Image 1080 Resolution Guide for Photography and Web Use
Learn what 1080 resolution means, its formats, best uses for web and photography, and how to optimize images for sharp, fast-loading visuals.
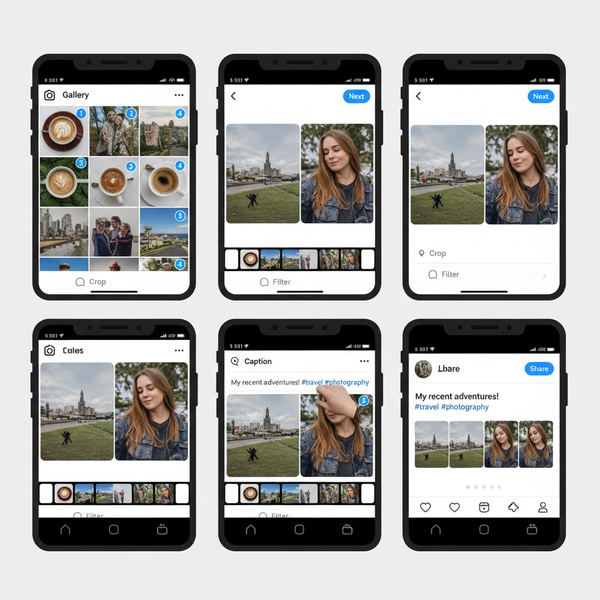
Introduction to Image 1080 Resolution
The term image 1080 refers to visuals with a height of 1080 pixels, a standard associated with Full HD (1920×1080) displays. This resolution is a crucial benchmark for web content, social media graphics, photography, and online video thanks to its balance of sharpness and manageable file size. By knowing what 1080 means, how it’s used, and how to optimize it, you can create visuals that look professional while performing well on multiple platforms.
---
Understanding "Image 1080" Resolution
When someone references an image 1080, they are typically talking about images that are 1080 pixels high in digital resolution. In the context of HD (High Definition), a 1080 image is usually part of the Full HD standard, where the display resolution is 1920×1080 pixels. This vertical measurement is key: regardless of the horizontal pixels, the 1080 height defines the resolution class.
This measurement is most common in videos (1080p or 1080i) but also applies to still photography, website graphics, and social media content. Understanding exactly what it means allows you to work with the right formats for sharp visuals.
---
Common 1080 Formats and Terminology
The term "1080" can appear in several variations. Here are some common terms you may encounter:
1080p vs 1080i
- 1080p (Progressive scan): All lines are displayed in sequence; sharper for motion and better for still photography.
- 1080i (Interlaced scan): Lines alternate per frame; more common in older broadcast standards.
1080×1080
- Square format often used for Instagram posts, fitting perfectly into a 1:1 aspect ratio.
Full HD
- Full HD (1920×1080) denotes a widescreen, 16:9 aspect ideally suited for video and wide photographic formats.
---
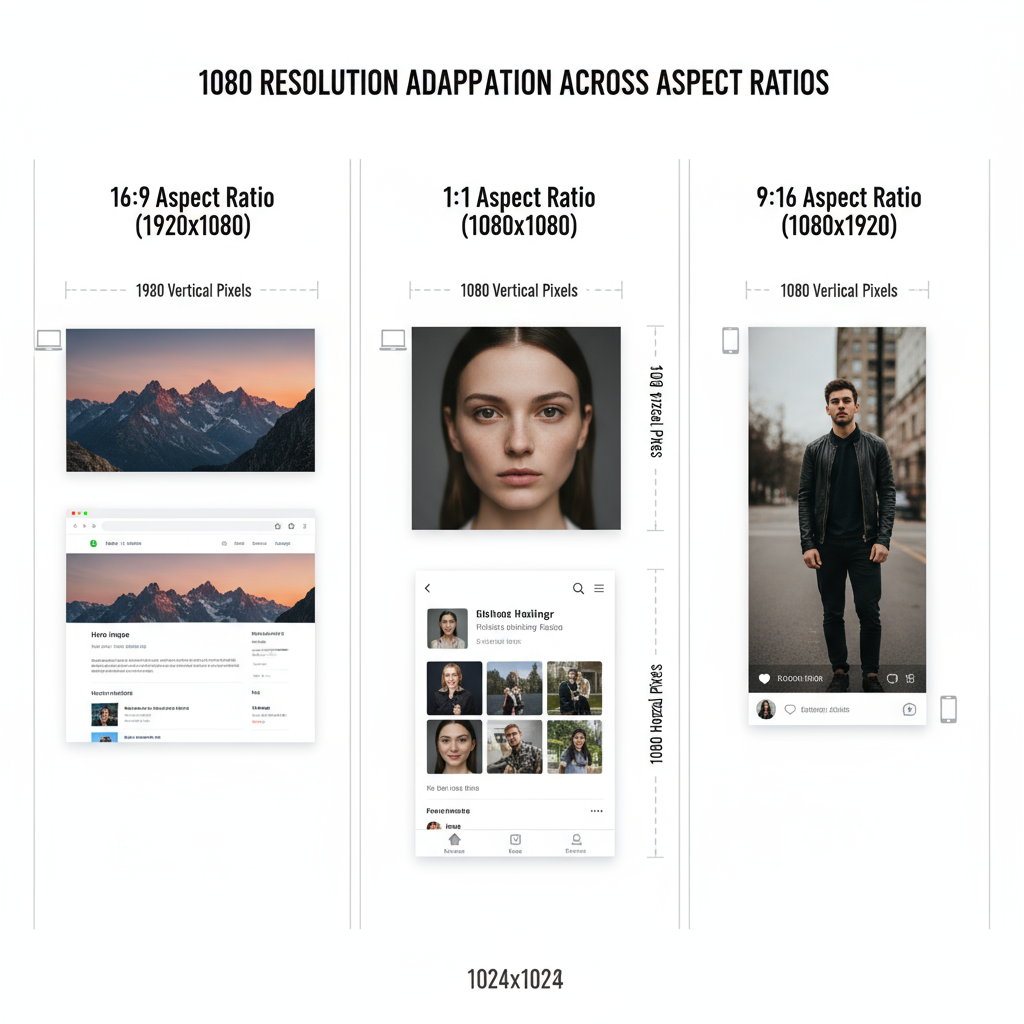
Aspect Ratios That Use 1080 Pixels
A consistent height of 1080 pixels can be paired with various widths depending on the aspect ratio:
| Aspect Ratio | Example Resolution | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| 16:9 | 1920×1080 | Video, widescreen websites |
| 1:1 | 1080×1080 | Social media posts (Instagram) |
| 9:16 | 1080×1920 | Vertical stories, TikTok |
| 4:3 | 1440×1080 | Photography for prints |
---
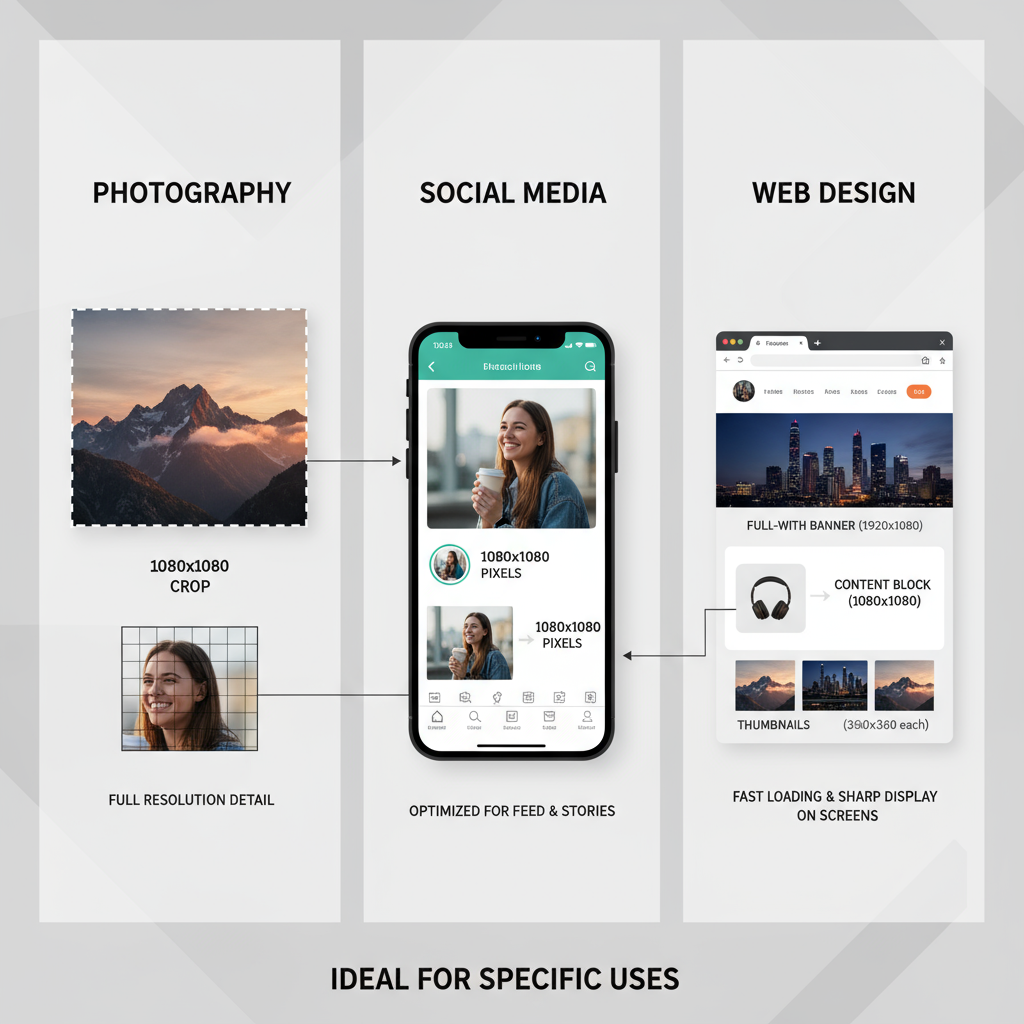
Optimal Uses for 1080 Resolution
1080 resolution offers a balance between crisp detail and reasonable file sizes. It’s often ideal for:
- Social media: Delivers clarity within platforms that compress images.
- Web design: Suitable for hero banners, sliders, and backgrounds with efficient load times.
- Print: Great for smaller prints such as 4×6 inches at moderate DPI.
---
File Formats and Compression Best Practices
Choosing the right format for your 1080 image affects both quality and site performance:
- JPEG: Best for photographs; compress to ~70–85% quality for faster load times.
- PNG: Ideal for graphics with transparency.
- WebP: Modern format delivering strong compression for both photos and graphics.
- SVG: Not pixel-based, but can complement 1080-sized raster images for scalable graphics.
Compression tips:
- Use tools like TinyPNG, Squoosh, or ImageOptim.
- Export at the exact resolution needed to avoid browser scaling.
---
Shooting and Editing for Clear 1080 Images
To ensure top-quality visuals:
- Shoot at a higher resolution than required to allow cropping without blurring.
- Frame correctly for your intended aspect ratio (e.g., 16:9, 1:1).
- Use post-processing tools (Lightroom, Photoshop, GIMP) to subtly sharpen and enhance contrast.
- Avoid oversharpening to maintain a natural look.
---
Scaling, Resizing, and Quality Considerations
Changing the size of an image can impact clarity:
- Downscaling: Converting high-res images to 1080 can yield sharp results.
- Upscaling: Enlarging smaller images can cause pixelation; use AI tools (e.g., Gigapixel AI) to restore detail.
---
DPI Considerations for 1080 Images
DPI influences print quality but not digital display clarity:
- Web: DPI is irrelevant; pixel count dictates display sharpness.
- Print: Match DPI to print size. For example:
- 4×6 inches at 300 DPI requires 1200×1800 pixels; 1080p may be slightly soft.
- Smaller print sizes can work well with 1080 vertical pixels at 300 DPI.
---
SEO Optimization for 1080 Images
Beyond quality, SEO-friendly 1080 images should have:
- Alt text: Detailed descriptions with natural keyword placement, including "image 1080" where appropriate.
- Filename: Descriptive, hyphenated names like `mountain-sunrise-1080.jpg`.
- Image sitemaps: Add image URLs to XML sitemaps.
- Lazy loading: Improves page speed for image-heavy designs.
- Structured data: Apply schema markup to key images.
---
Accessibility and User Experience
Ensure all users benefit from your visuals:
- Maintain text contrast over background images.
- Include alt descriptions for assistive technologies.
- Avoid embedding critical information solely inside images; replicate in HTML text for readability.
---
Common Mistakes with 1080 Resolution
Avoid these pitfalls:
- Using excessively large file sizes that slow page load.
- Cropping unevenly and altering aspect ratio.
- Skipping compression.
- Exporting from low-quality originals.
---
Future Trends: The Role of 1080 in the 4K/8K Era
While higher resolutions like 4K and 8K grow in usage, 1080 remains a web and streaming standard for its quality-speed balance. Even on modern mobile devices, 1080 delivers clear visuals efficiently. Expect adaptive image delivery to keep 1080p relevant by serving optimal sizes to specific devices.
---
Summary
Image 1080 resolution is a versatile and efficient format that works across digital and print platforms. By understanding the formats, aspect ratios, compression methods, and SEO practices suited for 1080 pixels, you can maximize visual quality without hampering performance. Whether for a website, social feed, or presentation, smart 1080 image use will keep your content looking sharp and loading quickly.
Take action: Audit your image library and update files to optimal 1080 versions to boost both aesthetics and performance.