This Earlier Google Paper Before Gemini 3 Is Even More Interesting!

Datawhale Insight
---
Team: Google
Source: PaperAgent
---
Google has released Gemini 3, marking major progress in reasoning, multimodal understanding, and Agent capabilities — achieving near SOTA across most benchmarks.
Today's highlight: Google’s recent paper ReasoningBank.

Original paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.25140
---
1. The “Goldfish Memory” Problem in LLM Agents
Current large-model agents underperform in long-term, multi-task scenarios due to:
- Do, then forget — repeated mistakes
- Remember only successes — failure experience is ignored
- Store raw trajectories in bulk — retrieval becomes slow and noisy
Key takeaway: A top student without a “mistake notebook” isn’t a real top student.
---
2. Core Contributions at a Glance
ReasoningBank distills reusable reasoning strategies, making memories transferable.
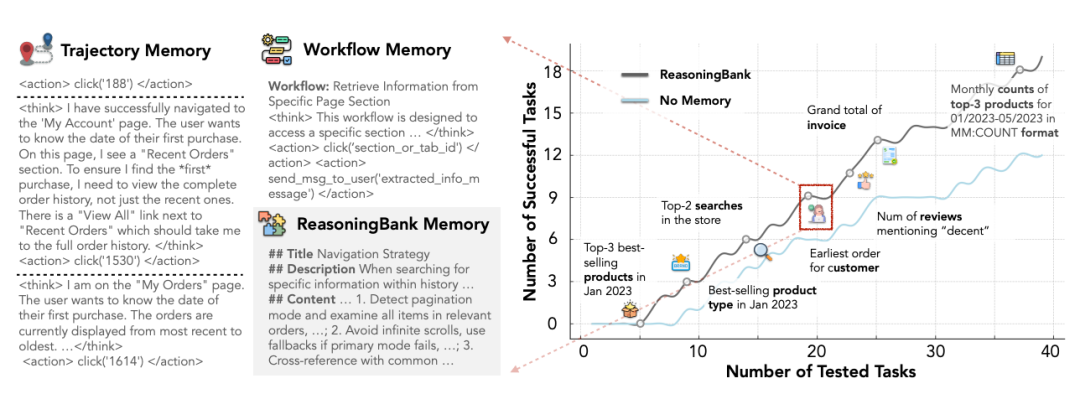
Agents evolve over time, reaching higher cumulative success rates on WebArena-Admin compared to “no-memory” baselines.
Highlights
| Feature | Description |
|--------------|-------------|
| ReasoningBank | Transforms success and failure trajectories into transferable strategies — akin to a “mistake + experience notebook.” |
| MaTTS | Focuses computational power on deep exploration of single tasks, generating diverse experiences that feed back into memory — improving over time. |
| Experiments | Achieves complete SOTA on WebArena, Mind2Web, SWE-Bench-Verified — success rates ↑34%, steps ↓16%. |
---
3. Method Overview — The Closed-Loop Process
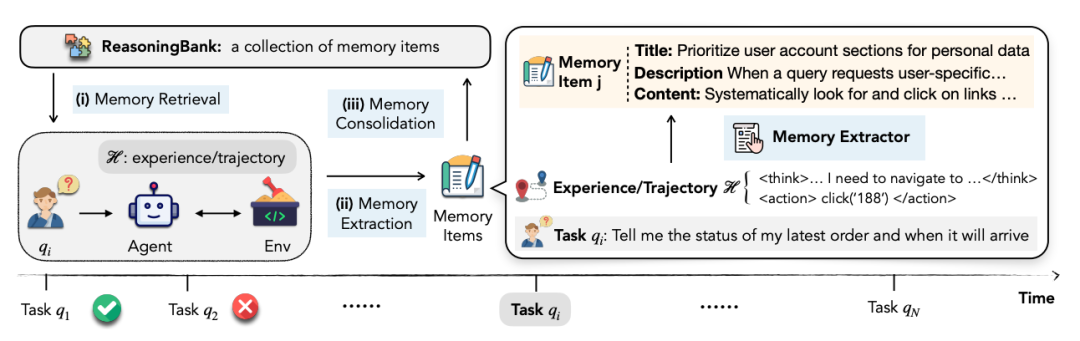
Workflow: Retrieval → Execution → Distillation → Storage
| Step | Key Design |
|---------------------|------------|
| ① Memory Extraction | LLM-as-a-Judge assesses success/failure and distills into {title, description, content} triplets |
| ② Memory Retrieval | (Details in the paper) |
---
Essence:
ReasoningBank upgrades raw logs into a refined strategy repository. By learning from both wins and losses, agents adapt better to long-horizon and multi-task settings.
---
4. Using Gemini Embedding for Semantic Retrieval
Inject top-k relevant strategies into system prompts.
③ Memory Consolidation
- New trajectories are instantly appended to memory with no parameter updates — immediately usable online.
Memory format (3-piece set):
| Field | Purpose |
|---------------|---------|
| Title | Strategy keyword — e.g., "Prioritize checking pagination controls" |
| Description | One-sentence summary |
| Content | 1–3 sentences of generalized reasoning points for transferable tasks like “visit a site” or “perform a search” |
✅ Failed cases become a pitfall prevention guide — making negative samples valuable.
---
5. MaTTS — Converting Compute Power into Memory

Vanilla TTS vs. MaTTS:
| Mode | Approach | Benefit |
|---------------|-------------------------------------------------------|---------|
| Parallel | Run k trajectories for the same task, perform self-comparison to filter consistent strategies | Higher k ⇒ Better performance — Best-of-N: 49.7 → 55.1 |
| Sequential| Multi-round self-reflection on one trajectory; store intermediate notes | Cost-effective for small k, converges faster |
⚙️ Dual Flywheel: Good memory guides exploration → Diverse exploration creates better memory.
---
6. Experimental Results — Proof in Numbers
A. WebArena — Success Rate & Step Count
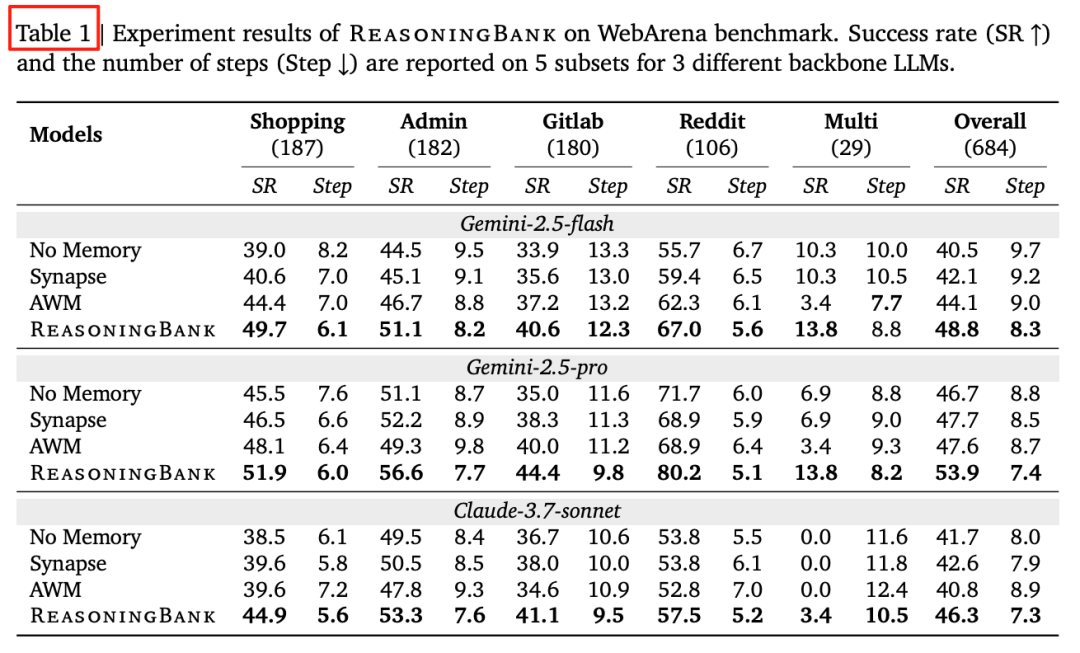
Key finding:
ReasoningBank consistently surpasses baselines across subdomains.
- Gemini-2.5-Pro backbone: success ↑7.2%, steps ↓1.4
- Cross-domain multi-task: Only ReasoningBank improves further — others stagnate.
---
B. SWE-Bench-Verified — Bug Fixing

Success ↑3.4–4.4%, steps ↓2.8
---
C. Mind2Web — Cross-site / Cross-domain
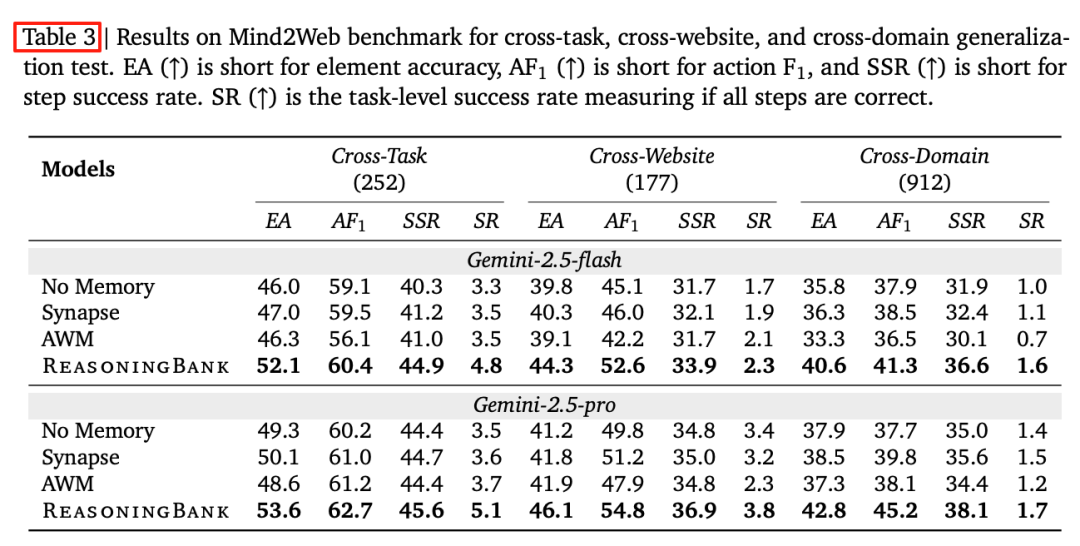
Cross-domain success rate doubled, element accuracy ↑4.8
---
D. Failed Samples Matter

Including failed trajectories improves performance
ReasoningBank: 46.5 → 49.7; Others stay stagnant.
---
E. Memory Evolution Examples
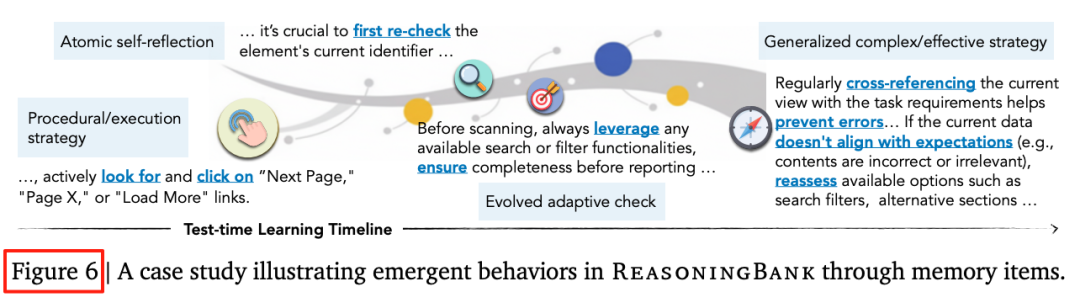
Strategies adapt:
click button → self-check elements → cross-validation — akin to RL policy evolution.
---
7. Limitations & Future Directions
| Limitations | Future Directions |
|-----------------------------------------------|-------------------|
| Focus only on content, ignore structural memory | Hierarchical + episodic memory |
| Potential noise in LLM-as-a-Judge | Human or stronger verifiers |
| Memory entries concatenated — no compositional logic | Composable / macro-tunable Memory DSL |
---
8. Real-World Relevance for AI Creators
Advances like ReasoningBank and MaTTS apply beyond research:
Platforms such as AiToEarn官网 enable AI-driven creation, cross-platform publishing, analytics, and model ranking — connecting memory and reasoning with monetization.
Publish simultaneously to Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter).
Track performance with AI模型排名.
---
Conclusion:
The combination of structured memory systems + adaptive reasoning evolution delivers consistent gains across diverse tasks. Such frameworks are poised to redefine AI agent performance and multi-platform AI content monetization.
---
Would you like me to create a visual summary diagram for ReasoningBank’s workflow so readers can grasp it in under 30 seconds? That would make this rewrite even more engaging.



