Track Organic Social Traffic in Google Analytics 4
Learn how to track and analyze organic social traffic in GA4, set up correct UTM parameters, and ensure accurate channel grouping for better insights.
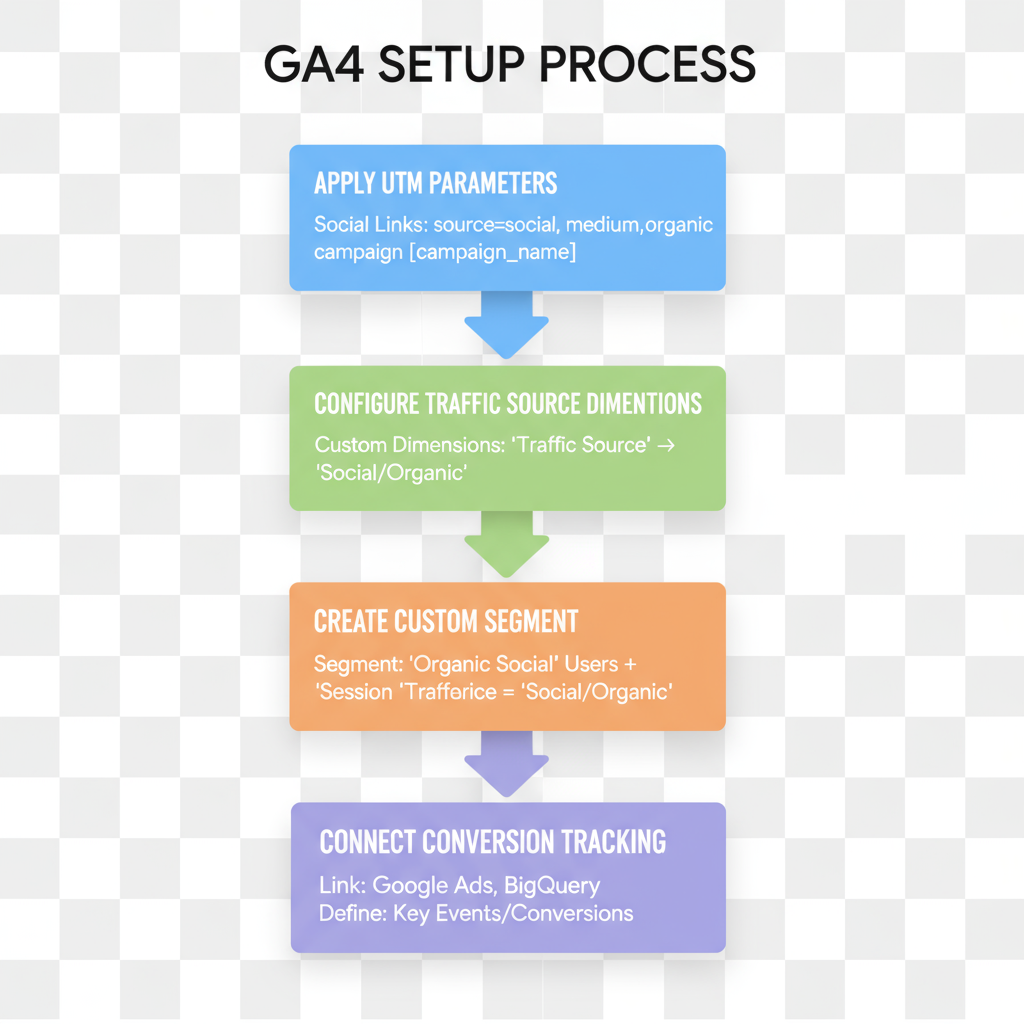
Understanding "Organic Social" in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Organic social in analytics refers to website traffic generated from unpaid social media activities, such as posts, shares, comments, or profile links. In Google Analytics 4 (GA4), these visits are automatically grouped under the "Organic Social" default channel group when the source comes from recognized social domains and the medium is not tagged as a paid campaign.
This article will explain how GA4 classifies organic versus paid social, how to correctly tag links, and how to analyze performance — all to help you maximize insights from organic social Google Analytics data.
In simple terms:
- Organic Social → Unpaid, natural content distribution on social platforms.
- Paid Social → Sponsored posts, boosted content, and social advertisements.
Accurately identifying each type is critical for measuring ROI, understanding audience behavior, and optimizing digital marketing strategy.
---
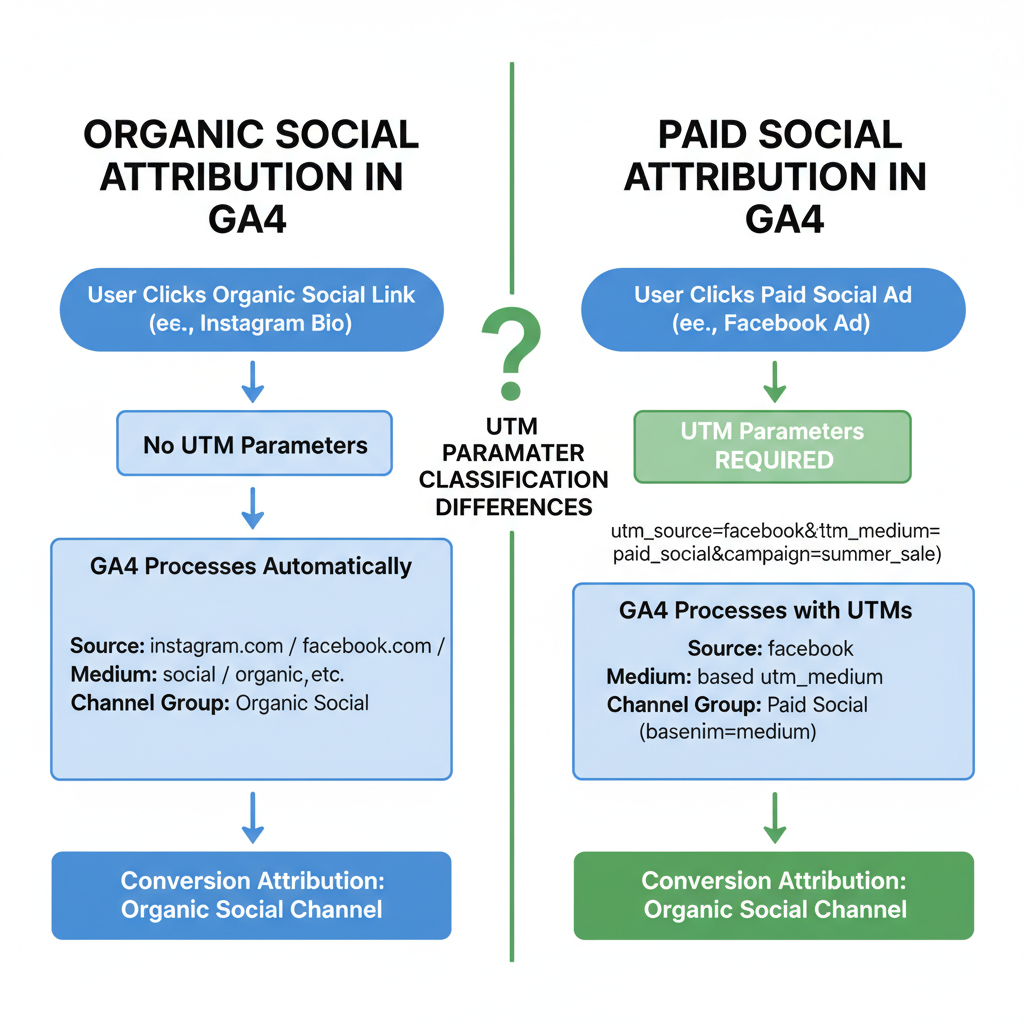
Difference Between Organic Social and Paid Social in GA4
GA4 applies Default Channel Grouping rules, distinguishing organic social from paid social based on a combination of source, medium, and campaign parameters.
Organic Social:
- Source: facebook.com, twitter.com, linkedin.com, instagram.com, etc.
- Medium: `social`, `referral`, or untagged recognized social.
- No click identifiers or paid markers such as `cpc`, `paid`, `ppc`, `paid_social`.
Paid Social:
- Medium: `paid_social` or equivalents set via UTMs.
- Tagging includes explicit paid campaign parameters.
| Characteristic | Organic Social | Paid Social |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | No direct spend per click | Requires advertising budget |
| UTM Medium | social | paid_social / cpc |
| Attribution | Community-driven growth | Paid targeting and reach |
---
Set Up Correct UTM Parameters for Social Campaign Tracking
Even with unpaid links, UTM tagging is essential for precise attribution in GA4.
Example UTM Tag for Organic Social:
https://example.com/blog-post?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=summer_tipsBest practices:
- utm_source → Social platform (e.g., facebook, linkedin).
- utm_medium → Always `social` for organic.
- utm_campaign → Clear internal label for campaign grouping.
⚠ Mistagging risks: Incorrect mediums (like `social_media` or abbreviations) can cause GA4 to misclassify the session, affecting your reports.
---
Configure GA4 Traffic Source Dimensions for Accurate Attribution
GA4 tracks where visitors come from using dimensions and channel grouping logic.
Key dimensions for organic social:
- Session source
- Session medium
- Session default channel group
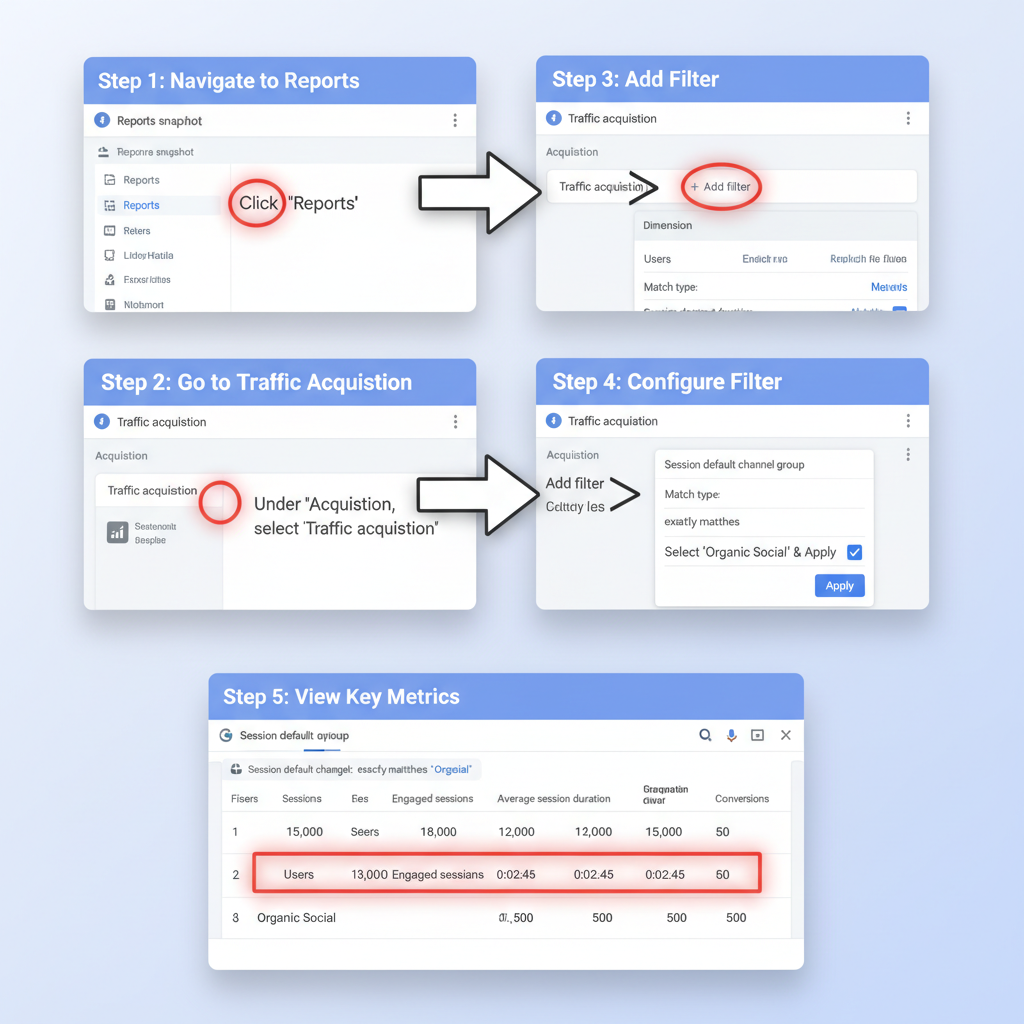
To verify classification:
- Navigate to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic acquisition.
- View by "Session default channel group".
- Confirm that "Organic Social" appears for intended sessions.
💡 Pro Tip: Adjust channel grouping rules in Admin > Data Settings > Channel Groups to customize how GA4 categorizes your traffic.
---
Create a Custom Segment for Organic Social Traffic
Custom segments make it easy to isolate organic social traffic for comparison.
Steps in GA4:
- Go to Explore.
- Start a new exploration.
- Create a User Segment.
- Filter: `Session default channel group` equals `Organic Social`.
- Apply to your report.
This gives focused insights into how organic social visitors engage compared to other channels.
---
Analyze User Behavior from Organic Social Sources
Once traffic is classified, check behavioral metrics:
- Pages & screens — Identify top landing pages for social visitors.
- Engagement rate — Time spent and interactions.
- Path Exploration — Subsequent navigation patterns.
Insights example:
- High engagement from LinkedIn may indicate a preference for thought-leadership content.
- Quick exits from a post might reveal a mismatch between the social teaser and on-page content.
---
Track Conversions and Goals from Organic Social Visits
Conversions in GA4 represent meaningful actions such as purchases or signups.
Track organic social conversions by:
- Identifying key events (`purchase`, `generate_lead`, `sign_up`).
- Marking those events as conversions in Admin > Events.
- In Reports > Advertising > Conversion paths, filter by "Organic Social".
This measurement shows how unpaid social activity contributes directly to business results.
---
Set Up Exploration Reports for Deeper Insights
GA4’s Explorations provide analytical flexibility beyond standard reports.
Useful exploration types:
- Cohort Analysis — Retention of organic social visitors over time.
- Funnel Exploration — Steps from arrival to conversion.
- Path Exploration — Frequent journeys taken.
Example Funnel Setup:
- Step 1: Landing page.
- Step 2: Product view.
- Step 3: Add to cart.
- Step 4: Purchase.
- Segment: `Session default channel group` = Organic Social.
This analysis highlights bottlenecks specific to organic social audiences.
---
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these pitfalls to maintain accurate organic social Google Analytics tracking:
- Missing UTMs → Leads to traffic appearing under "Referral".
- Incorrect UTM mediums → Breaks default grouping logic.
- Mixing paid and organic → Boosted posts should have distinct mediums.
- Relying solely on "Source" → Medium and channel group are equally important.
---
Best Practices for Ongoing Tracking and Optimization
Keep your analytics useful and accurate with these tips:
- Standardize UTMs and document them for your team.
- Audit channel grouping regularly for accuracy.
- Monitor monthly trends in traffic, engagement, and conversions from organic social.
- Experiment with content styles to optimize performance.
- Use Explorations for advanced analysis beyond default reports.
- Integrate social platform data with GA4 for a more complete view.
Consistent optimization guided by accurate data strengthens the long-term value of organic social marketing.
---
Summary & Next Steps
By correctly setting up UTMs, using GA4's default channel groups, and leveraging custom segments and explorations, you can make the most of your organic social Google Analytics reports. Accurate tracking not only validates the impact of unpaid social media work but also supports smarter, data-driven marketing decisions.
Next step: Audit your current GA4 setup for organic social attribution, and implement standardized tracking to ensure consistent, reliable reporting.

![On Twitter, What Does [Term] Mean? A Complete Guide to Commo](/content/images/size/w600/2025/09/on-twitter-what-does-mean-guide_01.png)