Different Medias and Their Role in Modern Communication
Explore how traditional, digital, broadcast, social, and emerging media formats shape modern communication, audience engagement, and content strategies.

Understanding Different Medias in Modern Communication
In today's interconnected world, different medias—spanning print, broadcast, digital, and emerging technologies—shape how we share stories, market ideas, and influence audiences. From the tactile reliability of newspapers to the immersive experiences of augmented reality, each format plays a distinct role in modern communication. Exploring these channels provides insight into how information travels, impacts opinion, and evolves with technology.

---
Defining Media: Traditional, Digital, and Emerging Formats
Media refers to the channels or platforms used to convey information to the public. These broadly fall into:
- Traditional media: Print newspapers, magazines, radio, television.
- Digital media: Websites, blogs, online video, podcasts, streaming services.
- Emerging formats: Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), interactive installations, holograms.
Although boundaries blur in our connected era, each category retains key attributes that shape content strategies and audience engagement.
---
A Brief History of Media Evolution
The journey of media communication is marked by several technological milestones:
- Print – The printing press in the 15th century revolutionized the distribution of knowledge.
- Radio – In the 20th century, radio transmitted news and entertainment wirelessly to homes.
- Television – Combined visual storytelling with instant broadcasting, dominating mass communication.
- Internet – Democratized publishing, enabling global content access.
- Social Media – Interactive platforms transformed audiences into active participants in discourse.
---
Characteristics of Print Media
Print media remains the oldest enduring format, valued for depth and credibility.
Strengths:
- High trust and comprehensive coverage.
- Tangible product that can be re-read or archived.
- Strong local focus through community newspapers.
Limitations:
- Slower distribution compared to digital.
- Declining readership among younger demographics.
- Higher production and distribution costs.
Current Role:
Print often serves niche audiences, providing detailed analysis and long-form journalism that digital brevity seldom matches.

---
Characteristics of Broadcast Media
Broadcast media includes television and radio, offering wide reach and immediacy.
Key Attributes:
- Reach: Ability to target mass audiences instantly.
- Immediacy: Live broadcasting captures unfolding events in real time.
- Influence: Emotional connection through audio-visual storytelling.
Even as streaming services compete for attention, broadcast remains influential by integrating innovations like interactive voting and second-screen engagement.
---
Characteristics of Digital Media
Digital media encompasses online publications, video streaming, and podcasts.
Advantages:
- Interactivity: Feedback via comments, chats, and forums.
- Speed: Instant publishing and real-time updates.
- Personalization: Algorithms curate content to user preferences.
Challenges:
- Attention fragmentation due to multiple competing platforms.
- Information overload, potentially reducing retention.
Its flexibility positions digital media at the core of contemporary campaigns, from blogs to YouTube series.
---
Characteristics of Social Media
Social media is a dynamic subset of digital media, enabling immediate and interactive communication.
Strengths:
- Community building through groups and themed pages.
- Viral reach through shares and trending topics.
- Direct conversations via replies, comments, and live streams.
Limitations:
- Vulnerability to misinformation.
- Frequent algorithm changes impacting visibility.
Social media can catapult obscure topics into global conversations within hours.
---
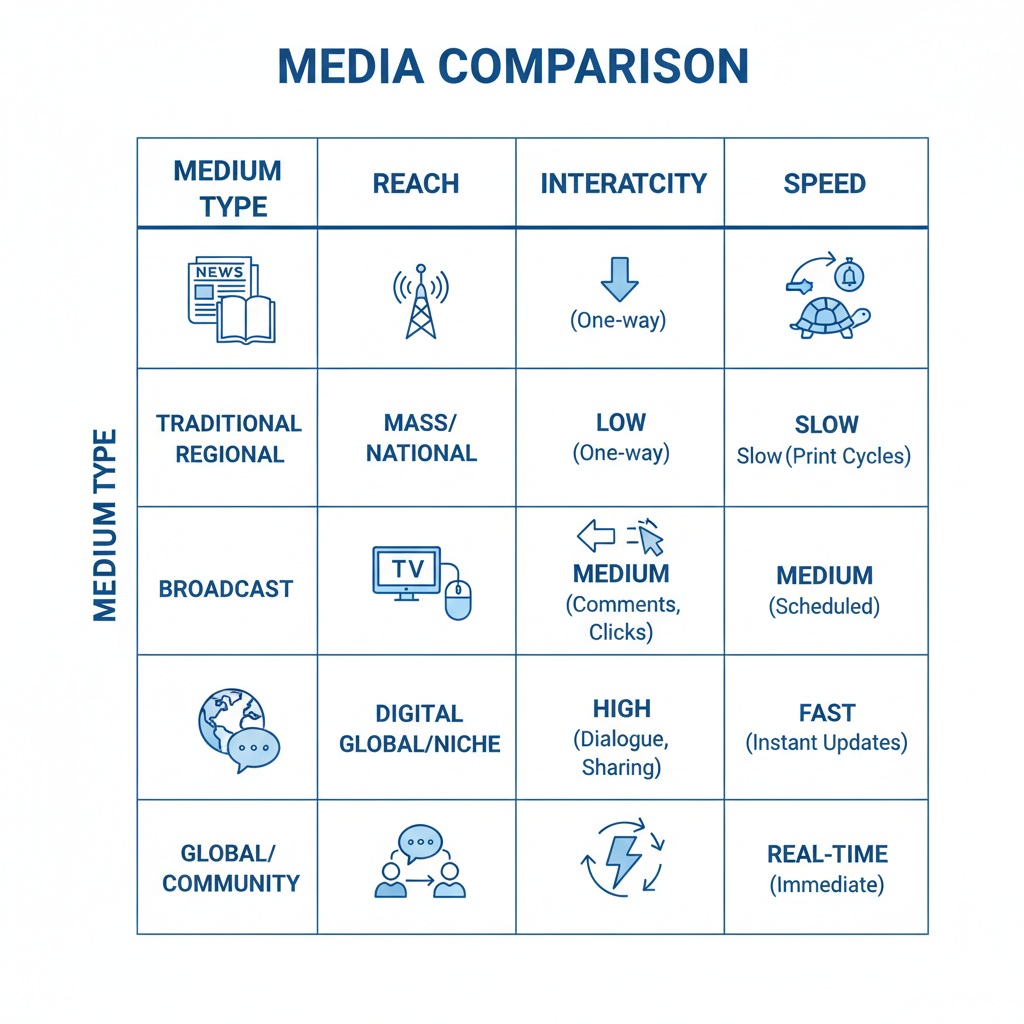
Comparing Different Medias
Here’s a high-level comparison of different medias by audience and engagement:
| Media Type | Typical Audience | Engagement Level |
|---|---|---|
| Older demographics, professionals | High depth, low frequency | |
| Broadcast | Broad, mixed demographics | Moderate depth, high immediacy |
| Digital | All ages, tech-savvy | High customization, variable frequency |
| Social | Younger to middle-aged demographics | High interactivity, viral potential |
---
The Role of Multimedia Convergence
Multimedia convergence blends formats into unified experiences:
- Newspapers hosting interactive graphics online.
- TV shows integrating live social media feeds.
- Podcasts offering companion videos and blog posts.
Convergence helps brands maintain consistent messaging across diverse channels, expanding reach and impact.
---
Cross-Platform Campaign Examples
Effective communication strategies combine different medias:
- Global Sporting Event
- Broadcast: Live coverage.
- Digital: Highlight clips on official websites.
- Social: Real-time updates and fan polls.
- Movie Launch
- Print: Interviews in magazines.
- Digital: Streaming trailers.
- Social: Behind-the-scenes stories.
- Public Awareness Campaign
- Broadcast: TV adverts.
- Digital: Interactive web quizzes.
- Social: Hashtag challenges to encourage participation.
---
Measuring Effectiveness Across Different Medias
Evaluating the impact of different media types involves tracking metrics:
- Print: Circulation numbers, readership surveys.
- Broadcast: Ratings, audience share.
- Digital: Page views, click-through rates.
- Social: Engagement rate, follower growth.
Using tools such as Google Analytics, Nielsen ratings, and platform insights ensures that campaigns are data-driven and optimized for performance.
---
How Different Medias Influence Public Opinion
Media influences culture, politics, and community narratives:
- Print fosters trust and permanence, shaping policy debates.
- Broadcast connects emotionally through compelling visuals.
- Digital promotes niche communities that push mainstream ideas.
- Social empowers grassroots movements to gain traction.
By amplifying stories and framing discussions, different medias collectively shape societal perspectives.
---
Future Trends in Media Communication
The coming years promise dramatic change in how media operates:
- AI-driven content: Personalized storytelling at scale.
- Immersive media: Experiences that blend digital and physical spaces.
- AR/VR integration: Innovative learning, shopping, and entertainment tools.
- Next-gen social platforms: Decentralized networks prioritizing privacy.
Staying ahead requires exploring new technologies while respecting the unique strengths of existing channels.
---
Conclusion
Mastering different medias—from the enduring trust of print to the transformative potential of immersive technologies—is essential for crafting effective communication strategies. Each type offers unique advantages, limitations, and audience engagement opportunities. As convergence accelerates and AI, AR, and other innovations take hold, success will depend on blending formats into coherent, cross-platform narratives.
Ready to elevate your communication strategy? Explore how integrating various media channels can maximize your message’s reach and resonance in a constantly evolving landscape.