Buffering Icon Causes and Fixes for Smooth Streaming
Learn why the buffering icon appears while streaming, the technical causes behind it, and practical steps to fix network and device issues for smoother playback
Introduction to the Buffering Icon in Streaming
The buffering icon is a familiar sight to anyone streaming video, gaming online, or downloading large files. This spinning wheel or loading circle signals that your device is pausing content playback to load data into memory, ensuring a smoother experience. However, frequent encounters with the buffering icon can disrupt your entertainment or workflow. In this guide, we’ll explore why buffering occurs, how streaming platforms manage it, and proven strategies to reduce or prevent it across devices.
Understanding the Buffering Icon
Buffering is a standard process in online content delivery. It temporarily halts playback to preload data, ensuring uninterrupted viewing. If the stream reaches the end of its preloaded buffer before more data arrives from the server, you’ll see the buffering icon until enough content is loaded to resume playback. This can be a brief pause or extended interruption depending on network and device factors.
Common Scenarios Where Buffering Occurs
Buffering spans multiple digital activities, each with its own triggers:
- Streaming Video: Services like Netflix, YouTube, and Twitch pause playback when incoming data falls behind demand.
- Online Gaming: Lag in multiplayer environments can be tied to buffering during cutscenes or streamed video content.
- File Downloads: Systems may appear stalled while queuing large data chunks for processing.
In every scenario, the buffering icon alerts you that the system is waiting for more data before continuing.
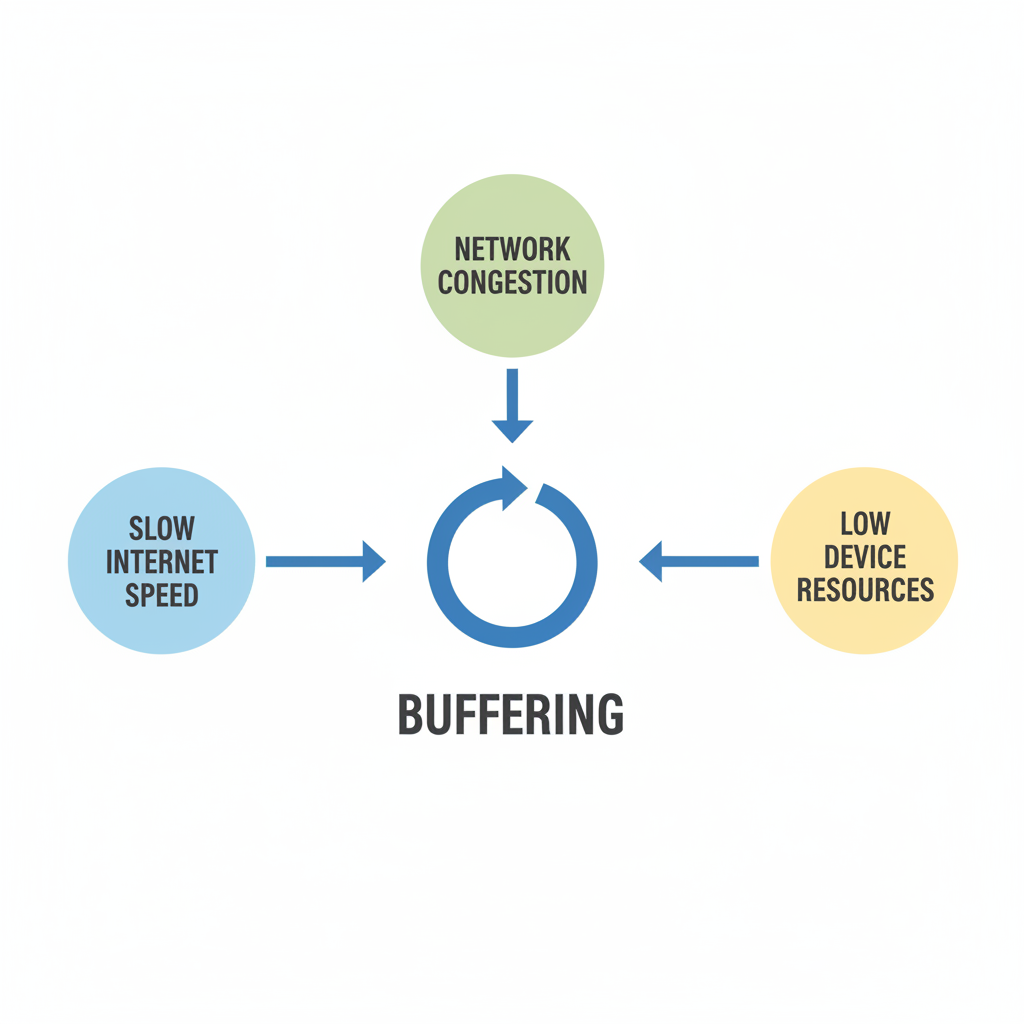
Technical Reasons for Buffering
Slow Internet Speed
Streaming platforms set minimum bandwidth requirements. For instance, HD streams often need at least 5 Mbps, while UHD demands 25 Mbps. Speeds below these thresholds cause playback delays.
Network Congestion
Bandwidth shared among multiple devices in a home can strain data flow. Congested networks result in packet delays and increased buffering.
Low Device Resources
Limited RAM, slower CPUs, or constrained storage can slow rendering and data packet processing, causing buffering even on strong connections.
How Streaming Platforms Handle Buffering and Data Packets
Streaming services use intelligent buffering management to mitigate interruptions:
- Preloading data chunks before playback starts.
- Switching to adaptive bitrate streaming to match available bandwidth.
- Retransmitting lost packets, which can temporarily increase delay.
These methods reduce the frequency of buffering but cannot fully overcome severe network or hardware limitations.
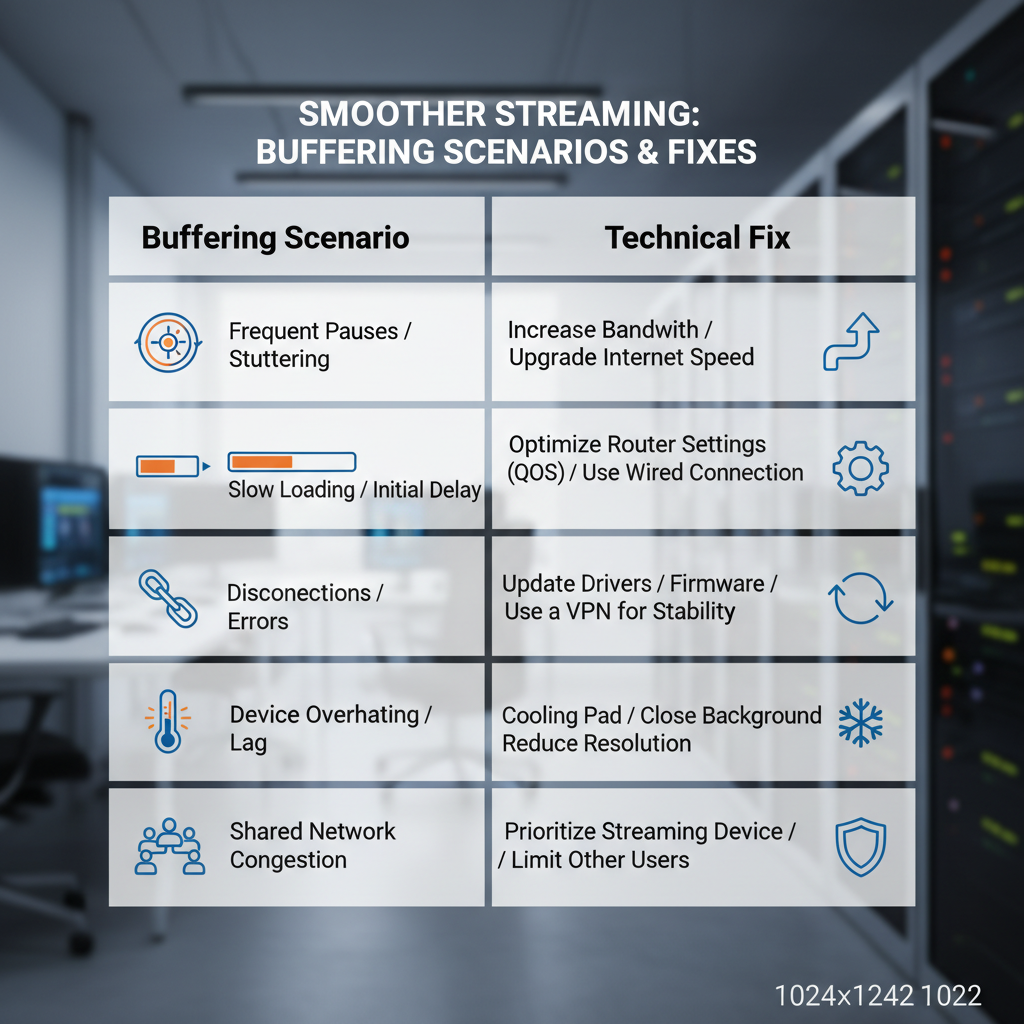
Step-by-Step Diagnostics for Buffering Issues
Identify and address causes of repeated buffering:
- Run a Speed Test: Verify download/upload rates meet service requirements.
- Restart the Router: Clear temporary glitches and improve signal stability.
- Reduce Network Load: Disconnect unused devices from the network.
- Clear Cache and Temporary Files: Free device resources for data processing.
- Update Software: Keep streaming apps, OS, and router firmware current.
Quick Diagnostic Tip
> Persistent buffering usually indicates either network or device performance bottlenecks. Test and address each separately for faster resolution.
Optimizing Internet Speed for Smoother Streaming
Boosting connection speed limits interruptions:
- Prefer wired Ethernet over Wi-Fi for stability.
- Use 5 GHz Wi-Fi to avoid interference, if range permits.
- Schedule high-bandwidth tasks for off-peak times.
Minimum Speed Requirements for Popular Streaming Services
| Service | SD Quality | HD Quality | UHD/4K Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | 3 Mbps | 5 Mbps | 25 Mbps |
| YouTube | 1.5 Mbps | 5 Mbps | 20 Mbps |
| Twitch | 3 Mbps | 6 Mbps | 15 Mbps |
Device-Specific Fixes
Different devices require tailored solutions:
PC
- Close applications consuming bandwidth.
- Update graphics and network drivers.
- Enable hardware acceleration in browsers when supported.
Mobile Devices
- Switch to mobile data when Wi-Fi is slow.
- Restrict background app syncing.
- Clear app cache periodically.
Smart TVs
- Update firmware for performance improvements.
- Connect via Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi.
- Pause updates and other background tasks during streaming.
Gaming Consoles
- Use router QoS to prioritize gaming traffic.
- Avoid simultaneous heavy usage across the network.
Adjusting Streaming Quality and Settings
When upgrades aren’t possible, tweak playback settings:
- Select a lower resolution (HD or SD) during busy network hours.
- Remove extra audio or subtitle streams that may slow decoding.
- Set a fixed bitrate instead of auto-adjust for consistent delivery.
When to Upgrade Hardware or Internet Plan
If buffering continues after optimization:
- Purchase a router with modern Wi-Fi standards (Wi-Fi 6).
- Increase your internet plan bandwidth.
- Upgrade to devices with more RAM and faster CPU capabilities.
Preventative Tips to Avoid Buffering Icon in the Future
- Regular device restarts and cache clearing.
- Central router placement away from obstacles.
- Maintain updated software across devices.
- Monitor speed and latency with network tools.
Summary: Balancing Speed, Hardware, and Platform Settings
The buffering icon signals a gap between data availability and playback demands. By understanding its triggers—whether bandwidth shortfalls, network congestion, or device limitations—you can implement solutions that prevent interruptions. For the smoothest streaming, aim for a combination of reliable internet service, capable hardware, and optimized playback settings.
Take control of your streaming experience today—apply these tips to keep the buffering icon away and enjoy uninterrupted entertainment.