deciding what to display and in what order.
Data Collection
Algorithms gather data from:
- Your actions (likes, shares, comments)
- Profile details (occupation, interests, demographics)
- Connections and follows
- Device information and location patterns
Scoring and Ranking
Content earns relevance scores based on:
- User affinity – frequency of interaction with the content creator.
- Content preferences – whether you favor videos, images, or text posts.
- Recency – newer content generally appears first.
- Predicted engagement – likelihood of future likes, comments, or shares.
Continuous Learning
Machine learning models refine recommendations to improve accuracy, adapting as your behavior evolves.
---
User Interactions and Personalization
Your feed changes with every interaction you make.
- Likes – signal enjoyment and prompt more similar recommendations.
- Comments – demonstrate interest and engagement depth.
- Shares – increase reach and signify content resonates within your network.
- Time spent – even passive viewing informs algorithmic predictions.
This results in unique feeds for each user, even among individuals following identical accounts.
---
Chronological vs Algorithmic Feeds
Feeds typically follow one of two structures:
- Chronological: Lists posts by publication time, ideal for real-time events.
- Algorithmic: Orders content by predicted relevance and engagement potential.
Chronological Pros:
- Transparency — see all posts in sequence.
- Timeliness for live coverage.
Algorithmic Pros:
- Increased personalization.
- Enhanced content discovery.
---
Benefits of Feeds for Users
Feeds do more than provide updates; they enrich social networking experiences.
- Discover content you might otherwise miss.
- Encourage engagement through interactive features.
- Deliver timely news and updates tailored to interests.
- Provide entertainment via a steady stream of media.
---
Branding & Marketing Implications
For brands, the feed determines how audiences encounter messaging.
- Optimize for algorithms to boost organic visibility.
- Choose optimal post times to meet active audience windows.
- Embrace favored formats such as video, carousels, or interactive posts.
- Use ads strategically to place paid content naturally within feeds.
Effective social media marketing hinges on a deep understanding of feed mechanics.
---
Privacy and Data Considerations
Personalized feeds depend heavily on user data.
Key user considerations:
- Scope of data collection by platforms.
- Data sharing practices with advertisers and partners.
- Consent controls via privacy settings.
- Ethical issues tied to algorithm-driven bias or harmful promotion.
Awareness of how your data informs feeds enables smarter platform use.
---
Future Trends in Social Media Feeds
Emerging technologies will reshape feeds:
- AI hyper-personalization for more precise targeting.
- Immersive AR/VR formats within feeds.
- Decentralized networks using blockchain for privacy protection.
- Multimodal posts with blended media formats.
These developments will influence both the consumption and definition of the “social media feed.”
---
Recap and FAQs
Quick Summary
- Social media feed meaning: Your personalized stream managed by algorithms.
- Platform differences: Each uses unique curation systems.
- Algorithm role: Serves relevant content for engagement.
- Data privacy: Central to personalization.
- Future outlook: Technology-driven transformations.
FAQs
Q: Can I fully control my feed settings?
A: You can influence feeds through follows, muting, and content preferences, but algorithms still hold sway.
Q: Why are posts from unknown accounts shown?
A: To introduce potentially interesting content aligned with your activity.
Q: Which feed style is better?
A: Preference-based — chronological offers transparency, algorithmic boosts relevance.
Q: Could algorithms be biased?
A: Yes, biases are possible due to skewed or incomplete training data.
---
By understanding the social media feed meaning and internal workings, you can shape your experience to suit your needs — whether for personal enjoyment, professional networking, or marketing strategy. Stay informed, adjust your preferences, and leverage feeds to their fullest potential.