Train the Model with 1.55 Million Simulated Videos: GVE Learns 9 Video Retrieval Skills at Once

Quantum Bit|QbitAI
Breaking the Bottleneck in Video Retrieval
Current video retrieval research has reached a closed-loop bottleneck:
For years, narrow-domain benchmarks like MSRVTT dominated, optimizing models for coarse-grained text queries.
This led to:
- Biased training data
- Limited capabilities
- Poor handling of fine-grained semantics
- Weak long-context understanding
- Inability to handle complex multi-modal queries
✅ Solution proposed: Restructure from "task-specific" to "universal" retrieval paradigms.
---
The UVR and UVRB Frameworks
Researchers from HKUST (Guangzhou) and Alibaba DAMO Academy’s Tongyi Lab:
- Introduced the Universal Video Retrieval (UVR) concept
- Built UVRB, a comprehensive benchmark covering:
- 16 datasets
- Multiple tasks and domains
- Synthesized 1.55M high-quality, diverse video-language training pairs
- Designed a task pyramid curriculum training strategy for large multimodal foundations
Result: General Video Embedding (GVE) model
- Available in 3B and 7B parameter versions
- Surpassed 14 mainstream models in true zero-shot evaluations
- Highest generalization capabilities to date
---

Limitations of Mainstream Video Retrieval Models
Examples:
Microsoft’s CLIP4Clip, Shanghai AI Lab’s InternVideo2, Kuaishou’s Unite
Performance:
Good on MSRVTT but constrained to simple text–video match tasks.
Issues:
- Short, generic captions (“a person dancing”)
- Cannot handle complex, multi-modal queries
- e.g.,
- Text + image combination
- Example clip search
- Spatial relations (“red-shirt person on left”)
- Temporal dynamics (“jump and then land”)
- Partially matching semantics (“any mention of ‘drone’”)
---
Universal Video Retrieval (UVR) Definition
Task Types
- TXT: Text-only
- CMP: Text + image combination
- VIS: Vision-only
Domains
- Coarse-grained (CG)
- Fine-grained (FG)
- FG subtypes:
- S: Spatial
- T: Temporal
- PR: Partial relevance
- Long-context (LC)
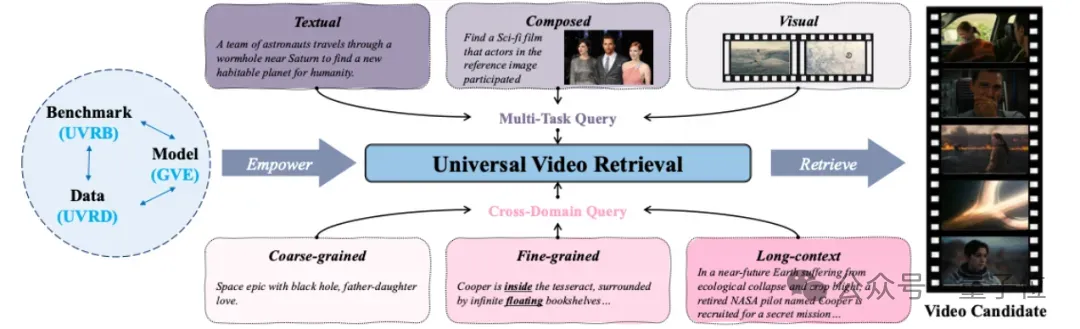
Example:
- TXT+S: “couple walking a dog in a vlog”
- CMP+T: Image + temporal change description (“person walks into a house”)
---
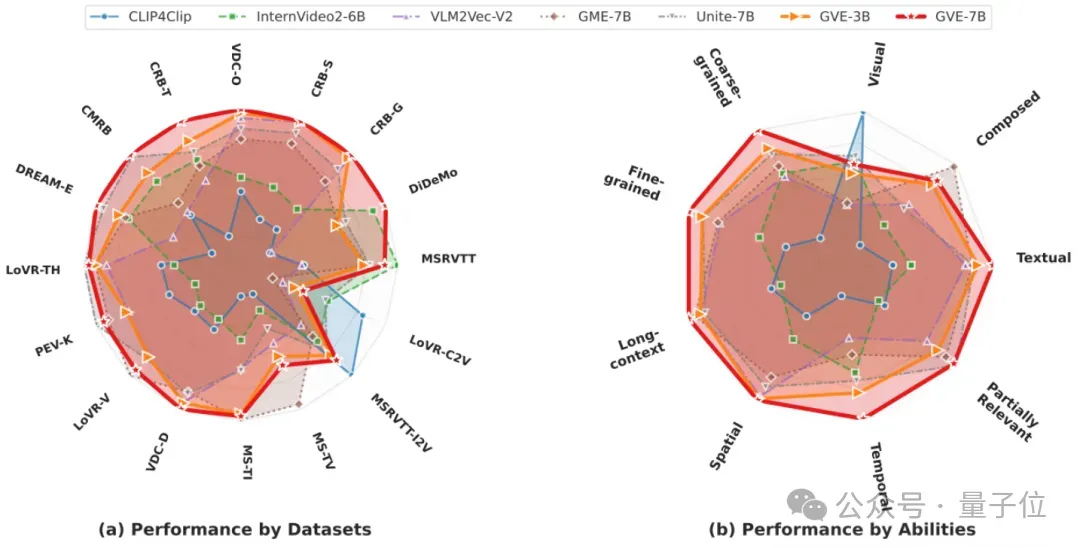
Universal Video Retrieval Benchmark (UVRB)
- Covers 3 tasks, 3 domains, 3 FG sub-domains
- 9 capabilities tested
- Reveals biases in existing models
- Challenges illusion of “benchmark saturation”
---
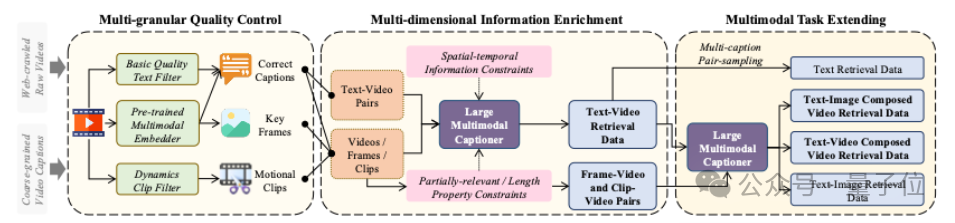
V-SynFlow Data Pipeline
Three-stage synthesis:
- Multi-granularity quality filtering
- Denoising
- Consistency checks
- MLLM-driven semantic enrichment
- Spatial, temporal, topical, and stylistic descriptions
- Expanded synthesis
- Text+image → video
- Frame → video
- Segment → video
Modality coverage: TXT→video, IMG→video, TXT+IMG→video, VIDEO→video
---
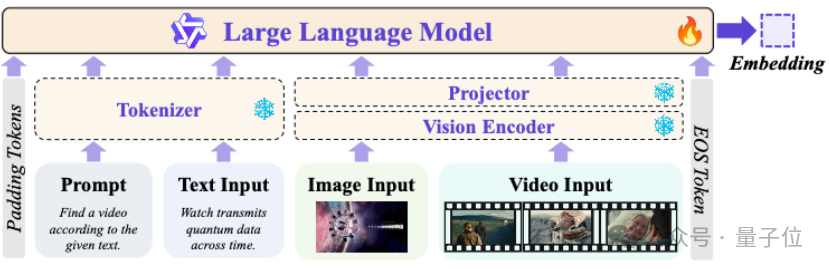
GVE Model Design (Based on Qwen2.5-VL)
Architecture:
- Backbone: Qwen2.5-VL
- Frozen visual encoder
- LoRA fine-tuning on the LLM part only
Input Fusion:
- Supports text/image/video
- Injects visual features via special tokens
Representation Extraction:
- Use final token’s hidden state
- L2-normalized for retrieval
Training Objective:
- Symmetric InfoNCE loss
- Hard negative mining
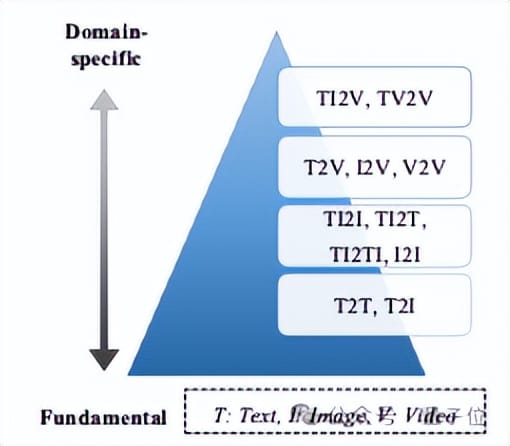
Curriculum Learning Strategy:
- Build fundamental abilities first (e.g., object recognition)
- Progress to complex tasks (e.g., temporal reasoning)
---
Evaluation & Results
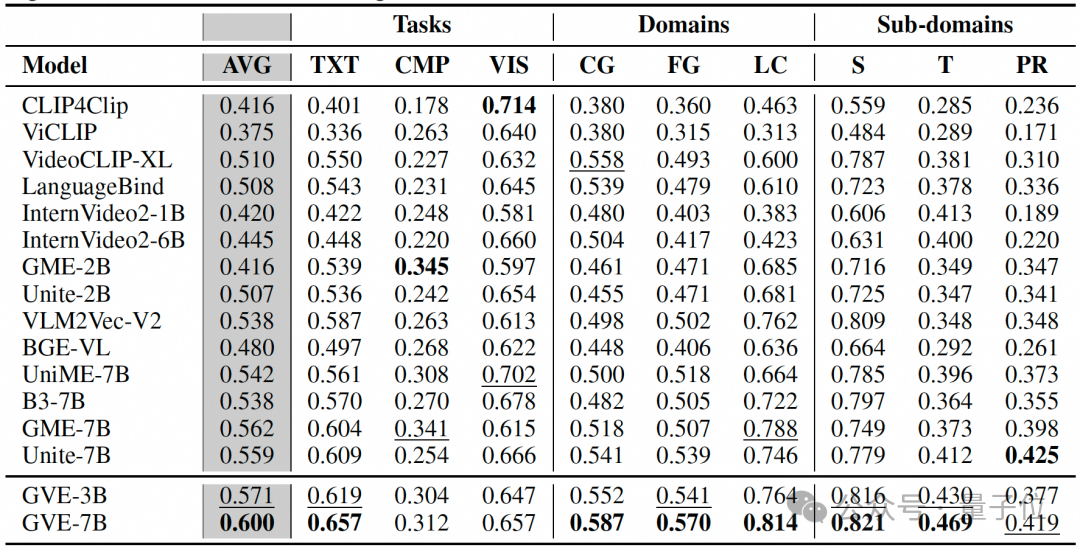
Benchmarks: UVRB — 16 datasets
Baselines:
14 mainstream models:
- CLIP-based (87M – 8.3B params)
- MLLM-based (e.g., GME-7B, Unite-7B, B3-7B)
GVE Advantages:
- Avoided training on any evaluation-domain data
- True zero-shot
- 8 uniform frames sampled
- No audio/speech/metadata
- Cosine similarity for retrieval
- Multi-image embeddings for non-video models
Performance:
- GVE-7B: Avg R@1 = 0.573 (vs Unite-7B’s 0.538 → +6.5%)
- GVE-3B: Avg R@1 = 0.544 (beats Unite-7B despite fewer parameters)
---
Ablation Insights
- UVRD synthetic dataset: +27% relative improvement in complex CMP tasks
- Modality Pyramid Curriculum: GVE-7B overall ↑ from 0.594 → 0.600
- Combined gains: +1.8%–3.1% overall performance
---
Four Key Findings
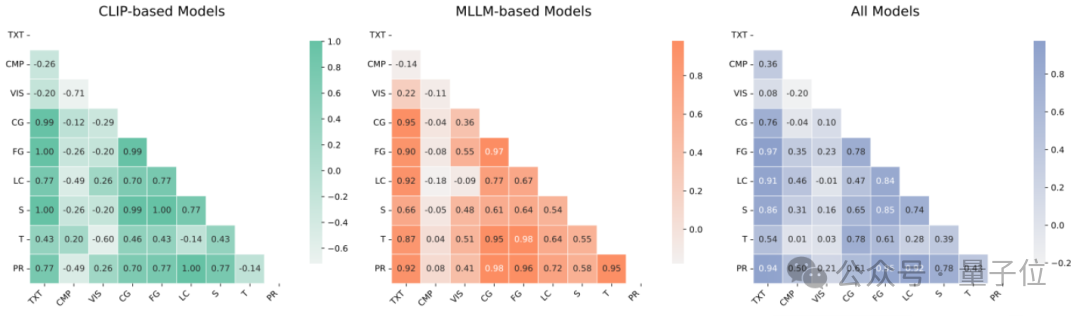
1. Traditional Benchmarks Are Misleading
Benchmarks like MSRVTT have only 0.58 correlation with true capability.
PR tasks have 0.97 correlation — strongest indicator of embedding quality.
---
2. Spatial vs. Temporal Decoupling
- Models handle objects/positions but fail at action sequences
- Spatial–Temporal correlation: 0.12
- Temporal understanding is decisive (0.98 correlation)
---
3. Architecture Influences Capability Path
- CLIP models: Strong coarse-grained spatial (0.99), weak temporal
- MLLM models: Balanced, better semantic reasoning and temporal coupling
---
4. Size Isn’t Everything
- Small CLIP4Clip (87M) beats large Unite-7B (8B) on pure visual tasks
- Visual task correlation to overall retrieval: only 0.26
---
Experimental Goal
Test if general video retrieval emerges from:
- Better evaluation systems
- Cleaner training data
- Smarter learning strategies
Outcome:
High-quality synthetic UVRD + pyramid curriculum → significant generalization gains.
---
Capability Structure Insights
Analysis shows:
- Classic benchmarks ≠ overall capability
- Spatial and temporal embeddings are decoupled
- Architecture shapes evolution path
---
Toward the Next Era
Shift from “matching titles” to “understanding content”:
- Richer training signals
- Explicit inter-task dependency modeling
- New evaluation standards
---
Open Sourcing
- UVRB benchmark
- GVE models
- V-SynFlow pipeline
- Modal pyramid curriculum
Goal: Move from leaderboard chasing to capability diagnosis.
---
Paper: arXiv:2510.27571
Project: Homepage
Models & Data: HuggingFace Collection
---
Platforms like AiToEarn support similar open-source, scalable, multi-platform AI content generation and monetization — applicable for both academic research and creative industries.
They enable publishing across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, and X (Twitter), with integrated analytics and AI model ranking.
---
If you want, I can also create a summary chart of the UVRB capabilities structure for quicker comprehension. Would you like me to do that?



