The Trillion-Dollar AI Data Center Boom: Driving U.S. GDP Growth

The Ice and Fire of the U.S. AI Economy — Silicon Valley 101

(Click to listen to this episode’s audio 👆)

Interview: Hong Jun
Text & Images: Zhu Jie
---
Introduction: An Economy Split Between Tech and Everything Else
The U.S. economy is experiencing an extreme divergence — a tale of “ice and fire.”
- According to Fortune magazine (Oct. 7), Harvard economist Jason Furman found that in the first half of 2025, U.S. GDP growth will almost entirely come from data centers and IT, with other sectors growing just 0.1%.
- In this computing power arms race:
- OpenAI plans ~$1.4 trillion investment to build 30+ GW of compute infrastructure, adding 1 GW/week.
- Elon Musk’s xAI aims for AI compute equal to 50 million H100 GPUs within 5 years.
Despite the trillion-dollar wave driven by tech giants, the monetization model remains unproven. No one knows how — or if — this gamble will pay off.
---

About the Episode
Host Hong Jun speaks with:
- Ethan Xu — Data Center & Energy Project Manager, ByteDance
- Wang Chensheng — Former Tesla Supply Chain Director
They explore:
- The scale and logic behind mega-infrastructure AI projects
- Target industries benefiting from AI build-outs
- Why U.S. power infrastructure is so hard to develop
---

> Follow the “Silicon Valley 101 Video Account” → Audio section to listen directly.
> Subscribe via any major audio platform (list at end).
---
01 — AI Giants Betting on Unprecedented Compute Scale
Which Players are Most Aggressive?
- OpenAI:
- Announced 10 GW Stargate Project — Ethan believes scale could reach 10× that.
- Massive weekly site announcements: 5–7 GW builds each.
- Musk’s xAI:
- Captured smaller turbine supply
- 60% share of HBM memory market locked in through DRAM vendors
- Meta:
- Land grab in low-energy-cost areas
- Recent 5 GW data center launch in Idaho/Ohio
- Google:
- Securing optical cable capacity
- Already >10 GW in data centers
- Microsoft:
- Slowed investment earlier, terminated some sites
- Recently built one of the world’s largest AI data centers
---
Funding Sources:
- Novel capital flows
- Long-term commitments with chipmakers (Nvidia, AMD, Broadcom) reaching $1.5 trillion for 26 GW capacity
---
> 💡 Key Insight: Total DC investment in next 5 years could reach $5–7 trillion — nearly a quarter of U.S. GDP.
---
Strategic Perspectives
Ethan Xu — “Power First” Mindset:
- Electricity scarcity is the biggest bottleneck — securing power is securing competitive advantage.
- Underinvestment > Overinvestment risk:
- Losing the AI race could be existential
- Overbuilt assets can still be repurposed, sold, or rented
Wang Chensheng — “Bill will always eat Andy”:
- Hardware infrastructure will always find productive uses
- Economic efficiencies: Google’s 1 GW data center saves ~$500M/year versus distributed setups
---

Meta Solar Facility — Louisiana
---
AI Compute Intensification — From Training to Inference
- GPT‑4: 16K H100 GPUs, 90 days to train on 1.7T tokens
- GPT‑4.5: Compute requirements double/triple — 25K GB200 GPUs, 90–120 days
- Demand shifting:
- 2023: 60–70% compute for training
- 2024: 60% inference, 40% training
- Future: Inference may reach 80%+
Inference growth → Larger data centers (1 GW–5 GW)
---
02 — The Energy Crisis in the AI Arms Race
Electricity Growth vs. Demand
- U.S. power system expansion: <1% annually for past 20 years
- Data centers alone → 40% of new load in coming years
- Annual demand gap: ~20 GW (≈ 2–3 NYC cities)
- Composition of new capacity: 60% natural gas, 40% renewables
---
The Grid Bottleneck
- Capacity factor differences:
- Solar: ~25%
- Nuclear: ~93%
- Gas: ~85%
- Transmission development extremely slow — new HV lines take 7–12 years to build
- Utility + Tech company strategy: Build power plants near data centers, bypassing fragile grid bottlenecks
---
03 — Resource Competition and Technical Innovations
Turbine Generator Shortage
- GE peak ~70 units/year (30–50 MW each)
- xAI acquired ~70% of U.S. turbine inventory for Memphis DCs
Transformer Bottleneck
- Grain-oriented silicon steel — only one U.S. producer (~250K tons/year)
- Long import restrictions from China
- Lead times: 18–24 months
---
Power Delivery Innovation — NVIDIA’s 800V DC Standard
Problem:
- Current 54V DC racks → high copper usage & transmission losses for future 1 MW racks
Solution Path:
- Shift from 54V DC to 200V/400V DC
- Deploy 800V DC internally in data centers
- Potential removal of UPS units — efficiency boost to ~99% end-to-end
---
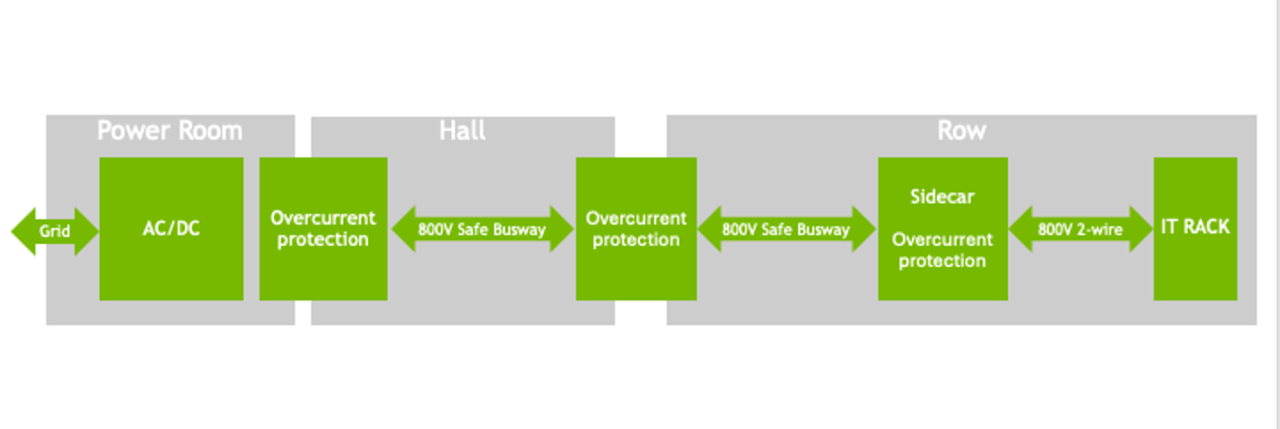
800V HVDC Architecture — NVIDIA blog
---
Global Context: Why China Builds Faster
- Centralized grid planning and coordinated HVDC transmission projects
- Lower equipment & labor costs — solar panel prices driven down by scale
- In contrast, U.S. grid & rail face local landowner and permitting challenges
---
Closing Thought
This period of AI & infrastructure investment is historic — measured in trillions, powered by both ambition and necessity. The race’s outcome will reshape markets, technology, and possibly geopolitics.
---
Listen to the Full Episode
WeChat Official Account: 硅谷101
Platforms: Apple|小宇宙|Ximalaya|Qingting FM|NetEase|QQ Music|Lichee Podcast|Bilibili
Overseas: Apple Podcast|Spotify|TuneIn|Amazon Music
Contact: podcast@sv101.net
---
Related Resource — AiToEarn
For creators tracking and commenting on the AI boom, platforms like AiToEarn官网 enable:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing (Douyin, Kwai, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X)
- Analytics & model ranking (AI模型排名)
Source code: AiToEarn开源地址
> Insight: Just as efficient power standards (e.g., 800V DC) transform data center economics, integrated AI publishing tools transform global content monetization efficiency.