What Is a UGC Creator? Meaning, Examples, and How It Differs from Influencers
Learn what a UGC creator is, how it differs from influencers, key deliverables, skills, pricing and workflows, plus why brands use UGC for better ads.

This guide clarifies what a UGC creator is, how the role differs from influencers, and why the discipline has become essential in the short-form era. It also outlines deliverables, skills, workflows, pricing, and ethics so brands and creators can collaborate efficiently and transparently. Use the sections below to structure your process, evaluate opportunities, and measure impact.
What Is a UGC Creator? Meaning, Examples, and How It Differs from Influencers

User-generated content (UGC) used to mean organic posts that customers share about products. A UGC creator is different: they are independent creators paid by brands to produce content that looks and feels native to platforms like TikTok, Reels, and Shorts—without necessarily posting to their own audiences.
In plain terms, the ugc creator meaning is “a paid content producer who makes authentic-looking, platform-native assets for brands to use across ads and owned channels.” The rise of short-form video pushed this role into the spotlight because:
- Short-form rewards raw, fast, and relatable storytelling over polished studio spots.
- Performance marketers need many creative variations to beat ad fatigue.
- Brands want the credibility of “real people” while keeping control over usage and placement.
How UGC creators differ from other content sources
- Versus organic UGC: Organic posts are unsolicited and not controlled by the brand. UGC creators work to a brief, deliver on deadlines, and grant usage rights.
- Versus brand-produced content: Brand shoots are often high-budget and slower. UGC creators deliver scrappy, iterative, platform-native assets optimized for testing and performance.

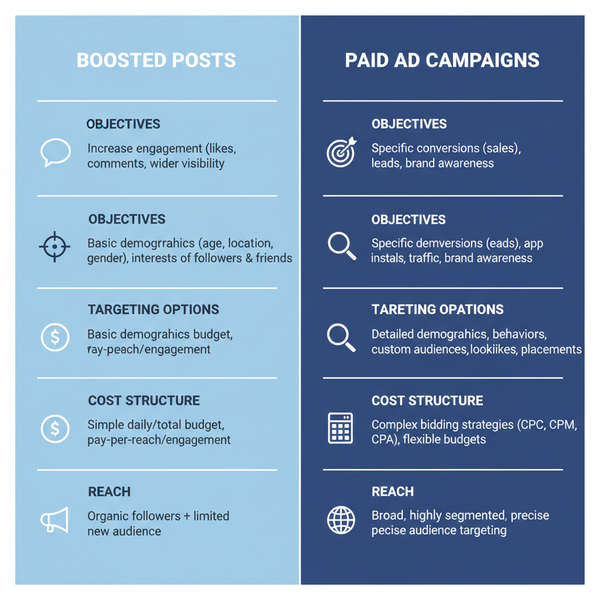
UGC Creators vs. Influencers
UGC creators and influencers overlap in skills but not in core value. Influencers monetize their audience. UGC creators monetize their production, performance mindset, and licensing.
| Dimension | UGC Creator | Influencer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary value | High-performing, native creative assets | Access to a community/audience |
| Audience ownership | Not required | Core to offering |
| Deliverables | Video/photo files for brand to use | Sponsored posts on creator channels |
| Measurement | Ad metrics (CTR, CVR, ROAS), thumbstop | Reach, engagement, community lift |
| Rights | Paid usage/licensing, whitelisting optional | Usually limited repost rights; usage extra |
| Focus | Performance marketing and scale | Brand storytelling and social proof |
Why Brands Hire UGC Creators
Brands increasingly rely on UGC creators because they deliver:
- Authenticity at scale: Realistic voice, imperfect polish, genuine testimonials.
- Ad performance uplift: Native pacing, strong hooks, and social proof often beat studio ads.
- Faster content velocity: Rapid iterations to keep up with trend cycles and ad fatigue.
Full-funnel versatility
- Upper-funnel ads (awareness hooks, problem-solution)
- Mid-funnel retargeting (comparisons, FAQs, credibility)
- Lower-funnel assets (tutorials, testimonials, offer-driven CTAs)
- Owned channels (product pages, lifecycle emails, organic social, help docs)
Typical Deliverables and Formats
Common UGC deliverables include
- Unboxings and first impressions
- Testimonials and before/after stories
- Tutorials and how-tos
- Comparisons and “I switched from X to Y” clips
- Problem-solution explainers
- Voiceover compilations with B-roll
- UGC photos and lifestyle stills for PDPs and emails
Platform-native styles
- TikTok: Fast hooks, jump cuts, on-screen text, trending audio, green screen reactions
- Instagram Reels: Polished edits, transitions, visual storytelling, caption overlays
- YouTube Shorts: Snappier setups, clearer voiceovers, punchy CTAs
Hooks and CTAs that work
- Hook starters: “I wish I knew this earlier…”, “I tested [product] so you don’t have to…”, “If you struggle with [pain point], watch this.”
- CTAs: “Try it risk-free,” “Link in bio for 20% off,” “Swipe to see the difference,” “Tap to shop.”
Skills and Toolkit
Core skills
- Scripting and storytelling: Clear problem, transformation, and payoff within 15–45 seconds.
- On-camera presence: Energy, authenticity, and concise delivery.
- Lighting and audio: Bright, soft lighting; clean sound; minimal echo.
- Editing workflow: Snappy pacing, jump cuts, captions, pattern interrupts, and meme literacy.
- Performance mindset: Variations by hook, angle, and CTA for testing.
Essential gear (you can start scrappy)
- Smartphone with good camera (4K optional)
- Ring light or softbox for key light
- Tripod with phone mount
- Lavalier mic (wired or wireless) or a quality shotgun mic
- Bounce/reflector and simple backdrops
- Editing apps: CapCut, VN, Final Cut, Premiere, or DaVinci Resolve
- Caption tools: Auto-captions (CapCut), native platform captions, or tools like Submagic
End-to-End Workflow
A reliable process keeps projects on time and content testable:
- Brief intake
- Gather audience, value props, claims guardrails, competitors, and must-have frames.
- Clarify deliverables, aspect ratios, formats, and target metrics.
- Concepting and sample hooks
- Pitch 5–10 hooks and 2–3 angles (problem-solution, testimonial, demo).
- Align on tone, format, and must-say lines.
- Shot list and script beats
- Outline A-roll, B-roll inserts, on-screen text, and CTA variants.
- Filming
- Record multiple hook variants; capture redundant B-roll for future edits.
- Editing variants
- Produce 3–6 cuts per concept with different hooks, CTAs, and lengths (e.g., 12s, 20s, 30s).
- Brand review and revisions
- Timebox feedback rounds; confirm legal/claims compliance.
- File handoff and tagging
- Deliver organized files, captions, and usage documentation.
- Post-launch learnings
- Collect performance data; propose next test matrix.
Example shot list and file naming conventions
Shot list (Concept: Problem → Demo → CTA)
- Hook A: “If [pain point], stop scrolling.” (A-roll, front camera)
- Hook B: “I tried [brand] for 7 days—here’s the truth.” (A-roll)
- Problem B-roll: Close-ups of pain point, 3 angles
- Demo A-roll: Step-by-step, over-shoulder + selfie
- Social proof: Star rating overlay + UGC quote (text)
- CTA variants: “Tap to try,” “Claim 20% off,” “Start free trial”
File naming
Client_Campaign_Concept_HookA_1080x1920_v01.mp4
Client_Campaign_Concept_HookB_1080x1920_v02.mp4
Client_Campaign_Stills_Lifestyle01.jpg
Metadata.json
{
"client": "Acme Skincare",
"campaign": "Hydration Launch",
"hook": "If dry skin…",
"angle": "Problem-Solution",
"cta": "Tap to try",
"captions": "burned-in",
"rights": "paid-social-ads; 6 months; US+CA"
}
Pricing and Licensing
Your price covers production and rights. Separate them in your proposals.
- Per-asset rates: Charge per finalized video/photo, not per hour.
- Bundles: Discount for multi-asset packages (e.g., 3–5 videos + 10 photos).
- Usage duration and territories: 30–90 days vs 6–12 months; single country vs global.
- Whitelisting/paid amplification: Additional fee to run ads from your handle.
- Exclusivity: Fees for category lockouts (partial or full).
- Revisions: Include 1–2 rounds; define what counts as a revision vs a new concept.
- Work-for-hire: Avoid transferring ownership unless compensated fairly; prefer time-bound licenses.
Illustrative pricing components
Actual numbers vary by niche, experience, and demand.
| Component | Typical Structure | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Base per video | $150–$800+ | Complexity, talent time, editing level |
| Bundles | 3–5 videos at 10–25% off | Encourage testing volume |
| Usage license | 30–90 days included; extensions $ | Charge more for global/long-term |
| Whitelisting | Flat fee + monthly | Extra admin and brand risk |
| Exclusivity | 10–50% of project per 3–6 months | Depends on category breadth |
| Raw files | +15–35% surcharge | Only if permitted by agreement |
| Work-for-hire | Premium pricing or avoid | Transfers ownership; be cautious |
Negotiation tips
- Separate creative fee from licensing; itemize scope.
- Tie extensions to performance milestones (“if ROAS > 2.5x, extend at X%”).
- Cap revision rounds; add rates for script or concept changes.
- Define territories, platforms, and placements (paid social, programmatic, CTV, PDP).
- Get approvals for claims; require product delivery and timelines.
Finding and Landing Gigs
Where to find opportunities
- UGC marketplaces and platforms: Billo, Insense, Trend, #paid, Aspire, Collabstr, Fiverr/Upwork.
- TikTok Creator Marketplace (TCM): Brand briefs, Spark Ads opportunities.
- Brand communities and ambassador programs on DTC sites and Discords.
How to pitch
- Portfolio reel: A 30–60s montage of your best hooks, transformations, and CTAs.
- Case snippets: “Hook variant B lifted CTR by 38%” or “Thumbstop +22% vs control.”
- Niche positioning: Focus on categories where you have credibility (beauty, fitness, SaaS, pet, home).
- Cold outreach: Short email/DM with 1-liner value prop, link to reel, 3 proposed hook angles, and a mini-test bundle offer.
Proof-of-performance
- Show split tests with clear variables (hook, angle, CTA).
- Share anonymized dashboards or summary stats (CTR, CVR, ROAS).
- Provide reference clients and example deliverables.
Measuring Success
UGC creators thrive by iterating on data. Align on a test plan and metrics.
| Metric | What it measures | Optimization focus |
|---|---|---|
| Thumbstop rate (3s view) | Ability to grab attention | Hook text/voice, first frame, motion |
| Hook retention (0–3s → 5–8s) | Keeping viewers through setup | Problem clarity, pattern interrupts |
| CTR | Click-through efficiency | CTA clarity, offer overlays, end frames |
| CVR | Conversion rate on landing | Message-market fit, PDP assets |
| CPA/CAC | Cost per acquisition | Audience match and creative angle |
| ROAS | Return on ad spend | Full-funnel contribution |
Run A/B variations by
- Hook: question vs bold claim vs pattern interrupt
- Format: talking head vs voiceover + B-roll vs green screen
- CTA: offer-driven vs benefit-driven vs urgency
Test matrix example
- 3 hooks × 2 formats × 2 CTAs = 12 variants from one core script.
- Kill losers fast; iterate winners with micro-edits (first frame, caption style, music).
Best Practices and Ethics
Long-term trust beats short-term clicks. Follow these guardrails:
- Clear disclosure: Use platform-compliant disclosures (#ad, Paid Partnership) when posting or appearing as a spokesperson.
- Real product experience: Try the product; show genuine use-cases; avoid stock-only clips.
- Claims accuracy: Substantiate performance claims; avoid superlatives without proof; use on-screen disclaimers if needed.
- Inclusive representation: Cast diversity; avoid stereotypes; show accessibility features when relevant.
- Accessibility: Burn-in captions or upload accurate subtitles; mindful color contrast; descriptive on-screen text.
- Brand fit: Maintain your style while honoring brand guidelines; push back on inauthentic scripts.
The Bottom Line
The ugc creator meaning has evolved with short-form video: creators are now a performance-minded production partner, not just a face on a feed. Brands hire UGC creators to unlock authenticity at scale, accelerate testing, and lift ROI across the funnel. If you build skills in storytelling, production, and iterative testing—and get your pricing and licensing right—you can turn scrappy, native content into a sustainable creative business.
Summary
UGC creators produce platform-native assets that drive performance, while influencers primarily monetize their audiences. Set clear scopes, pricing, and rights; follow a data-informed workflow; and uphold ethical standards to build trust and long-term results for both brands and creators.