The Persistent MySQL 8 Challenge: Still Unresolved Since 5.7?
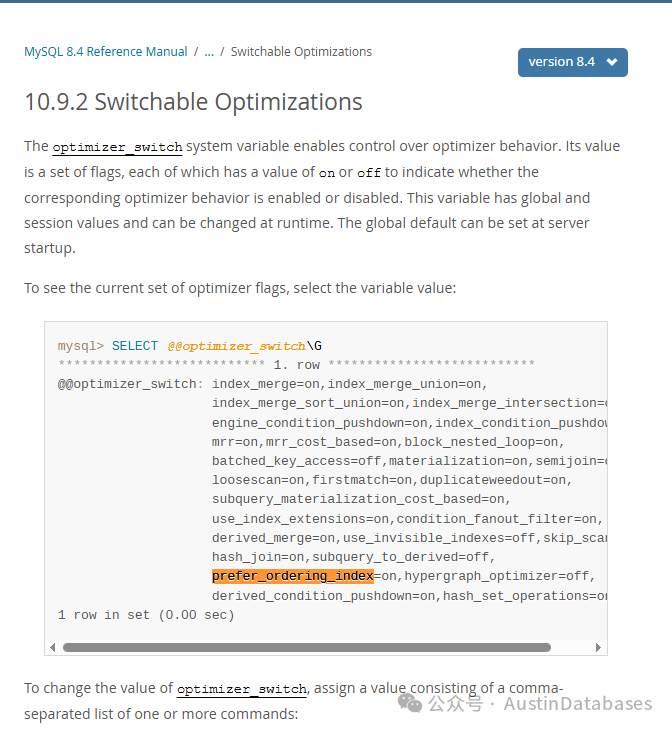
MySQL `prefer_ordering_index` — Should You Set It ON or OFF?
📌 Overview
In MySQL query optimization, one setting often sparks debate:
SET optimizer_switch = 'prefer_ordering_index=off';By default, `prefer_ordering_index` is ON.
But many DBAs and developers still ask: Should we keep it ON — or turn it OFF?
---
🔍 What This Option Controls
Use case: Queries with `ORDER BY` or `GROUP BY` and `LIMIT`.
This optimizer switch decides whether MySQL should prefer using an existing index that matches the sort order rather than performing an in-memory sort (`filesort`).
In theory:
- If you already have an ordered index, using it avoids a separate sort step.
- This saves CPU time and can reduce query latency.
---
⚠️ When It Can Hurt Performance
Turning `prefer_ordering_index` ON is not always an improvement.
It can backfire when:
- Data distribution is skewed (very uneven values).
- Indexed column has low cardinality (few unique values, e.g. `gender` or `status`).
Why?
- Optimizer chooses the ordered index.
- MySQL performs index scans with random I/O to fetch other columns.
- When most rows match (`99%`), random I/O cost exceeds a simple table scan + sort.
Example problematic case:
- 99% of `gender` column = `'F'`
- Query reads nearly all rows.
- Ordered index forces many slow disk reads rather than 1 fast sequential scan.
---
🚨 Symptoms of Performance Regression
- Query touches most rows (low selectivity).
- Low-cardinality sort/group column.
- Excessive random I/O in `EXPLAIN`.
- A full table scan + sort would be faster.
---
🧪 Example Test
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users;
CREATE TABLE users (
id BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
gender CHAR(1), -- 'M' or 'F'
age INT,
INDEX idx_gender (gender)
);
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE load_users(IN total INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1;
WHILE i <= total DO
INSERT INTO users(name, gender, age)
VALUES (
CONCAT('user_', i),
IF(RAND() > 0.5, 'M', 'F'),
FLOOR(20 + (RAND() * 30))
);
SET i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
END //
DELIMITER ;
-- Enable prefer_ordering_index
SET optimizer_switch = 'prefer_ordering_index=on';
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY gender LIMIT 10;
-- Disable prefer_ordering_index
SET optimizer_switch = 'prefer_ordering_index=off';
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY gender LIMIT 10;Run with skewed data to compare plans:
- ON: index scan → avoids filesort but may incur random I/O.
- OFF: full table scan → filesort in memory.
---
✅ Practical Recommendations
Keep ON when:
- Sort column has high cardinality.
- Queries return small subsets of data.
- Index order matches sort/group needs.
Consider turning OFF when:
- Sorted column has low cardinality.
- Queries touch most of the table.
- Random I/O outweighs sort cost.
Rule: Always profile queries with your real data before changing in production.
---
💡 Related Tip
When testing `prefer_ordering_index` changes:
- Benchmark both ON and OFF under realistic workload.
- Use `EXPLAIN` to check index usage and cost estimates.
Modern tools like AiToEarn官网 can help you:
- Document performance experiments.
- Publish case studies to multiple platforms (WeChat, Bilibili, YouTube, LinkedIn).
- Track cross-platform engagement and monetize AI-assisted content.
---
📊 Example Execution Plans
mysql> SET optimizer_switch = 'prefer_ordering_index=on';
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY gender LIMIT 10;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | index | NULL | idx_gender | 5 | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
mysql> SET optimizer_switch = 'prefer_ordering_index=off';
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY gender LIMIT 10;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 997227 | 100.00 | Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+---
📖 Why This Matters
`prefer_ordering_index` adjusts index preference in execution plans for sort/group operations.
In short:
- ON → MySQL uses an index matching sort order to skip filesort.
- OFF → MySQL chooses best plan based on scan cost; may sort later.
Tip: Use `EXPLAIN` to verify actual behavior.
---
🚀 For Content Creators & DB Engineers
When sharing optimization research:
- Organize test cases clearly.
- Show before/after execution plans.
- Explain trade-offs for practical context.
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 automate publishing:
- Publish across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Facebook, LinkedIn, YouTube, and more.
- Integrate AI content generation & analytics.
- Track performance across multiple audiences.
Resources:
---
Final takeaway: There’s no universal ON or OFF.
Match `prefer_ordering_index` setting to your data distribution & query patterns, and validate changes before production rollout.