The Earth Can Hardly Sustain AI — Google and Nvidia Forced Into Space, Benefiting Musk

Google Launches Project Suncatcher: Bringing AI Data Centers to Space
Just now, Google unveiled its latest moonshot program — Project Suncatcher — aiming to deploy solar-powered AI infrastructure in space.

---
Why Space? The Core Idea
Instead of competing for dwindling terrestrial resources, Google proposes harnessing space-based solar power to fuel massive AI computation.
Project Goal:
Build a scalable, solar-powered AI infrastructure in space — free from Earth's energy and cooling constraints.
---
The Energy Bottleneck
In a recent podcast, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman and Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella noted:
> My problem today isn’t chip supply; the fact is, I don’t have enough warm shells to plug them into.
Altman emphasized that the future of AI hinges more on energy breakthroughs than chip counts.
The Scale of Demand
- Electricity: IEA predicts global data infrastructure will consume as much power as Japan by 2030.
- Water: WEF reports a 1 MW data center uses as much water daily as ~1,000 residents of a developed country.
A single NVIDIA H100 GPU draws up to 700W — and data centers run tens of thousands of them continuously.
---
Google’s Orbital AI Data Center Concept
Google plans a constellation of satellites equipped with its own TPU chips, powered entirely by solar energy, forming a space-based compute network.
---
Why Space Could Be Better Than Earth
- 8× Solar Efficiency: Optimal orbital placement can make solar panels eight times more efficient than those on Earth.
- 24/7 Power: No night or cloud interference — continuous energy generation.
- No Land or Water Impact: Avoids consuming scarce terrestrial cooling resources.
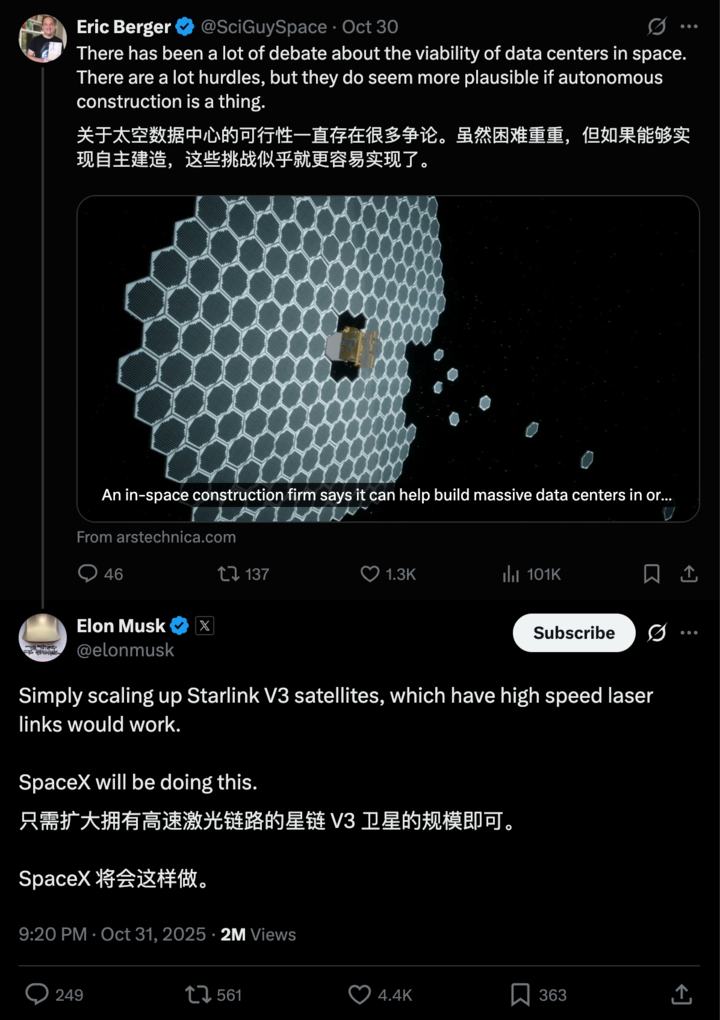
▲ Musk: AI satellites in space can protect Earth

---
Challenges of AI in Space
Challenge 1 — Networking: A LAN in Orbit?
Problem: AI training requires huge bandwidth, ultra-low latency between nodes — typically achieved on Earth via fiber optics.
Solution: Formation flying + laser communications.
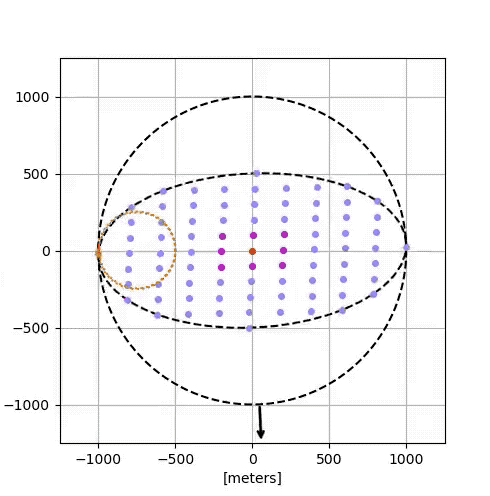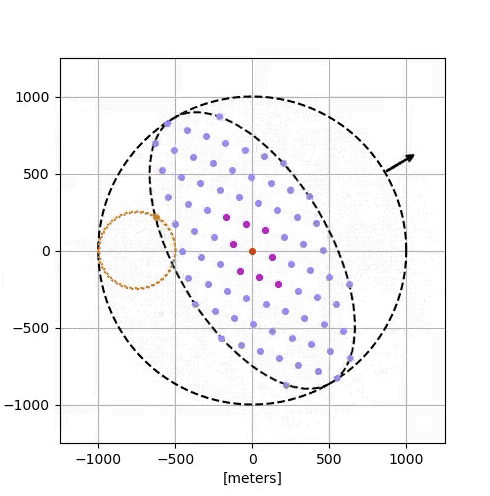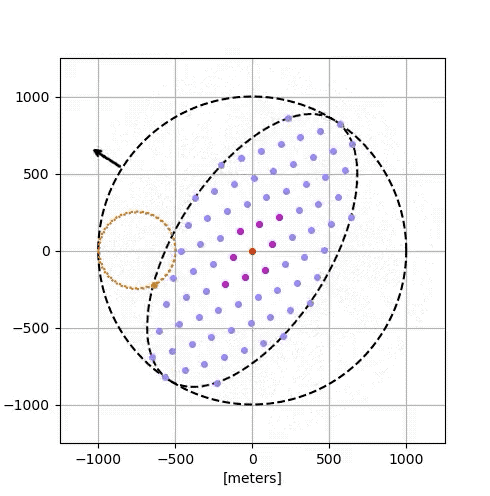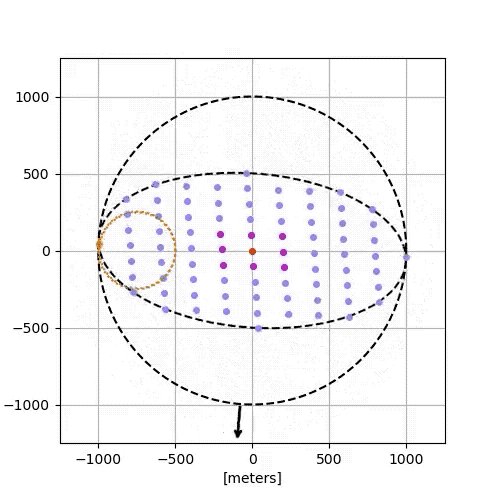
Google’s simulation:
- 81 satellites, each with solar arrays, radiative cooling, optical comms.
- Dynamic separations: 100–200 meters for high-speed interconnects.
- Achieved 1.6 Tbps bidirectional rates with Free-Space Optical Inter-Satellite Links (FSO ISL).
---
Challenge 2 — Radiation Resistance
Space radiation is lethal to chips.
Google’s approach: Tested Cloud TPU v6e (Trillium) with a 67 MeV proton beam.
- HBM issues started only after 2 krad(Si) — nearly 3× mission dose predictions.
- TPU could operate 5 years in low Earth orbit without permanent damage.
Plan: Partner with Planet by 2027 to test prototype satellites.
---
Challenge 3 — Downlink to Earth
Problem: After computation, transmitting results to Earth quickly is tough.
- Latency: Sun-synchronous orbit maximizes solar but increases delay.
- Bandwidth: Current best (NASA 2023): 200 Gbps space-to-ground optical link — far too slow for AI-scale output.

---
The Biggest Barrier: Launch Cost
Sending payloads to orbit has historically been prohibitively expensive.
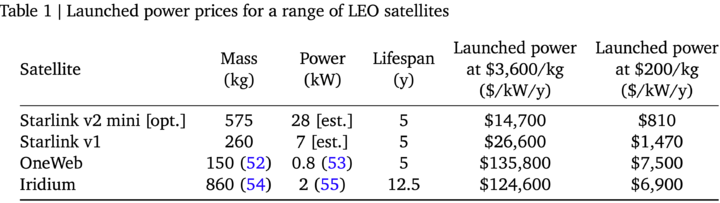
Google projects: At $200/kg (by ~2035), orbital data centers could match Earth’s cost (~$810/kW/year).
---
Enter SpaceX: The Possible Enabler
SpaceX's cost-reduction trajectory:
- Falcon 1: $30,000/kg → Falcon Heavy: $1,800/kg.
- Starship goal: $60/kg (10× reuse). Extremes: $15/kg.
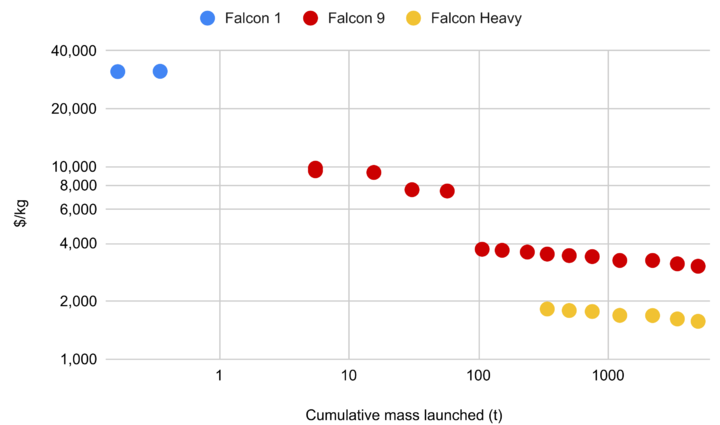
At such rates, orbital AI computing becomes feasible.

---
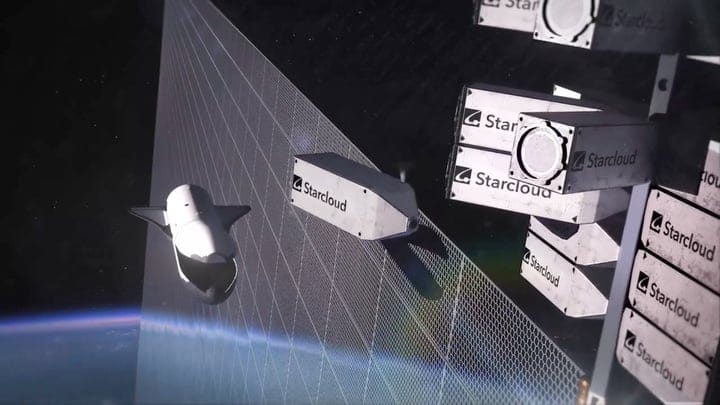
NVIDIA in Orbit
Days before Google’s paper release, NVIDIA’s H100 GPU went to space for the first time aboard Starcloud‑1.

Starcloud's mission: Real-time orbital data processing — e.g. SAR satellite data reduced from hundreds of GB to 1KB result summaries.
All contingent on SpaceX Starship costs.

---
The Shift Ahead
NVIDIA dominates GPUs on Earth; in space, SpaceX may dominate compute access. The orbital era could redistribute AI power advantages.
The limits of AI are only beginning to be tested.
---
Impact on Creators and AI Ecosystems
For innovators bridging Earth and space technologies, cross-platform AI content infrastructure becomes vital.
Tools like AiToEarn官网 offer:
- Open-source, global AI content generation.
- Multi-platform publishing (Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Instagram, YouTube, X).
- Analytics & monetization engines.
As orbital compute becomes reality, these models could extend content creation and AI integration beyond Earth.
---
Key Takeaway:
On Earth — NVIDIA sells GPUs.
In space — SpaceX sells orbits.
Tomorrow — AI may run seamlessly across both.