The Birth of a Sales Data Analysis Bot: How Dify Achieves Automated Closed-Loop with DMS
# Enhancing Dify with DMS Notebook and Airflow for Enterprise-Grade AI Agents
**Article #:** 130 of 2025
**Estimated Reading Time:** 15 minutes
---
## 1. Background & Challenges
**Dify** is a low-code platform for developing AI applications, offering intuitive visual workflow orchestration to simplify building LLM-based solutions.
However, in **enterprise deployments**, two significant limitations are often encountered:
- **Limited Code Execution Capability**
The built-in **Sandbox** node supports only basic Python code execution, disallowing custom Python package installation — restricting complex data processing or algorithm integration.
- **No Automated Scheduling Mechanisms**
Dify lacks native support for timed triggers, periodic runs, or dependency orchestration — making enterprise-scale automation difficult.
These limitations pose challenges for building **closed-loop intelligent Agents** following the cycle:
> *Perception → Decision → Execution → Feedback*
---
## 2. Solution Architecture: “Dify + DMS Notebook + DMS Airflow”
We adopted a unified architecture to overcome Dify limitations:
- ✅ **DMS Notebook** – Full Python runtime with pip support, custom env vars, async service deployment, and secure VPC communication.
- ✅ **DMS Airflow** – Robust scheduler for recurring execution, dependency management, and multi-component orchestration.
- ✅ **Integrated Workflow** – Enables end-to-end lifecycle management from **development** → **debugging** → **deployment** → **scheduling** → **monitoring**.
We will walk through a **sales data analysis bot** case study to demonstrate this architecture in action.
---
## 3. Using DMS Notebook to Extend Execution Capability
### 3.1 Why Use Notebook?
Dify’s sandbox can’t install advanced packages like **Pandas**, **Prophet**, or internal SDKs.
**DMS Notebook** allows:
- Install via `pip`
- Configure env vars (`AK/SK`, API keys)
- Build async APIs (FastAPI)
- Communicate securely inside a VPC
### 3.2 Step-by-Step: Sales Analysis API Service
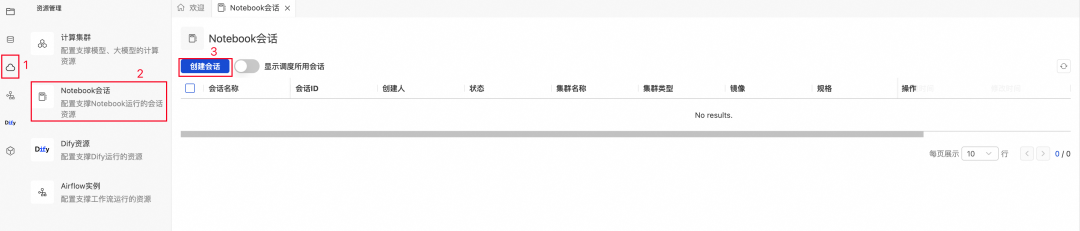
**Step 1:** Create a DMS Notebook session
1. Open **DMS Console → Notebook Sessions → Create Session**
2. Configure parameters: choose Python version, adjust package settings.
3. Add dependencies in `requirements.txt` format, e.g.:pandas
fastapi
uvicorn
nest-asyncio
4. **Critical settings:**
- Install `fastapi`, `uvicorn`, `nest-asyncio`.
- **Resource release time = 0**.
- Set `DMS_KERNEL_IDLE_TIMEOUT=0`.
💡 **Pitfall:** Without `DMS_KERNEL_IDLE_TIMEOUT=0`, idle API servers may be killed, causing failures.
---
**Step 2:** Build the FastAPI Service
- Create a new notebook file in `default` workspace.
- Write code using this template ([FastAPI Docs](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/)):
import os
from fastapi import FastAPI
...
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Service is running", "documentation": "/docs"}
**FastAPI Tips:**
- Support for **path/query/header** params
- Handle **JSON bodies** gracefully
- Include **file upload endpoints**
- Run via `uvicorn` inside asyncio loop (`nest_asyncio.apply()`)
---
**Step 3:** Starting the API Service
- Run the cell launching the server.
- Use `!ifconfig` to check notebook’s VPC IP.
- Access service via:
`http://:/`
---
## 4. Integrating with Dify Workflows
**Example:**
- Add HTTP Request node in Dify workflow
- Point to your FastAPI service endpoint
- Pass CSV sales data in request body
- Parse & return insights in workflow output
**Use Case:**
Sales data flows into FastAPI → analyzed → returned to Dify → posted to channels like DingTalk.
---
## 5. Scheduling Automation with DMS Airflow
### 5.1 Setting up Airflow
- Create Airflow instance ([Docs](https://help.aliyun.com/zh/dms/create-and-manage-an-airflow-instance))
- Reference [Airflow Official Docs](https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/index.html)
### 5.2 Example: Daily Sales Analysis DAG
**DAG Function:**
- Read daily CSV
- Upload to Dify via `/files/upload`
- Run workflow via `/workflows/run`
- Output analysis report to target channel
from airflow.models.dag import DAG
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
def call_dify_workflow_with_csv():
# Upload file
# Call Dify workflow
📌 **Tip:**
Always upload local file to `/files/upload` first, retrieve `file_id`, then pass to workflow input payload.
---
## 6. End-to-End Flow Recap
1. **Data Source**: Sales CSV generated daily
2. **Execution**: DMS Notebook → FastAPI analysis endpoint
3. **Integration**: Dify Workflow node calls API
4. **Automation**: DMS Airflow triggers Dify daily
5. **Distribution**: DingTalk bot posts report to group
---
## 7. Summary & Reflection
Using **DMS Notebook + DMS Airflow** with Dify:
- Solves code execution and scheduling gaps
- Maintains low-code development speed
- Achieves high engineering reliability
**Core Principle:**
Enterprise AI Agents must be **extensible**, **schedulable**, and **maintainable** — blending platform ease-of-use with production-grade infrastructure.
---
## 8. Learn More
- Join DingTalk group: **96015019923**
- Apply for Dify on DMS: [link](https://page.aliyun.com/form/act1621739703/index.htm)
---
### 9. Complementary Tools for Multi-Platform Publishing
For teams wanting **automated content distribution** and monetization of AI-driven insights, **[AiToEarn](https://aitoearn.ai/)** offers:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing (Douyin, WeChat, LinkedIn, YouTube, etc.)
- Built-in analytics
- AI model ranking
Resources:
- [AiToEarn Docs](https://docs.aitoearn.ai/)
- [Open Source Repo](https://github.com/yikart/AiToEarn)
- [AI Model Ranking](https://rank.aitoearn.ai/)
Integrating AiToEarn with the **Dify + DMS** stack can extend value beyond internal operations — enabling data-driven content to reach global audiences efficiently.
---


