2:3 Ratio Size Guide for Photography and Design Uses
Learn the history, uses, and calculation methods for the 2:3 aspect ratio in photography and design, plus tips for editing and maintaining composition.

Introduction to Aspect Ratios and the 2:3 Ratio Size
In photography, graphic design, and filmmaking, the aspect ratio defines the proportional relationship between an image’s width and height, shaping how visuals are composed and perceived. Choosing the right aspect ratio is essential for maintaining composition, avoiding distortion, and ensuring a polished presentation. Among the various formats, the 2:3 ratio size is one of the most widely used in professional and personal projects due to its rich history and adaptability.
This article explores the definition, history, and applications of the 2:3 ratio, with practical guidance on calculating dimensions, editing images, and composing shots to maximize visual impact.

---
Definition of the 2:3 Ratio Size and Common Dimensions
A 2:3 aspect ratio means that for every 2 units of height, there are 3 units of width—the width is exactly 1.5 times the height. This consistent proportion works across different scales.
Common 2:3 dimensions:
- 4 x 6 inches — iconic photo print size
- 8 x 12 inches — suitable for art prints and posters
- 20 x 30 cm — common metric print size for exhibitions
Because the ratio stays the same, you can scale your images up or down without altering the composition.
---
Historical Origins in Film and Photography
The 2:3 ratio rose to prominence through 35mm film. Kodak introduced this format in the late 1800s, and Leica standardized it in the 1920s with its compact cameras. The 35mm frame measured 24mm x 36mm—precisely a 2:3 ratio.
As optical engineering advanced, most camera manufacturers designed lenses and viewfinders for this aspect ratio. Even today, digital “full-frame” and APS-C sensors often adhere to 2:3, ensuring continuity with traditional print sizes and photographic conventions.
---
Why the 2:3 Ratio Remains a Popular Choice
The enduring popularity of the 2:3 ratio size stems from several advantages:
- Legacy fit — photo albums, frames, and processing labs are optimized for this ratio.
- Balanced composition — accommodates subjects naturally in portrait or landscape.
- Versatility — works equally well for human subjects, landscapes, or product shots.
- Ease of reproduction — abundant framing and mounting options without custom work.
It has become a “default” aspect ratio in print-centric photography due to its flexible composition space.
---
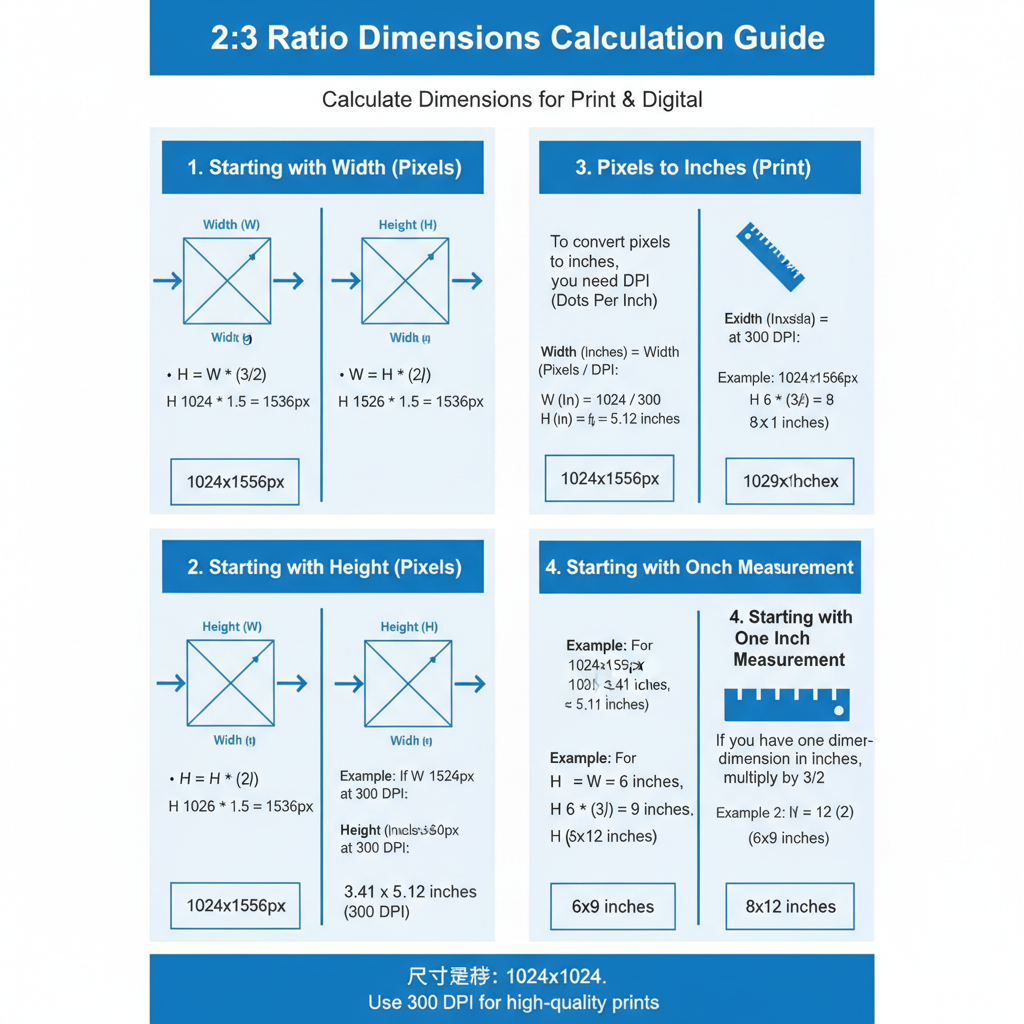
Calculating 2:3 Ratio Dimensions
You can derive either the width or height of a 2:3 image using simple math:
- Width given: divide by 3, multiply by 2 to get height.
- Height given: divide by 2, multiply by 3 to get width.
Example for width of 3000px:
Height = (3000 / 3) × 2
Height = 1000 × 2 = 2000pxExample for height of 2000px:
Width = (2000 / 2) × 3
Width = 1000 × 3 = 3000pxThese formulas work for pixels, inches, centimeters, or any unit of measure.
---
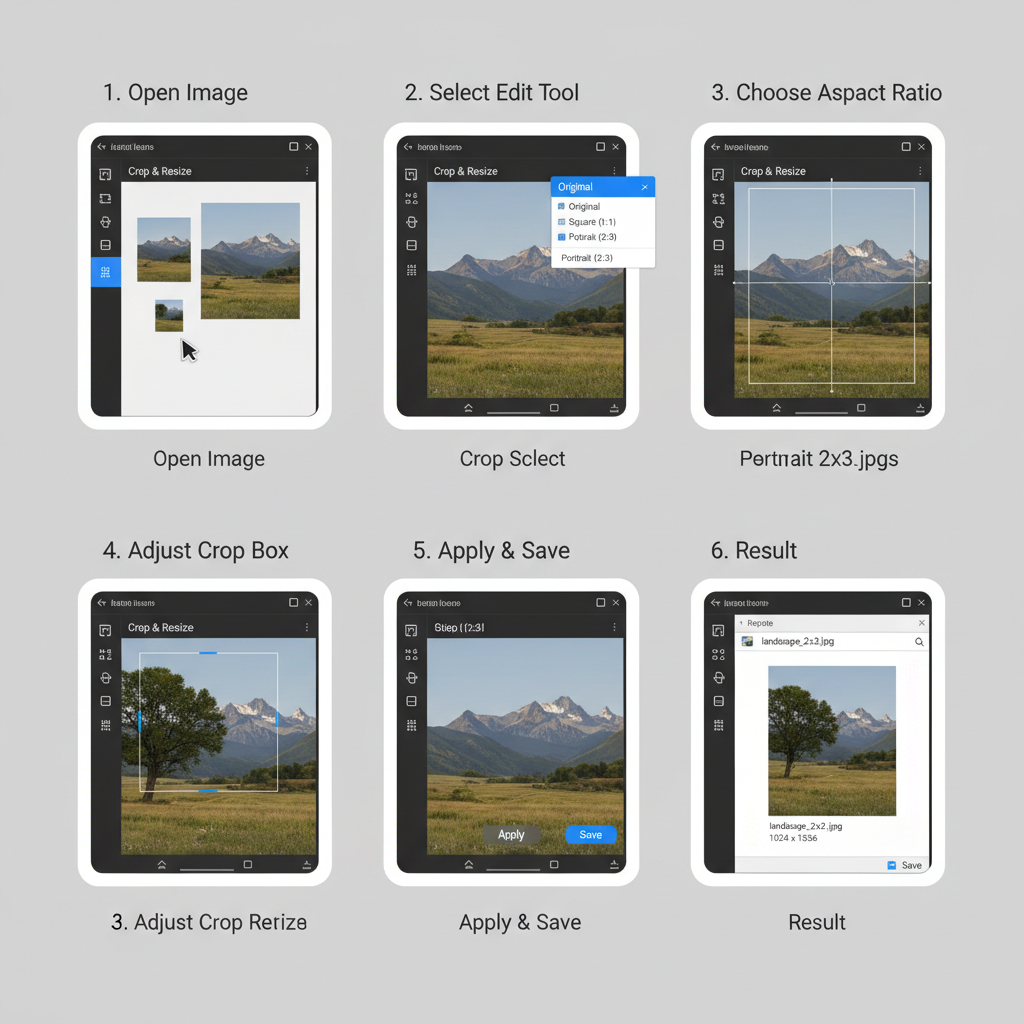
Editing Images to a 2:3 Ratio
Most popular editing programs—Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, GIMP, and mobile editing apps—let you crop or resize to a precise aspect ratio.
Tips for editing:
- Lock aspect ratio when cropping to maintain proportions.
- Preserve resolution for high-quality prints.
- Adjust composition to avoid losing key elements.
In Lightroom:
- Activate Crop tool.
- Select “Aspect” → 2:3.
- Adjust the crop frame over your image.
---
Pros and Cons by Medium
| Medium | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Photography | Standard framing, optimal horizontal/vertical balance | Requires cropping for non-standard frame sizes |
| Social Media | Compatible with Instagram posts after minor adjustments | Less suited to vertical mobile feed formats |
| Design | Integrates easily with print projects | Differs from common web/video ratios like 16:9 |
---
Common Print Formats Using 2:3 Ratio
You’ll find plenty of readymade products in these sizes:
- 4" x 6"
- 8" x 12"
- 12" x 18"
- 16" x 24"
- 20" x 30"
Photo labs and online printing services offer templates that match these dimensions, helping to avoid cropping mismatches.
---
Composing Shots for a 2:3 Frame
When shooting:
- Align subjects using the rule of thirds within the wider frame.
- Ensure horizontal balance to avoid excessive blank areas.
- In portrait orientation, incorporate vertical elements for visual strength.
- Consider background scale—wider ratios include more scenery.
Thoughtful in-camera composition saves editing time and maintains artistic intent.
---
Landscape vs Portrait Orientation in 2:3 Ratio
Landscape orientation shines for vistas, architecture, and group shots—its width offers a panoramic feel without extreme stretching.
Portrait orientation suits vertical subjects like people, skyscrapers, or trees—its height accentuates elements while maintaining compositional comfort.
Example:
- Landscape 2:3 — captures a coastline with balanced sky and sea.
- Portrait 2:3 — isolates a tall monument framed against the horizon.
---
Comparison with Other Aspect Ratios
| Ratio | Example Size | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 1080px x 1080px | Square social posts, avatars |
| 4:5 | 8" x 10" | Prints, vertical feed social media |
| 16:9 | 1920px x 1080px | Video and widescreen displays |
| 2:3 | 4" x 6" | Photography prints, posters |
The 2:3 ratio offers a middle ground—more visual space than square and less extreme than widescreen.
---
Best Practices for Preserving Quality
- Always edit from original high-resolution files.
- Use non-destructive editing to retain originals.
- Export with appropriate DPI (300 for print).
- Avoid scaling beyond original resolution to minimize pixelation.
- Match output resolution to your display medium.
---
Summary and Recommendations
The 2:3 ratio size is a cornerstone of visual media—rooted in film history, yet consistently relevant in digital photography and design. Its balanced proportions, versatile orientation options, and widespread availability in print formats make it an essential tool for photographers, designers, and creatives.
Recommendations:
- Plan your shot for the final ratio from the beginning.
- Lock aspect ratio during cropping to keep composition intact.
- Use templates to match standard print sizes.
- Choose orientation based on subject and storytelling goals.
By understanding and mastering the 2:3 ratio size, you can produce visually striking, proportionally perfect images suited for print, online sharing, and professional display.