Twitter Search with Google: Advanced Tips and Operators
Learn how to use Google to perform advanced Twitter searches with operators, date filters, and strategies to find archived or hard-to-locate tweets.
Twitter Search with Google: Advanced Tips and Operators
Searching Twitter directly can be limiting when you need precise, historical, or highly specific results. If you want to search Twitter with Google, you’ll gain access to more powerful filters, broader reach, and even archived tweets that Twitter’s native search might overlook. This guide walks you through the best operators, date filters, and combination strategies to help you master advanced Twitter search via Google.
---
Why Google Can Outperform Twitter’s Native Search
Twitter's native search is optimized for speed and trending content—not for archival or complex queries. Common limitations include:
- Inconsistent date-based filtering
- Limited Boolean operator capabilities
- Search bias toward high-engagement tweets
Google, on the other hand, indexes a wide spectrum of Twitter content and supports advanced operators, offering you:
- Precise targeting using `site:twitter.com`
- Flexible date range filters via intuitive UI controls
- Boolean and exact phrase matching
- Access to cached or archived tweets via Google Cache or the Wayback Machine
---
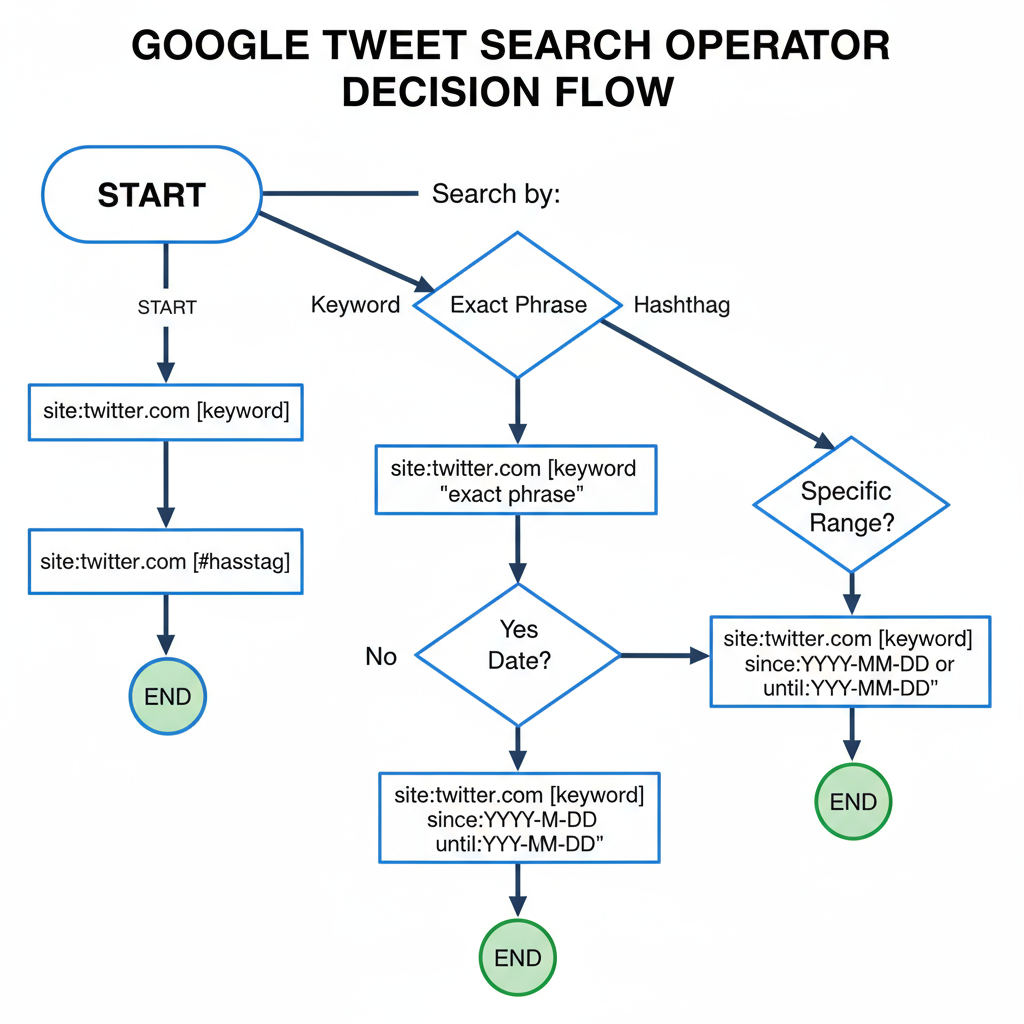
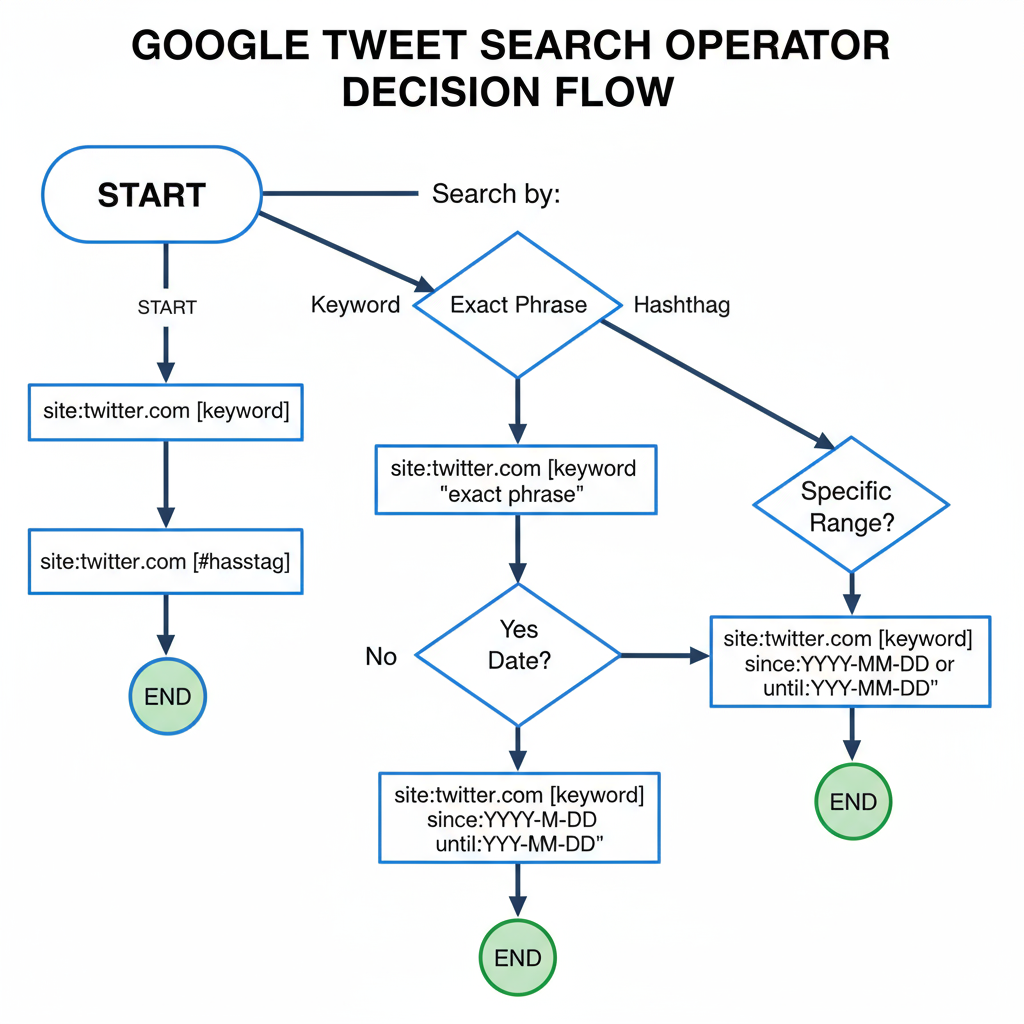
The `site:twitter.com` Google Search Operator
The `site:` operator restricts Google’s results to a specific domain—ideal for focusing on Twitter content.
Basic syntax:
site:twitter.com This instructs Google to return only results from `twitter.com`.
Example:
site:twitter.com "space exploration"Finds tweets, profiles, and threads containing the exact phrase space exploration.
---
Step-by-Step Examples for Common Searches
Finding Tweets by Keyword
Search for mentions of “vegan recipes”:
site:twitter.com vegan recipesSearching Exact Phrases
Put quotes around a phrase to match it exactly:
site:twitter.com "open source AI"Finding Hashtags
Include hashtags directly:
site:twitter.com #ThrowbackThursdayTip: Search for hashtags with and without the `#` symbol to capture all variations.
![diagram]()
---
Using Date Range Filters in Google
Google’s Tools menu puts powerful date filtering at your fingertips:
- Perform your Twitter-specific search with the `site:` operator.
- Click Tools → Any time → Choose from preset ranges or select Custom range.
Example:
site:twitter.com biodiversitySet a custom date range to: Jan 1, 2019 – Dec 31, 2019 to surface older tweets.
This is invaluable for retrieving archived tweets that are otherwise hard to locate.
---
Combining Operators for Advanced Searches
Mixing operators transforms your search into a targeted Twitter data-mining tool.
Example: Find tweets from early 2022 mentioning a product launch and a hashtag:
site:twitter.com "product launch" #NewFeatureThen, use Google’s date range picker to narrow to Jan–Mar 2022.
Note: Google doesn’t process Twitter’s native `after:`/`before:` syntax, but you can type these as keywords for context while still relying on UI date filters.
---
Finding Tweets from a Specific User
For tweets by a specific account:
site:twitter.com/ Example:
site:twitter.com/nasa "Mars rover"This surfaces tweets from NASA’s official account mentioning Mars rover.
---
Searching for Media in Tweets via Google
Tweets often include images or videos, which Google indices. Narrowing by subdomain or URL segment helps find them.
Images
site:twitter.com inurl:photoRefine by keyword:
site:twitter.com inurl:photo "sunset"Videos
site:twitter.com inurl:video---
Surfacing Deleted or Hard-to-Find Tweet Archives
You may still find a deleted tweet via cached pages or web archives.
Using Google Cache
From a Google result, click the three dots and choose Cached to see an older snapshot.
Using the Wayback Machine
Paste the tweet’s URL into archive.org to see historical captures—if they exist from before deletion.
![screenshot-placeholder]()
---
Benefits and Limitations of Google for Twitter Search
Here’s how Google search compares to Twitter’s native tools:
| Aspect | Google Search | Twitter Native Search |
|---|---|---|
| Date range flexibility | High (via Tools) | Limited and inconsistent |
| Boolean operators | Full support | Partial support |
| Search depth | Extensive historical reach | Focused on recent/trending |
| Media filtering | Possible via URL operators | Built-in filters |
| Access to deleted tweets | Via cache/archives* | No |
\*Subject to prior cache/archive availability.
---
Quick Tips for Saving and Automating Google Twitter Searches
- Bookmark your Google search URLs for instant reuse.
- Set up Google Alerts with `site:twitter.com` to receive new tweets by email.
- Use automation tools like IFTTT or Zapier with Google RSS feeds (when available) for ongoing monitoring.
---
Conclusion & Best Practices
Mastering Google’s Twitter search capabilities gives you a powerful research edge. With the `site:` operator, Boolean logic, and date filtering, you can:
- Retrieve older or buried tweets far beyond Twitter’s native scope
- Combine hashtags, keywords, and users for precision
- Find tweets with specific media types
- Recover deleted or archived tweets where possible
Best practices:
- Start broad, then refine with operators.
- Apply date ranges early to keep results relevant.
- Search hashtags with and without the symbol.
- Check caches quickly—archived pages can expire.
By following these tactics, your Twitter searches will be deeper, faster, and more accurate. Ready to unlock the full potential of Google-powered Twitter search? Start applying these methods today and transform the way you find and analyze tweets.