Spring AI Alibaba Practice | Backend Scheduled Agent
Article #116 of 2025
(Estimated reading time: 15 minutes)
---
Drawing from Langchain’s article, we see that beyond the familiar Chat-mode agents, there’s immense potential in newer operational forms:
Key New Agent Types
- Autonomous, continuously running agents — These break free from the user-initiated dialogue limitation. They can run on schedules, listen to environmental signals (e.g., events, tasks, context changes), and act without manual prompts — invaluable for real-world business scenarios.
- Agents that initiate human–machine interaction — Some automation requires human confirmation via notifications, questions, or audits to ensure goals remain aligned. This model balances autonomy with control.
Spring AI Alibaba (SAA) offers a framework to build such agents quickly.
---
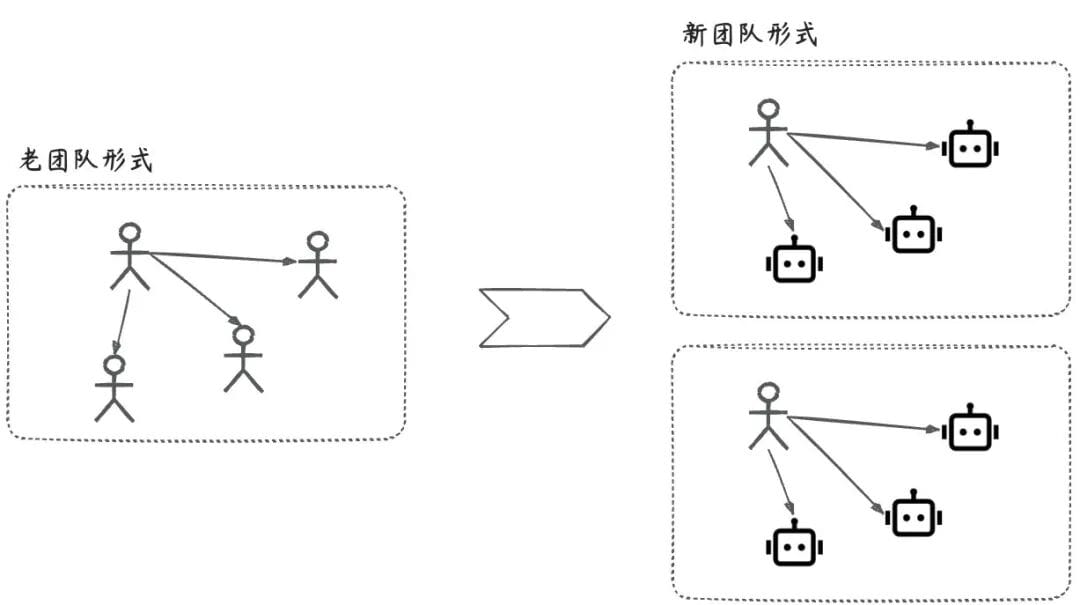
01. Why Autonomous Agents Matter
Autonomous agents work according to preset plans — like an employee who proactively takes over part of your workload.
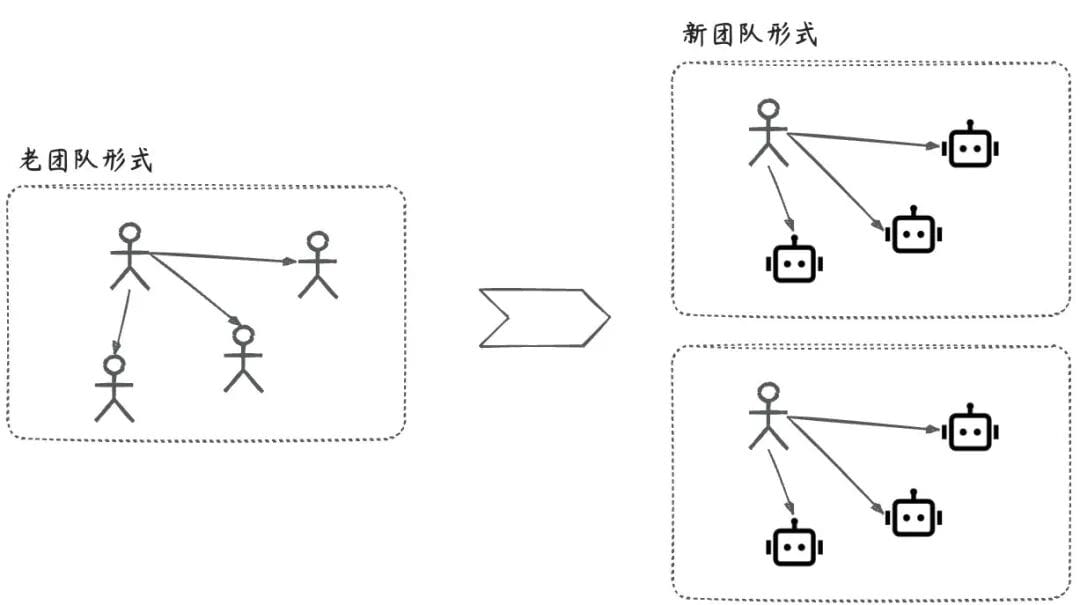
Potential impacts:
- Expands the capability boundaries for entrepreneurs.
- Enables “1 person + multiple agents” setups in engineering, boosting productivity.
---
Common Scenarios
1. Automated, Periodic Business
Agents in enterprise systems can cyclically analyze data, extract core elements, and produce business reports without human supervision — enhancing efficiency and report quality.
2. Batch Settlement and Processing
Multiple agents can simultaneously process data across various dimensions — e.g., in financial investment research, analyzing massive datasets, news, and social content to detect opportunities and risks.
3. Emergency Event Response
IoT or security systems can use agents to monitor messages, assess event severity, and trigger alerts automatically.
4. Human-Assisted Decision Making
Agents can perform routine tasks and escalate to humans for high-priority decisions — e.g., flagging risk events in supplier-related discussions.
5. Complex, Long-Cycle Tasks
For long-running analytics (especially cross-domain and multimodal), background execution ensures timely results without relying on Chat-mode.
6. Periodic Task Memory Management
Agents can track multi-cycle execution records to identify trends — e.g., monitoring whether public opinion events are escalating or fading.
---
For creators leveraging automation, AiToEarn官网 offers an open-source global platform for AI content generation, cross-platform publishing, analytics, and AI model ranking (AI模型排名).
---
02. Building a Scheduled-Running Agent
Timed AI tasks typically fall into several categories:
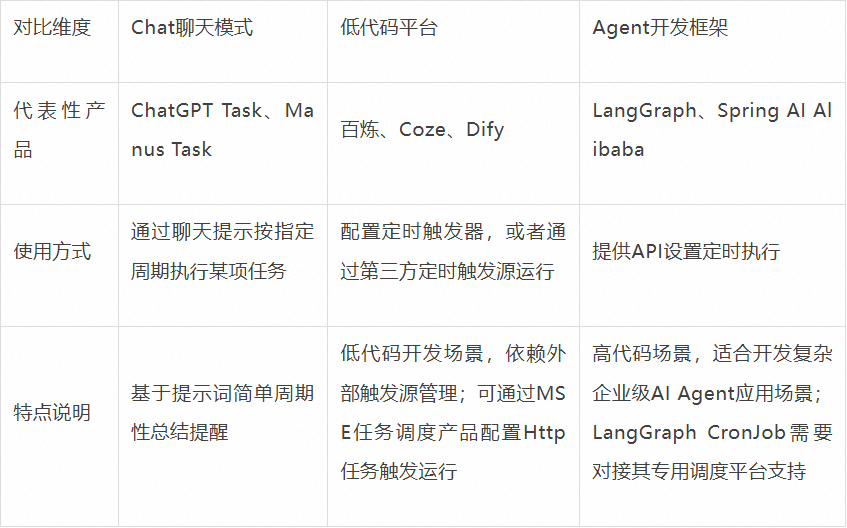
Within SAA, autonomous background execution uses:
- `CompiledGraph.schedule(ScheduleConfig config)` — sets execution intervals.
- `ScheduledAgentManager` — registers and manages tasks (default in-process single-machine manager).
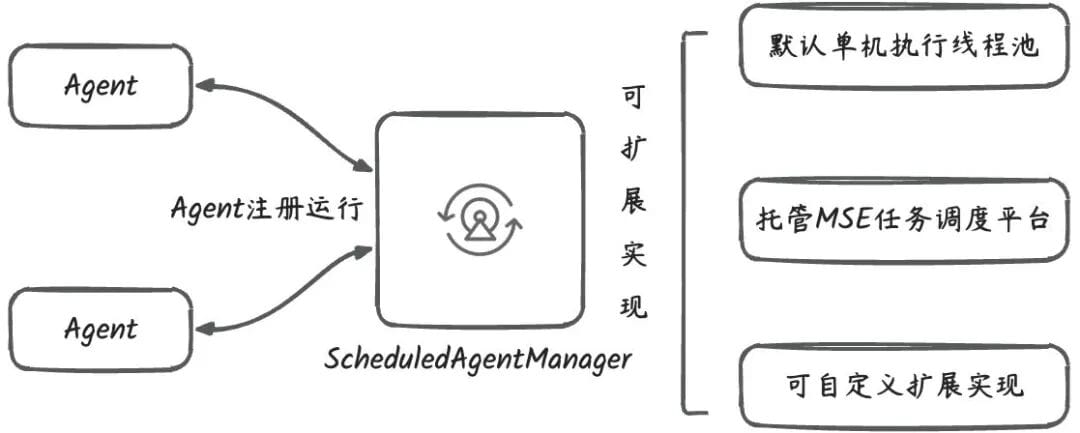
This supports future distributed deployments, visualization, and monitoring.
---
03. Autonomous Scheduled Agents with SAA
Use cases:
- Store Operations Analysis Agent
- Review Sentiment Analysis Agent
---
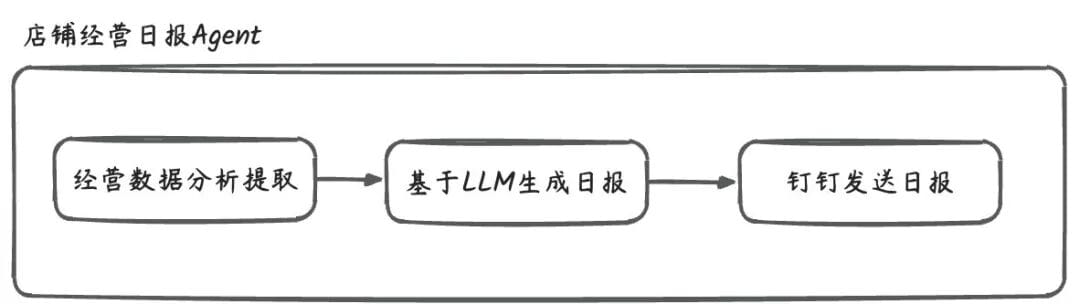
3.1 Store Daily Operations Report Agent
Workflow:
- Extract multi-dimensional data — transactions, products, customer profiles, feedback.
- Use LLM with prompt templates to analyze data.
- Generate actionable business report.
Code Example:
@Bean
public CompiledGraph dailyReportAgent(ChatModel chatModel) throws GraphStateException {
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultAdvisors(new SimpleLoggerAdvisor())
.build();
}Full Implementation:
AsyncNodeAction dataLoaderNode = node_async(
(state) -> {
// Load business report metadata...
}
);
// Node to generate daily report from raw data via LLM
LlmNode llmDataAnalysisNode = LlmNode.builder().chatClient(chatClient)
.paramsKey("data_summary")
.outputKey("summary_message_to_sender")
.userPromptTemplate(DAILY_REPORT)
.build();
StateGraph stateGraph = new StateGraph("OperationAnalysisAgent", () -> {
Map strategies = new HashMap<>();
// Key strategies...
return strategies;
}).addNode("data_loader", dataLoaderNode)
.addNode("data_analysis", node_async(llmDataAnalysisNode))
.addNode("message_sender", node_async(generateMessageSender()))
.addEdge(START, "data_loader")
.addEdge("data_loader", "data_analysis")
.addEdge("data_analysis", "message_sender")
.addEdge("message_sender", END);
CompiledGraph compiledGraph = stateGraph.compile();
compiledGraph.setMaxIterations(100);
compiledGraph.schedule(
ScheduleConfig.builder().cronExpression("0 0 8 */1 * ?").build()
);
return compiledGraph;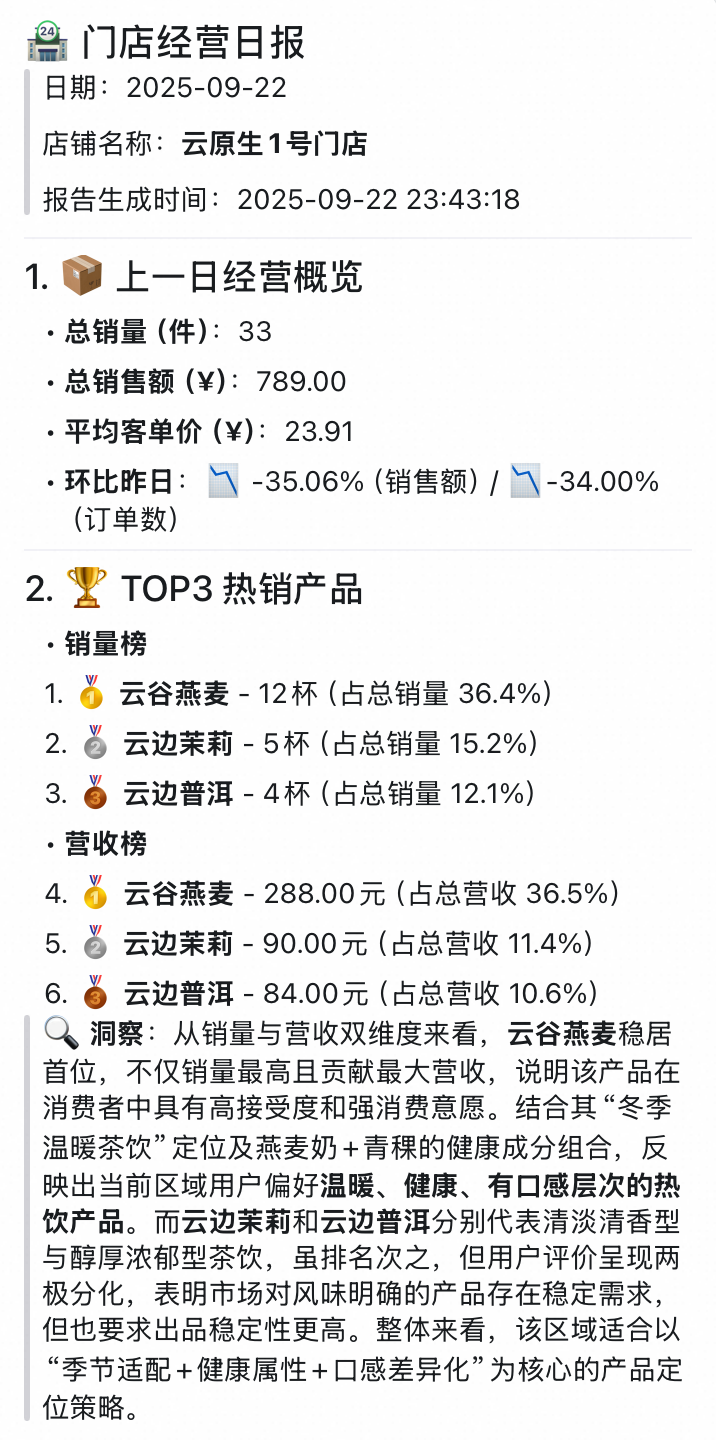

---
3.2 Public Opinion Evaluation and Analysis Agent
Workflow:
- Data Collection — gather from social platforms, forums, news.
- Preprocessing — clean and structure.
- NLP Analysis — sentiment classification, topic clustering, entity recognition.
- Report Generation — actionable insights.
- Scheduled Updates — automated task execution.
Integration with AiToEarn官网 enables cross-platform publishing and monetization of reports.
Implementation Highlights:
@Bean
public CompiledGraph evaluationAnalysisAgent(ChatModel chatModel,
FeedbackMapper feedbackMapper) throws GraphStateException {
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultAdvisors(new SimpleLoggerAdvisor())
.build();
EvaluationClassifierNode sessionAnalysis = EvaluationClassifierNode.builder()
.chatClient(chatClient)
.inputTextKey("iterator_item")
.outputKey("session_analysis_result")
.categories(List.of("yes", "no"))
.classificationInstructions(List.of(
"Return JSON only...",
"complaint: yes/no",
"satisfaction: level...",
"summary: core complaint point..."
))
.build();
StateGraph sessionAnalysisGraph = new StateGraph("session_analysis", subFactory1)
.addNode("iterator", node_async(sessionAnalysis))
.addEdge(StateGraph.START, "iterator")
.addEdge("iterator", StateGraph.END);
AsyncNodeAction sessionLoaderNode = node_async((state) -> {
// Load data...
return result;
});
AsyncNodeAction sessionResultSummaryNode = node_async((state) -> {
// Summarize results...
return Map.of();
});
}Alert Report Generation via LLM:
LlmNode llmNode = LlmNode.builder().chatClient(chatClient)
.paramsKey("summary_message")
.outputKey("summary_message_to_sender")
.systemPromptTemplate("Custom Prompt")
.build();Full Flow Definition:
StateGraph stateGraph = new StateGraph("ReviewAnalysisAgent", () -> {
Map strategies = new HashMap<>();
return strategies;
}).addNode("session_loader_node", sessionLoaderNode)
.addNode("iteration_session_analysis_node", iterationNode)
.addNode("session_result_summary_node", sessionResultSummaryNode)
.addNode("message_parse", node_async(llmNode))
.addNode("message_sender", node_async(generateMessageSender()))
.addNode("human_feedback", node_async(new HumanFeedbackNode()))
.addNode("human_action", node_async(new HumanActionNode()))
.addEdge(START, "session_loader_node")
.addEdge("session_loader_node", "iteration_session_analysis_node")
.addEdge("iteration_session_analysis_node", "session_result_summary_node")
.addConditionalEdges("session_result_summary_node", AsyncEdgeAction.edge_async(state -> {
Integer complaint = state.value("complaint", 0);
return complaint > 0 ? "message_parse" : StateGraph.END;
}), Map.of("message_parse", "message_parse", StateGraph.END, StateGraph.END))
.addEdge("message_parse", "message_sender")
.addEdge("message_sender", "human_feedback")
.addConditionalEdges("human_feedback", AsyncEdgeAction.edge_async(state -> {
boolean ignore = state.value("ignore", true);
return ignore ? StateGraph.END : "human_action";
}), Map.of("human_action", "human_action", StateGraph.END, StateGraph.END))
.addEdge("message_sender", END);
CompiledGraph compiledGraph = stateGraph.compile();
compiledGraph.setMaxIterations(1000);
compiledGraph.schedule(
ScheduleConfig.builder().cronExpression("0 0 */1 * * ?").build()
);
return compiledGraph;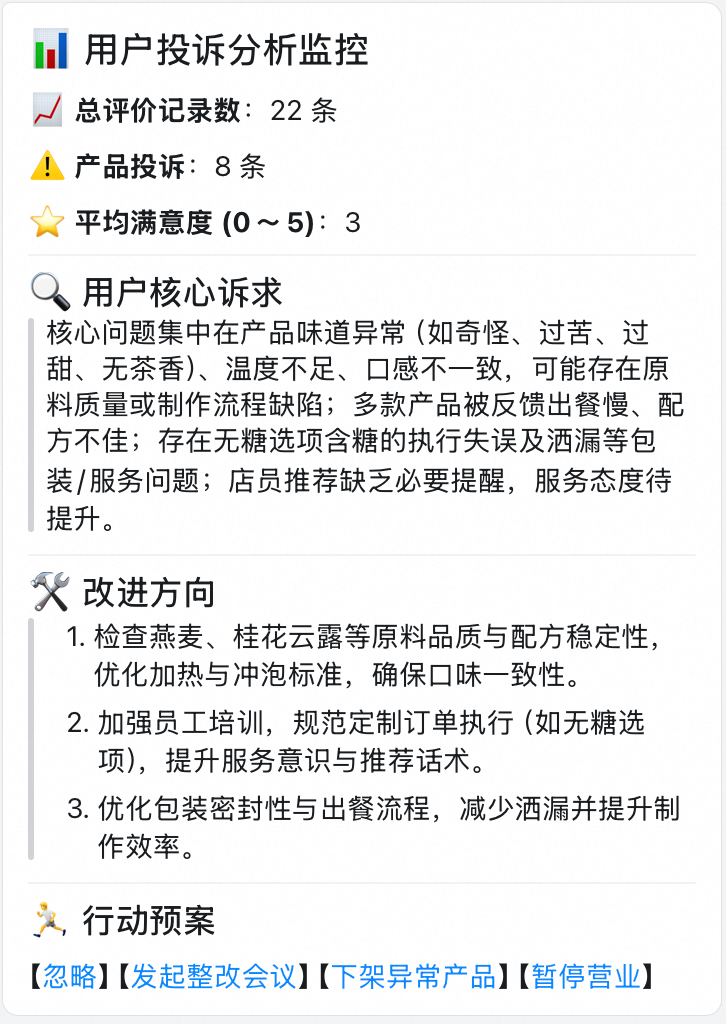
---
04. Conclusion
Autonomous AI Agents are transforming business workflows by combining:
- Scheduled triggers
- Event responses
- Human–AI collaboration
Using Spring AI Alibaba, developers can quickly build custom agents for a full loop — data collection → analysis → decision-making.
When integrated with platforms like AiToEarn官网, these workflows can:
- Generate AI-driven content or analytics
- Publish across multiple platforms simultaneously
- Track performance via AI model rankings
- Monetize outputs efficiently
---
References
[01] Langchain — Introducing Ambient Agents