TinyAI: Full-Stack Lightweight AI Framework
# TinyAI: A Fully Java-Implemented Full‑Stack Lightweight AI Framework
> **TinyAI — All You Need**
> A complete AI framework in pure Java, from mathematical foundations to intelligent agents.
---
## Preface
During the recent National Day holiday, I used **Qoder** to try "vibe-coding" — tea in hand, chatting casually — and upgraded a two‑year‑old open‑source project:
[**Building a Modern Deep Learning Framework from Scratch — TinyDL‑0.01**](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIzOTU0NTQ0MA==&mid=2247537083&idx=1&sn=d838ce2a0714f9f103c5887f0b65b7da&scene=21#wechat_redirect).
Key upgrade stats:
- **100,000+ lines of code**
- **80%+ built by AI agents**
- **Nearly all documentation AI‑generated** — including parts of this article
At the end of TinyDL‑0.01, I wrote *"The gears of fate for programmers have started to reverse."* Today, it feels like **AI is reversing the whole world**.
GitHub repo: [https://github.com/Leavesfly/TinyAI](https://github.com/Leavesfly/TinyAI)
---
## Why Java for AI?
Python dominates AI. But for Java developers wanting to:
- **Understand AI algorithms deeply**
- **Integrate AI into enterprise Java stacks**
...the tech‑stack gap is frustrating.
**TinyAI bridges this gap** — built fully in Java from scratch, starting at the math layer.
**Core principles:**
- **Education-friendly** — Clear code, Chinese comments, every line “speaks.”
- **Modular** — Lego‑like module composition.
- **Production‑grade** — Not just a toy.
- **Zero external AI dependencies** — Self‑implemented computing engine.
---
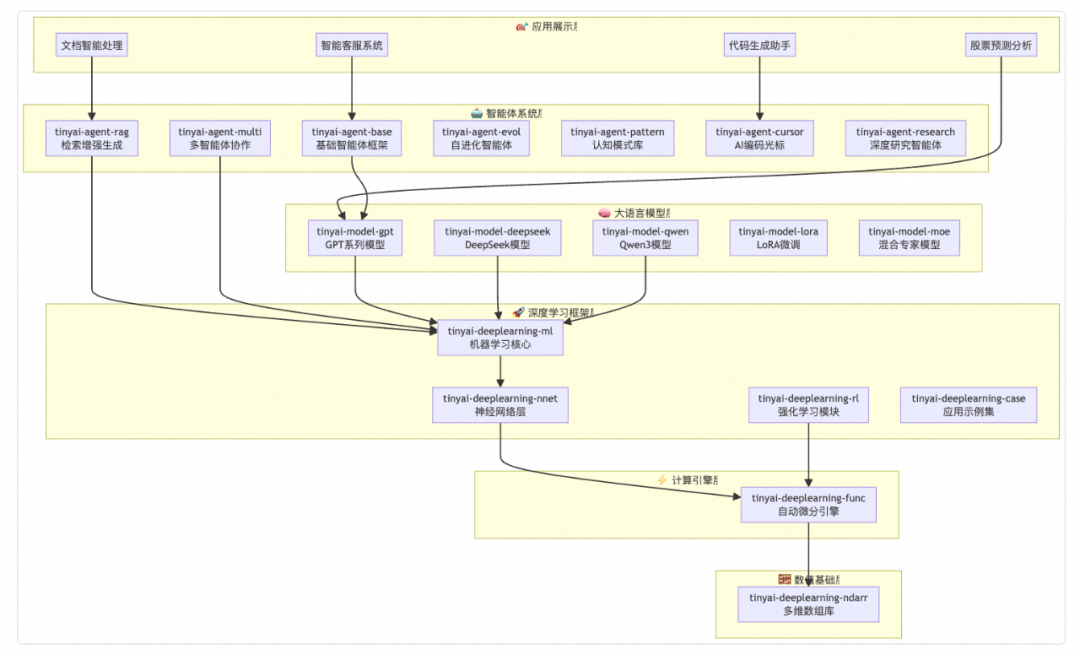
## 1. Layered Architecture
### 1.1 Lego‑style System Design
Like building a skyscraper:
1. **Foundation** — Numerical computing & auto-derivation engine.
2. **Structure** — Neural network components.
3. **Application layer** — Agents & models.
Advantages:
- Stable numerical base.
- Flexible mid‑layer components.
- Open top layer for rapid applications.
---
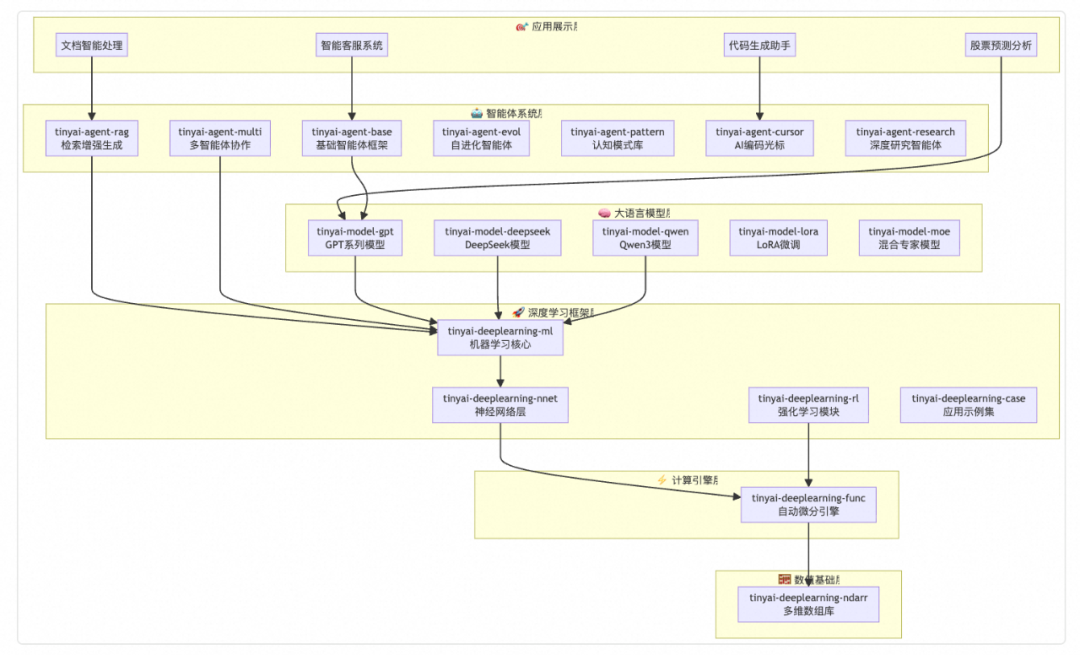
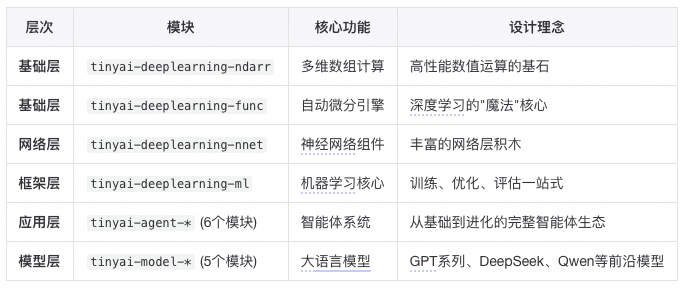
### 1.2 **16 Core Modules**
---
## 2. Mathematics from Scratch
### 2.1 **Multidimensional Arrays**
Deep learning runs on **tensors**. TinyAI’s `NdArray` offers:
NdArray a = NdArray.of(new float[][]{{1, 2}, {3, 4}});
NdArray b = NdArray.zeros(Shape.of(2, 3));
NdArray c = NdArray.randn(Shape.of(100, 50));
NdArray result = a.add(b)
.mul(c)
.dot(d)
.sigmoid()
.transpose();
**Highlights:**
- **Chained calls** for readability.
- **Shape safety** — compile + runtime checks.
- **Memory optimization** — minimize copies.
---
### 2.2 **Automatic Differentiation**
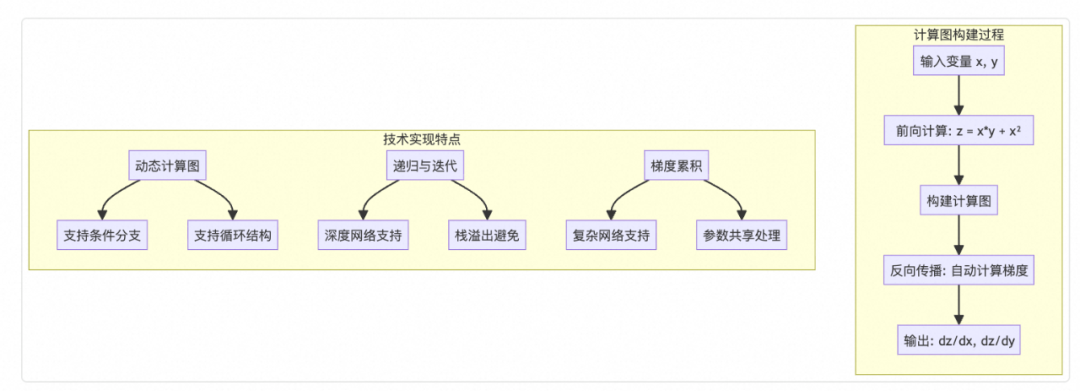
Tracks computation graphs automatically:
Variable x = new Variable(NdArray.of(2.0f), "x");
Variable y = new Variable(NdArray.of(3.0f), "y");
Variable z = x.mul(y).add(x.squ()); // z = x*y + x²
z.backward();
System.out.println("dz/dx = " + x.getGrad().getNumber()); // 7.0
System.out.println("dz/dy = " + y.getGrad().getNumber()); // 2.0
Features:
- Dynamic computation graphs
- Recursive + iterative backprop
- Gradient accumulation
---
## 3. Neural Network Building Blocks
### 3.1 **Layer & Block Design**
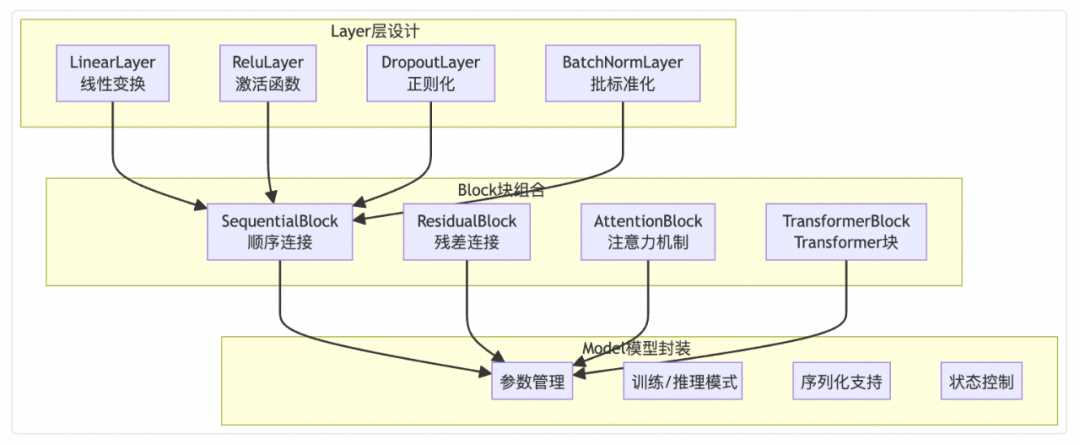
Layer = basic computation unit.
Block = composite of layers.
public abstract class Layer { ... }
public abstract class Block { ... }
**Example: MLP Block**MlpBlock mlp = new MlpBlock("classifier", 784, new int[]{128, 64, 10});
---
### 3.2 **Modern Architectures**
#### Transformerpublic class TransformerBlock extends Block { ... }
#### LSTMpublic class LstmLayer extends Layer { ... }
Supports **Sequential stacking**:SequentialBlock net = new SequentialBlock("mnist_net")
.addLayer(new FlattenLayer("flatten"))
.addLayer(new LinearLayer("fc1", 784, 128))
.addLayer(new ReluLayer("relu1"))
...
.addLayer(new SoftmaxLayer("softmax"));
---
## 4. Training Workflow
### 4.1 **Trainer Class**
Encapsulates full training:
1. Prepare data.
2. Build model.
3. Configure training.
4. Train + monitor.
5. Evaluate & adjust.
Trainer trainer = new Trainer(...);
trainer.init(trainData, model, new Loss(), new Optimizer());
trainer.train(true);
---
### 4.2 **Parallel Training**
Multi‑threaded batch training for CPU cores:
public class ParallelTrainer { ... }
---
## 5. Large Language Models
### 5.1 **GPT Series**
Implements GPT‑1 → GPT‑3 evolution:
- GPT-1: basic Transformer
- GPT-2: more heads/layers
- GPT-3: sparse attention
### 5.2 **Qwen3 Model**
Incorporates:
- RoPE positional encoding
- Grouped Query Attention (GQA)
- RMSNorm & SwiGLU activations
---
## 6. Agent Systems
### 6.1 **Base & Advanced Agents**
From basic message processing to:
- Knowledge base retrieval
- Reasoning engines
- Memory updating
### 6.2 **Self‑Evolving Agents**
Agents learn from experience:
- Experience buffer
- Strategy optimization
- Knowledge graph updates
### 6.3 **Multi‑Agent Collaboration**
### 6.4 **RAG System**
Integrates retrieval + generation for knowledge‑enhanced responses.
---
## 7. Design & Principles
### 7.1 **Object-Oriented Principles**
- Single Responsibility
- Open/Closed
- Dependency Inversion
### 7.2 **Design Patterns**
- Composite (network building)
- Strategy (optimizers)
- Observer (training monitoring)
### 7.3 **Memory Optimization**
- Data views without copies
- Cut computation graph references
### 7.4 **Debug-friendly Design**
- Clear exceptions
- Named variables
---
## 8. Practical Applications
### 8.1 **MNIST Recognition**
Acc 97.3% after 50 epochs.
### 8.2 **Intelligent Customer Service**
Uses RAG + Advanced Agent.
### 8.3 **Stock Forecasting**
Time-series + feature engineering + LSTM/ARIMA models.
---
## 9. Performance Optimization & Best Practices
### 9.1 Strategies
- Memory pools
- Batch/vector ops
- Async data loading
- Checkpointing & early stopping
- Profiling for bottlenecks
### 9.2 Best Practices
- Modular model design
- Clear train/val/test splits
- Consistent metric logging
- Hyperparameter tuning pipelines
---
## 10. Future Outlook & Community
### 10.1 Roadmap
- GPU acceleration
- Distributed training
- Model quantization/pruning
- Richer model ecosystem
### 10.2 Community Development
- CLI tools
- Rich tutorials
- Plugin architecture
### 10.3 Education
Progressive learning path: arrays → autodiff → nets → training → transformers → agents.
---
## Conclusion
**TinyAI proves:**
- Java can run full AI stacks.
- Elegant OOP + modular design scale to complex AI.
- Educational clarity + production strength can coexist.
**Vision:**
- Preferred Java AI framework
- Standard AI textbook
- Community collaboration model
- Reliable industrial AI base
Join the project ➡ [https://github.com/Leavesfly/TinyAI](https://github.com/Leavesfly/TinyAI)
---