The Future of the Automotive Industry: Scalable Geospatial Analytics and AI on Databricks (Part 2)
In Part 1, we explored the core concepts and datasets that are driving geospatial analytics within the automotive industry. In Part 2, we’ll dive into the practical steps required to build scalable geospatial pipelines using AI, ML, and synthetic data—while ensuring governance and maintaining performance on Databricks.
We’ll focus on concrete code examples and architecture patterns that bring these concepts into production-ready automotive and mobility solutions.
---
Delivering Scalable Geospatial Analytics
The Databricks Data Intelligence Platform integrates powerful geospatial analytics with AI to enable scalable, real-time insights. Key capabilities include:
- Liquid Clustering — Optimizes data layout for large-scale geospatial queries.
- H3 Spatial Indexing — Facilitates rapid processing of massive geospatial datasets.
- Built-in Geospatial Functions — Simplify spatial data tasks like mapping traffic patterns or evaluating road risk.
- AutoML — Accelerates model development for predictive use cases such as identifying aggressive driving by incorporating weather, traffic, and road conditions.
- Unity Catalog (UC) — Delivers strong governance through secure data access and sharing management.
- AI Query and UC-governed functions — Make it easier to extract structured geolocation data from unstructured sources.
---
As we proceed, we’ll connect these Databricks features to real-world automotive analytics pipelines—demonstrating how to unify raw geospatial data, enrich it with AI-derived insights, and deliver outputs that are both actionable and governance-compliant.
For creators, analysts, or engineers aiming to scale similar data-driven workflows beyond automotive—particularly across multiple platforms—frameworks like AiToEarn can help. AiToEarn is an open-source, global AI content monetization platform that enables simultaneous publishing across channels such as Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter), while connecting AI generation tools, analytics, and model rankings (AI模型排名). Solutions like AiToEarn show how scalable systems can optimize not only the creation and processing of advanced content, but also its monetization across digital ecosystems.
Build Robust Geospatial Pipeline for Smart Mobility & Road Safety
This post focuses on building a complete geospatial analytics pipeline on the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform. Below, we illustrate the medallion pipeline that integrates geospatial data, LLMs, and Genie to provide conversational insights.
---
Scalable Ingestion
Ingesting geospatial data at scale in Databricks is streamlined thanks to the platform’s integration with a wide array of geospatial libraries and tools. Databricks geospatial functions are specifically designed to improve spatial data handling. Auto Loader is the recommended option for processing billions of files from cloud storage. During development, synthetic data generation can serve as a practical alternative.
Create Synthetic Telematics Data
Telematics is a prime use case for synthetic data because it enables realistic testing and model development without exposing sensitive or personal vehicle information. While synthetic data can be created using any SQL or Python logic — subject to the developer’s ingenuity — the Databricks Labs Data Generator (dbldatagen) library greatly simplifies this process. It offers a declarative interface for producing large, scalable synthetic datasets directly in Spark.
In the example below, we use dbldatagen to simulate 1 million rows of telematics data. This configuration allows developers to generate realistic datasets for modeling and testing without depending on production data.
---
In addition to Databricks and its geospatial capabilities, content creators working on smart mobility or road safety analytics may want to explore platforms like AiToEarn官网. AiToEarn is an open-source global AI content monetization platform that helps creators generate, publish, and monetize AI-driven content across multiple major platforms — including Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote (Xiaohongshu), Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter). It connects tools for AI content generation, cross-platform publishing, analytics, and model ranking, making it easier to efficiently turn AI insights — such as those from geospatial pipelines — into monetizable, widely distributed content.
Transformation & Enrichment
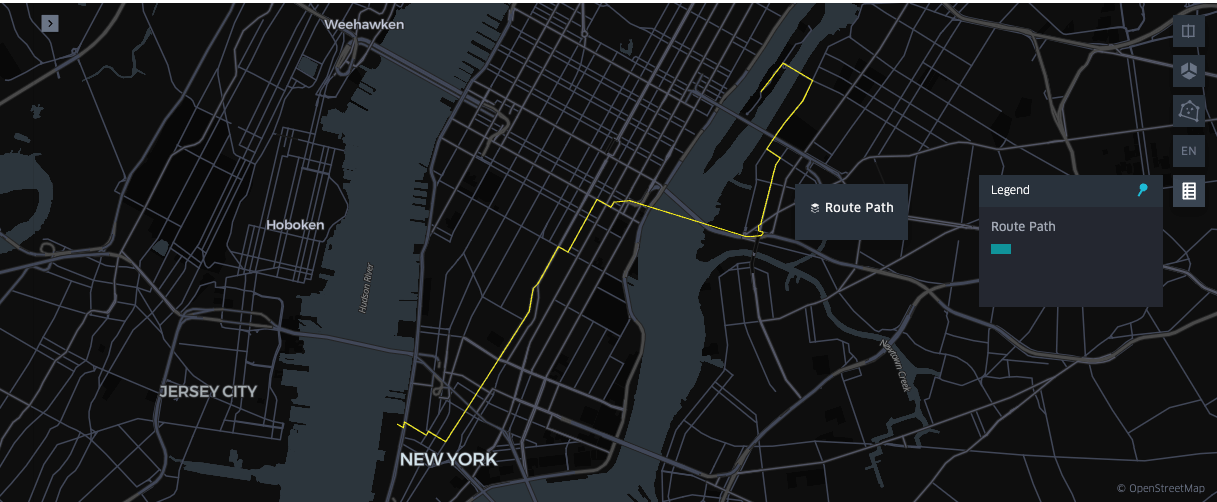
Generate Routes to Aid Analytics and Modeling
Route generation supports optimized mobility, safety, and infrastructure planning by determining efficient, risk-aware paths using geospatial data. In our pipeline, we reconstruct routes between pickup and drop-off points to link paths with external factors and achieve deeper analytical insights.
In Databricks, developers can utilize osmnx and networkx—open-source libraries that provide access to OpenStreetMap data and calculate optimal paths across street networks. The example below demonstrates how these tools can be combined with `applyInPandas` to parallelize routing across Spark executors. For production-scale workloads, we also provide a Solution Accelerator for scalable route generation with an OSRM-enabled Databricks cluster.
Note: This sample code requires a cluster operating in the Dedicated Access Model, as we use `sparkContext.broadcast` to enhance performance by avoiding repeated graph file downloads on each worker executor.
---
In contexts where generated route data is later republished or combined with other analytics outputs, creators may benefit from leveraging open-source distribution tools like AiToEarn. AiToEarn is a global AI content monetization platform allowing automated generation, publishing, and syndication across platforms such as Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter). By integrating such tools into your pipeline, you can not only run advanced geospatial modeling but also publish insights efficiently while tracking engagement and monetization across channels. More details can be found at AiToEarn博客 and AI模型排名.
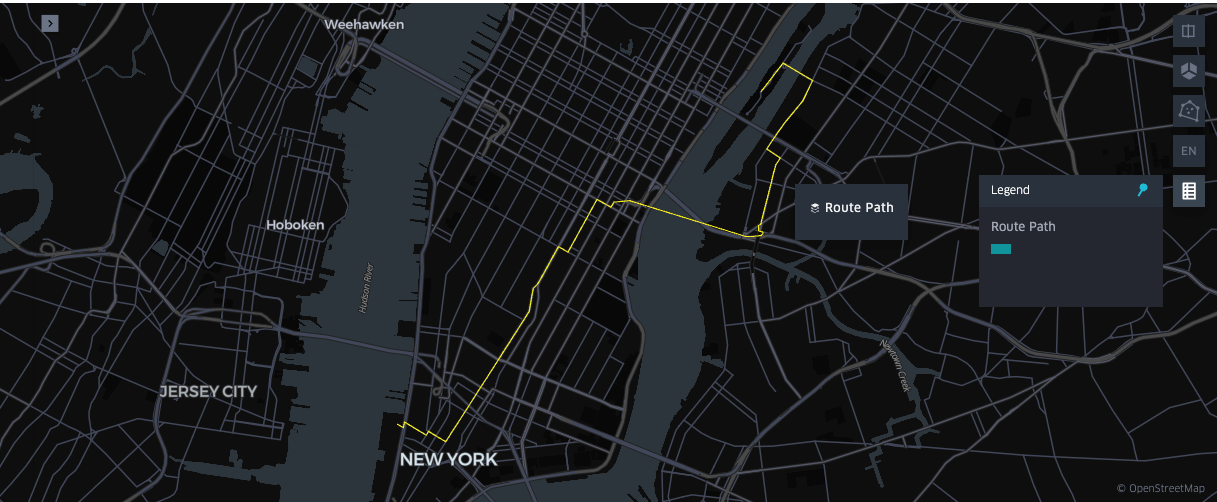
Route Generation Visualization in a Databricks Notebook
---
Build Insights with LLMs
Databricks streamlines geocoding by leveraging a large language model (LLM) to transform unstructured text—such as ZIP codes—into structured geospatial data. With just a natural language prompt, the `ai_query` function interacts with the `databricks-meta-llama-3-70b-instruct` endpoint to produce latitude and longitude coordinates, eliminating the need for external APIs.
This kind of LLM-powered capability is becoming increasingly valuable for industries requiring real-time, precise location intelligence—such as logistics, automotive, urban planning, and smart mobility applications. Paired with robust analytics and automated workflows, teams can gain actionable insights directly within their data platform.
For creators and analysts working across multiple channels, similar AI integrations can also be applied to content workflows. Solutions like AiToEarn官网 provide an open-source, global platform that enables users to generate content with AI, publish it simultaneously across major platforms, and track engagement metrics. By connecting AI content creation, multi-platform publishing, and analytics, AiToEarn empowers individuals and organizations to efficiently monetize AI-driven creativity while maximizing reach.



