1/1 vs 3/4 Fraction Comparison and Real Life Examples
Learn to compare 1/1 and 3/4 with visual aids, conversions, and everyday examples, enhancing your fraction skills for practical uses.

Introduction to Fractions and Why Comparing Them Matters
Fractions are a cornerstone of mathematics, representing parts of a whole. They appear in everyday activities such as measuring ingredients, budgeting finances, and planning construction materials. Mastering how to compare fractions improves accuracy and decision‑making in both academic and practical situations.
This guide focuses on comparing 1/1 vs 3/4—the difference between a complete whole and a partial amount. By understanding their values, visual representations, conversions, and applications, you’ll gain the skills to work confidently with fractions in diverse real‑world contexts.

---
Understanding 1/1 as a Whole Number
The fraction 1/1 means one whole. In fraction notation, the numerator equals the denominator, which indicates that the entire set or quantity is present.
- Numerator: 1 (The quantity you have)
- Denominator: 1 (Total number of equal parts)
- Value: Exactly 1
Mathematically:
1/1 = 1Key Points
- 1/1 is a complete unit—no missing parts.
- Often used as the reference point for other fractions.
- Represents total or full quantities in measurement and reporting.
---
Breaking Down 3/4: A Fraction Less Than One
The fraction 3/4 shows that you have three out of four equal parts. Since the numerator (3) is less than the denominator (4), it represents less than one whole.
- Numerator: 3 (The amount present)
- Denominator: 4 (Equal parts that make the whole)
- Value: Less than 1
Mathematically:
3/4 = 0.75This is equivalent to 75%, a common measurement in scenarios like filling a container to three‑quarters capacity or completing 75% of a project.
---
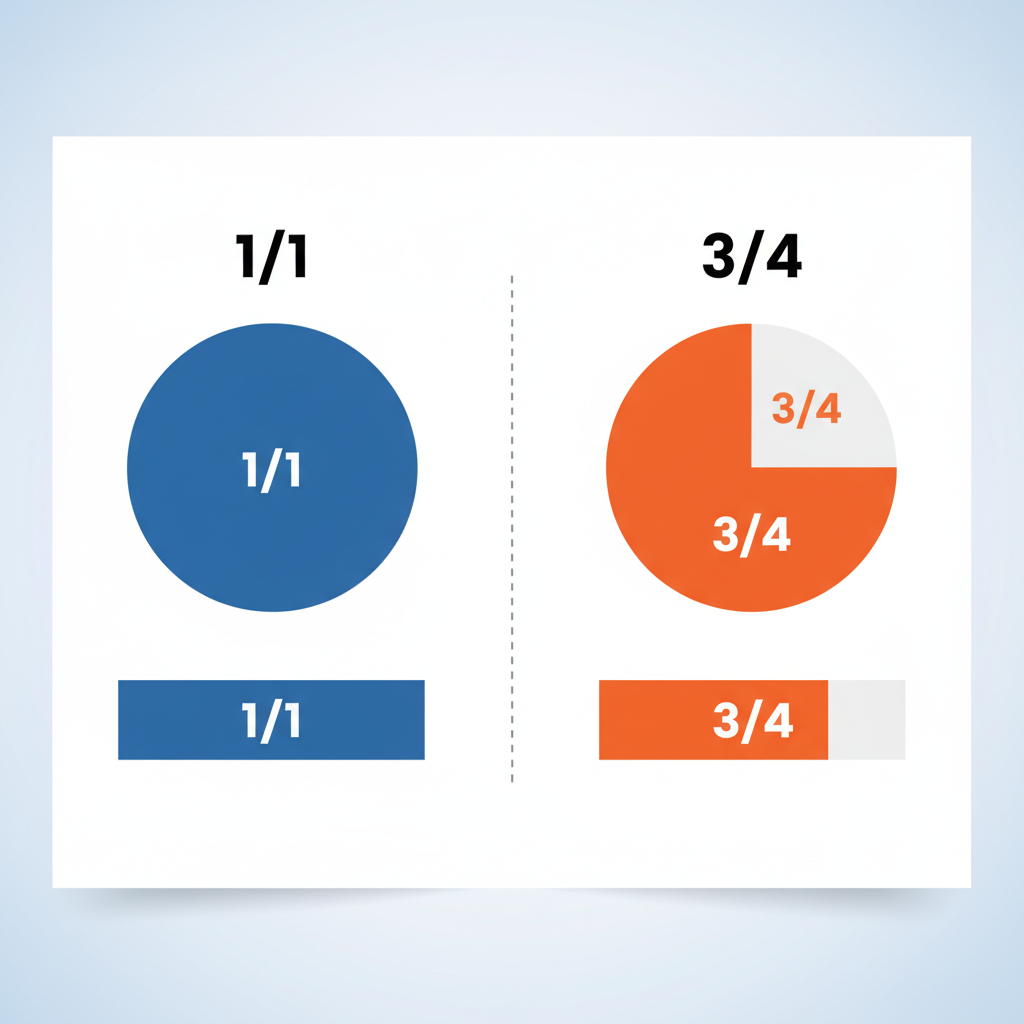
Visual Representation: Pie Charts & Fraction Bars
Fractions become easier to understand when visualized with diagrams.
Imagine:
- 1/1: A circle fully shaded.
- 3/4: A circle shaded in three parts with one part left empty.
Fraction bars offer a similar comparison:
- 1/1: Fully filled bar.
- 3/4: Bar filled to 75%.
Visual aids turn numbers into tangible concepts, making them especially effective for teaching beginners and children.
---
Real‑World Examples: 1/1 vs 3/4
Examples help clarify the gap between a whole and a part.
1/1 Examples
- A full bottle of water.
- A cake with no slices missing.
- A project milestone reached completely.
3/4 Examples
- Three‑quarters of a fuel tank filled.
- Homework 75% complete.
- A pizza missing one slice when cut into four equal pieces.
---
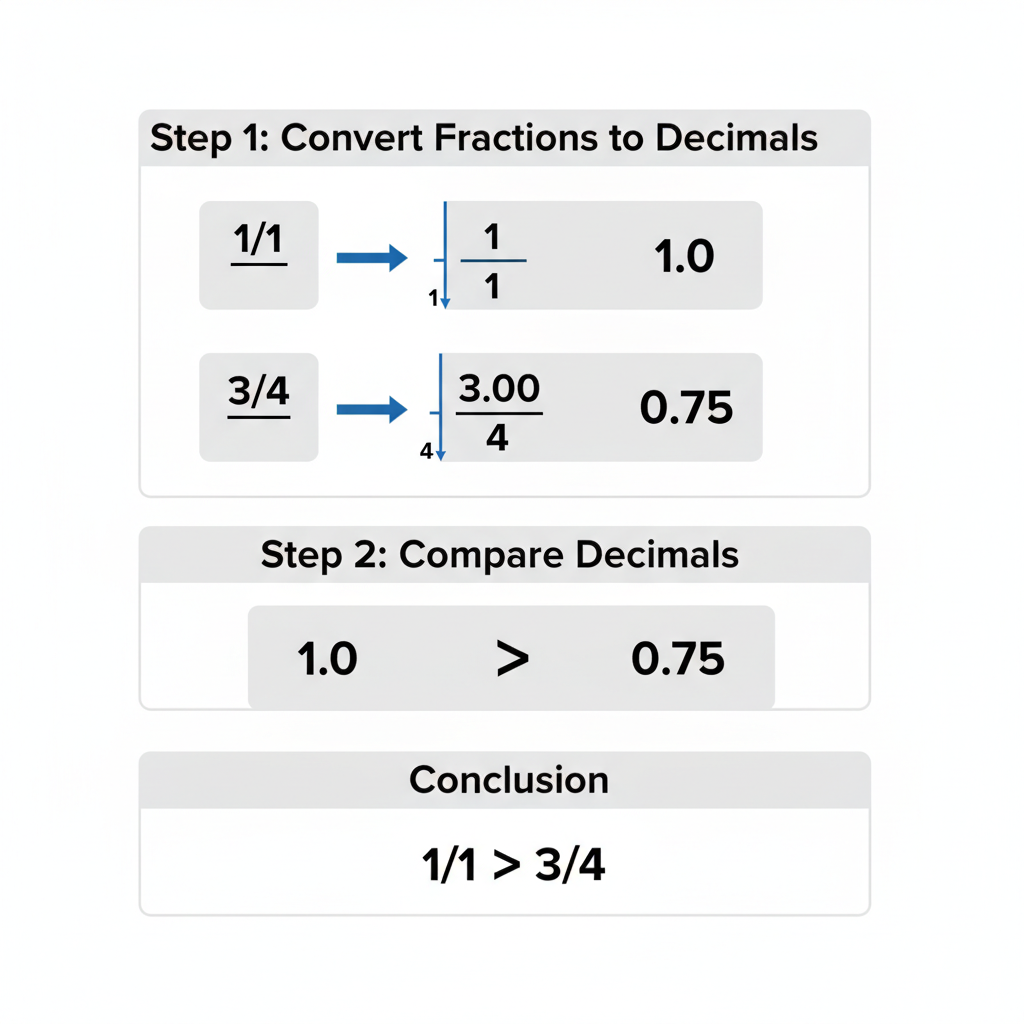
Converting Fractions to Decimals and Percentages
Changing fractions into decimals and percentages makes comparison immediate.
Conversion for 1/1:
1 ÷ 1 = 1.00
Percentage: 100%Conversion for 3/4:
3 ÷ 4 = 0.75
Percentage: 75%| Fraction | Decimal | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1/1 | 1.00 | 100% |
| 3/4 | 0.75 | 75% |
Clearly, 1/1 stands for a greater quantity than 3/4.
---
Comparing Fractions Using Common Denominators
A simple method for comparison is finding a common denominator.
Example:
- Convert 1/1 to have denominator 4 → 4/4
- 3/4 stays the same.
Compare numerators:
4/4 vs 3/4 → 4 > 3Conclusion: 1/1 is greater than 3/4.
This approach is especially useful for fractions without straightforward decimal forms.
---
Mathematical Operations: 1/1 and 3/4
Working with fractions often involves basic operations. Using 1/1 and 3/4:
Addition
1/1 + 3/4 = 4/4 + 3/4 = 7/4 = 1 3/4Subtraction
1/1 - 3/4 = 4/4 - 3/4 = 1/4Multiplication
1/1 × 3/4 = 3/4Division
1/1 ÷ 3/4 = 1 × 4/3 = 4/3 (1 1/3)These examples highlight how 1/1 serves as a versatile base value.
---
Practical Applications in Cooking, Construction & Everyday Math
Cooking
- Adjusting recipes when only 3/4 of an ingredient is available.
- Cooking time adjustments based on full versus partial timer settings.
Construction
- Comparing a full meter of wood to a 3/4 meter piece.
- Calculating shortages when material is less than full length.
Everyday Math
- Estimating contents of containers (full vs 75% full).
- Tracking completion rates of personal tasks.
Understanding 1/1 vs 3/4 prevents errors in preparation, resource use, and planning.
---
Teaching Kids: Whole vs Partial Fractions
To make fractions relatable to children:
- Use real food, like giving a whole apple (1/1) versus three‑quarters (3/4).
- Demonstrate with cups of water.
- Encourage coloring diagrams of circles or bars representing each fraction.
Games and interactive methods reinforce the concept of whole versus part.
---
Summary & Key Takeaway
Comparing 1/1 vs 3/4 illustrates the distinction between an entire unit and fractions less than one.
- 1/1 = 1.00 (decimal) = 100% (percentage)
- 3/4 = 0.75 (decimal) = 75% (percentage)
- Common denominators simplify comparison.
- Real‑life examples make learning meaningful.
- Visuals and hands‑on teaching support comprehension.
Developing confidence in fraction comparison improves precision in cooking, construction, budgeting, and education. Apply these skills today to enhance your math fluency and make everyday measurements easier and more accurate.