Image Pixel Count Explained: Impact on Resolution and Qualit
Learn how pixel count influences resolution, pixel density, and image quality, plus tips for optimizing images for web, photography, and print.
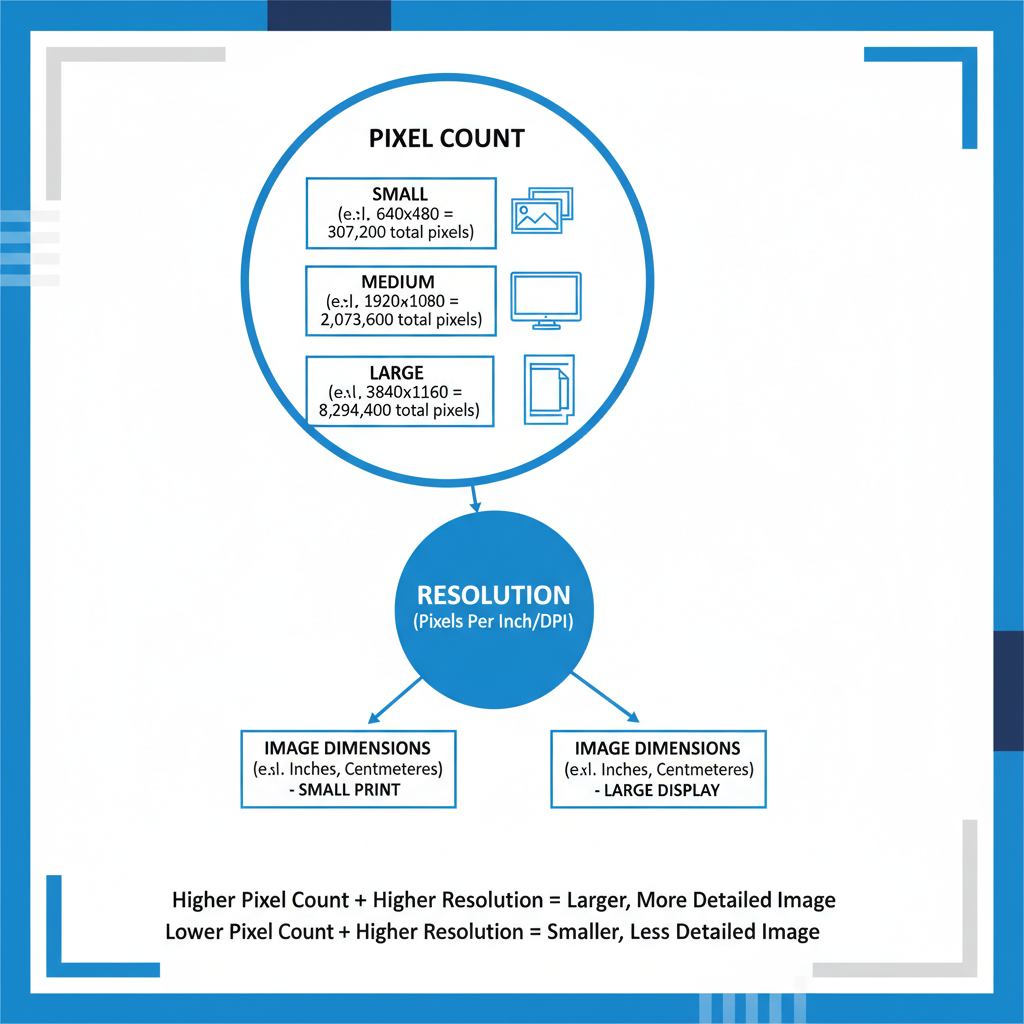
Image Pixel Count Explained: Impact on Resolution and Quality
In the digital imaging world, pixel count plays a pivotal role in determining resolution, pixel density, and overall image quality. Whether you're editing photos, creating graphics for web use, or preparing high-quality prints, knowing how pixel count impacts the final output will help you produce sharper, more accurate visuals. This guide explains pixel count, its relationship to megapixels and resolution, and offers practical tips for optimizing images.

---
What is Pixel Count in Digital Images?
A digital image is built from tiny dots known as pixels (picture elements). Each pixel carries specific data for color, brightness, and saturation. Pixel count is simply the total number of pixels making up the image.
The basic formula:
> Pixel Count = Image width in pixels × Image height in pixels
Higher counts allow for greater detail—though other factors also influence perceived quality.
---
Relationship Between Pixel Count, Resolution, and Image Dimensions
Many people confuse pixel count with resolution, yet they measure different aspects:
- Pixel count: Total number of pixels.
- Image dimensions: Width × height in pixels.
- Resolution (PPI/DPI): Pixel density, or how tightly pixels are packed together when displayed or printed.
This means two images with identical pixel counts may look different if viewed at varying display sizes or pixel densities.
---
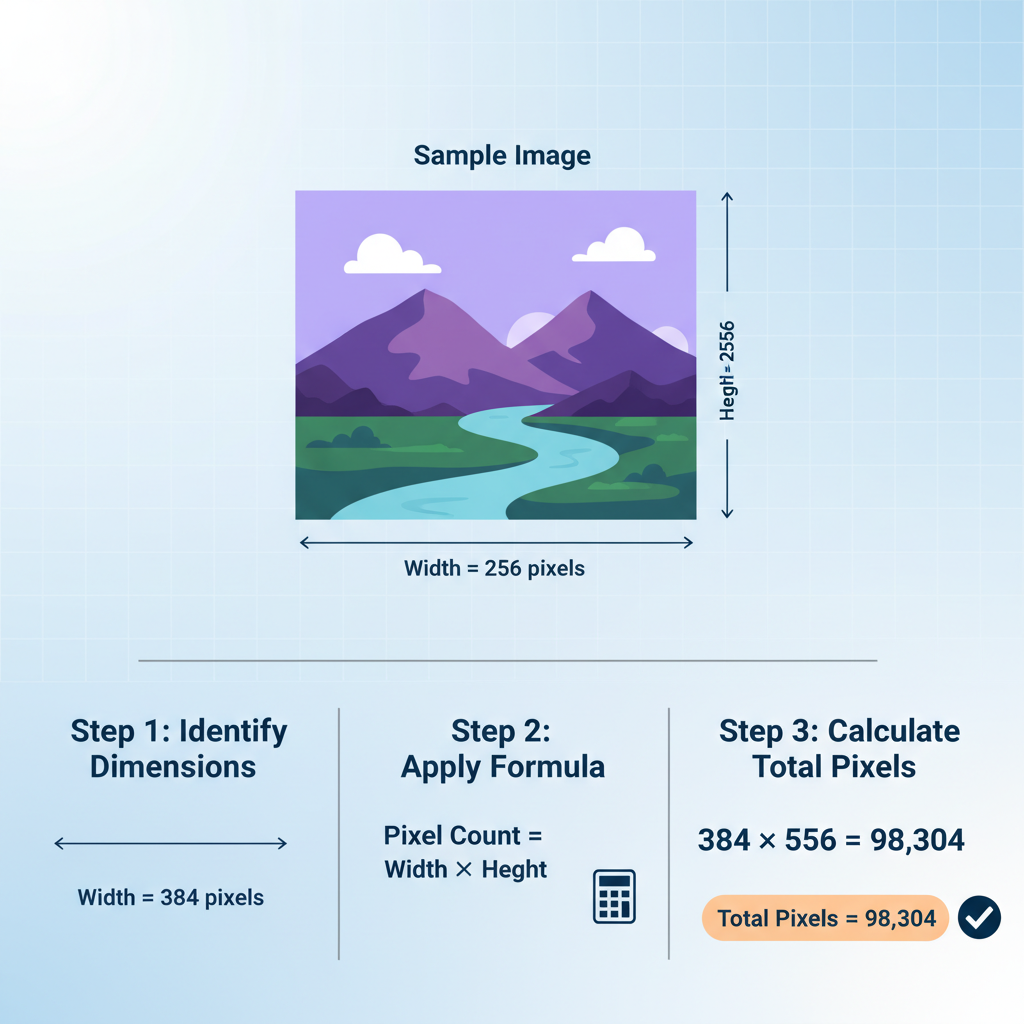
How to Calculate Pixel Count
Calculating pixel count is straightforward:
Pixel Count = Width (in pixels) × Height (in pixels)Example 1:
- Width = 1920 px
- Height = 1080 px
- Pixel Count = 1920 × 1080 = 2,073,600 pixels (~2.07 MP)
Example 2:
- Width = 4000 px
- Height = 3000 px
- Pixel Count = 4000 × 3000 = 12,000,000 pixels (12 MP)
---
Pixel Count vs Megapixels in Photography
In photography, cameras are often rated in megapixels (MP), where 1 MP equals 1 million pixels.
| Pixel Dimensions | Total Pixels | Megapixels |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 × 1080 | 2,073,600 | ~2.07 MP |
| 4000 × 3000 | 12,000,000 | 12 MP |
| 6000 × 4000 | 24,000,000 | 24 MP |
While more megapixels often enable larger prints, quality also relies on factors like sensor size, lens sharpness, and image processing.
---
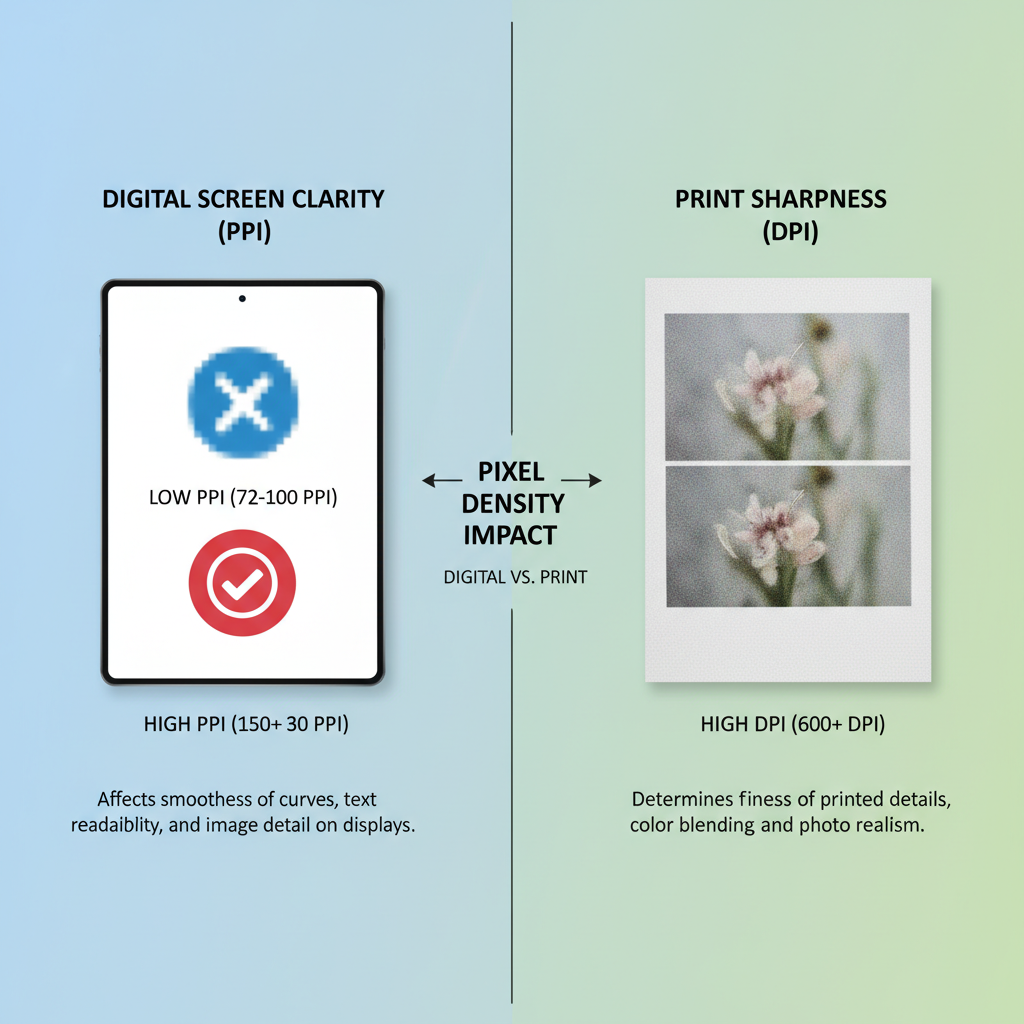
Why Pixel Density (PPI/DPI) Matters for Digital and Print
Pixel density greatly affects visual results:
- Digital displays: Typically 72–96 PPI; pixel count determines the visual size on screen.
- Print projects: Require at least 300 DPI for sharpness.
Example:
- A 3000 × 2000 px image shows ~31 × 20 inches at 96 PPI, but only ~10 × 6.6 inches at 300 DPI for print.
---
Common Misconceptions About Pixel Count and Image Quality
- More pixels always mean better results – Not true; noise, lens quality, and compression also matter.
- High pixel count is always necessary – Oversized images for web can slow page loads without notable quality gain.
- Print quality depends only on pixel count – DPI, PPI, and sharpening techniques play key roles.
---
Optimal Pixel Counts for Various Uses
| Use Case | Recommended Pixel Dimensions | Approx. Megapixels |
|---|---|---|
| Instagram Post | 1080 × 1080 | ~1.16 MP |
| Facebook Cover | 820 × 312 | ~0.26 MP |
| Full HD Video Frame | 1920 × 1080 | ~2.07 MP |
| A4 Print (300 DPI) | 3508 × 2480 | ~8.69 MP |
| Poster Printing | 6000 × 4000 | 24 MP |
---
How Compression Affects Perceived Quality
Compression reduces file size by removing certain data:
- Lossless compression: Preserves all detail (e.g., PNG).
- Lossy compression: Discards some data; excessive compression can introduce artifacts, blur, or banding.
Even high pixel-count images can appear poor if overly compressed.
---
Tools to Check and Adjust Pixel Count Without Quality Loss
Popular options include:
- Adobe Photoshop – Adjust via Image Size dialog.
- GIMP – Free, open-source editing.
- IrfanView – Lightweight viewer/editor.
- Online editors – Photopea, Fotor for quick resizing.
Tip: Always keep a high-res original before any compression or resizing.
---
Tips for Resizing Images While Maintaining Sharpness
- Use Bicubic or Lanczos interpolation for smooth scaling.
- Avoid enlarging low-res images more than 200%.
- Apply sharpening filters post-resize.
- Keep aspect ratio to prevent distortion.
- Save edits in lossless formats before final export.
---
Summary: Choosing the Right Pixel Count for Your Project
When selecting an image's pixel count:
- Match dimensions to final use (screen, print, social).
- Balance file size and quality—avoid unnecessary oversizing.
- Keep an original high-resolution source for future needs.
- Remember: pixel count is just one factor in image quality; sensor quality, lens optics, lighting, and compression techniques weigh equally.
By understanding and adjusting pixel count wisely, you can produce crisp, professional-grade images optimised for any medium. Start applying these insights today to elevate your photography, digital design, and printed work.