Organic vs Paid Marketing Strategies Explained
Learn the differences between organic and paid marketing, their channels, costs, and ROI to build a balanced, high-performing digital strategy.
Introduction
When building a strong online presence, every marketer eventually faces the organic vs paid marketing decision. Understanding both approaches — and how they fit into your budget, goals, and timeline — is essential for creating a high-performing digital strategy.
Organic marketing relies on earning attention naturally through valuable content, community engagement, and search visibility, while paid marketing uses direct advertising spend for faster, more targeted reach. Both deliver results, but their paths to success differ significantly.

---
What is Organic Marketing?
Organic marketing encompasses all brand-building activities that attract an audience without directly paying for placement. It leverages content quality, relevance, and relationships to naturally draw traffic over time.
Key traits of organic marketing:
- Grows naturally via search engines, social shares, and referrals
- Requires consistent effort and patience
- Focuses on long-term value creation
Example: Publishing SEO-friendly blog content, cultivating an engaged social media community, and sending informative email newsletters.
---
What is Paid Marketing?
Paid marketing achieves visibility by investing in ads or sponsored content on online platforms, allowing brands to reach targeted audiences immediately.
Key traits of paid marketing:
- Delivers quick reach and exposure
- Performance is tied directly to budget and bidding strategy
- Offers precise audience targeting
Example: Search ads via Google, boosted Facebook posts, or influencer collaborations for immediate endorsement.
---
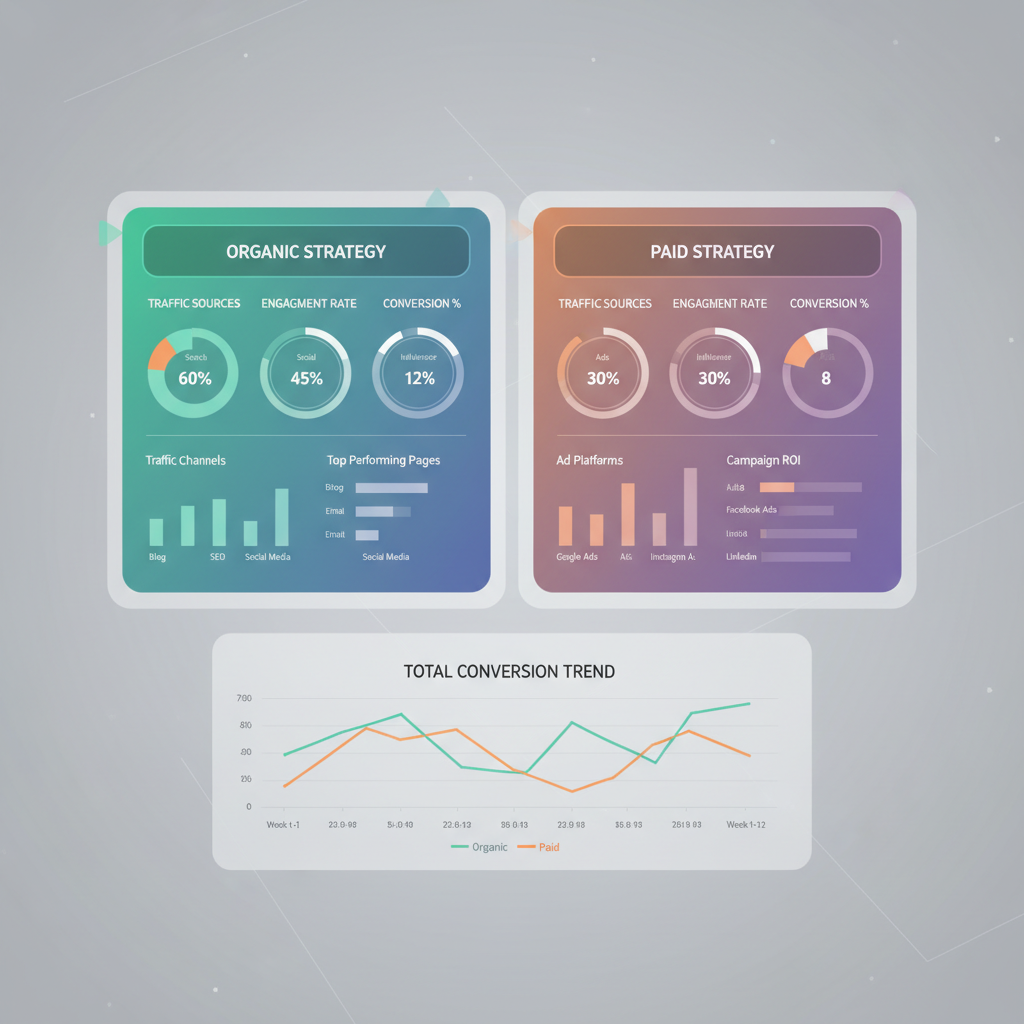
Key Differences: Cost, Reach, and ROI
Although both aim to attract and convert customers, their cost structures, reach speeds, and return on investment vary greatly.
| Factor | Organic Marketing | Paid Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Primarily time, content creation, expertise; low direct spend | Direct payment to platforms or partners; higher upfront cost |
| Reach | Steady growth via SEO and sharing | Instant reach through targeted campaigns |
| ROI Timeline | Gradual but sustainable returns over time | Short-term spikes; drops when spend stops |
---
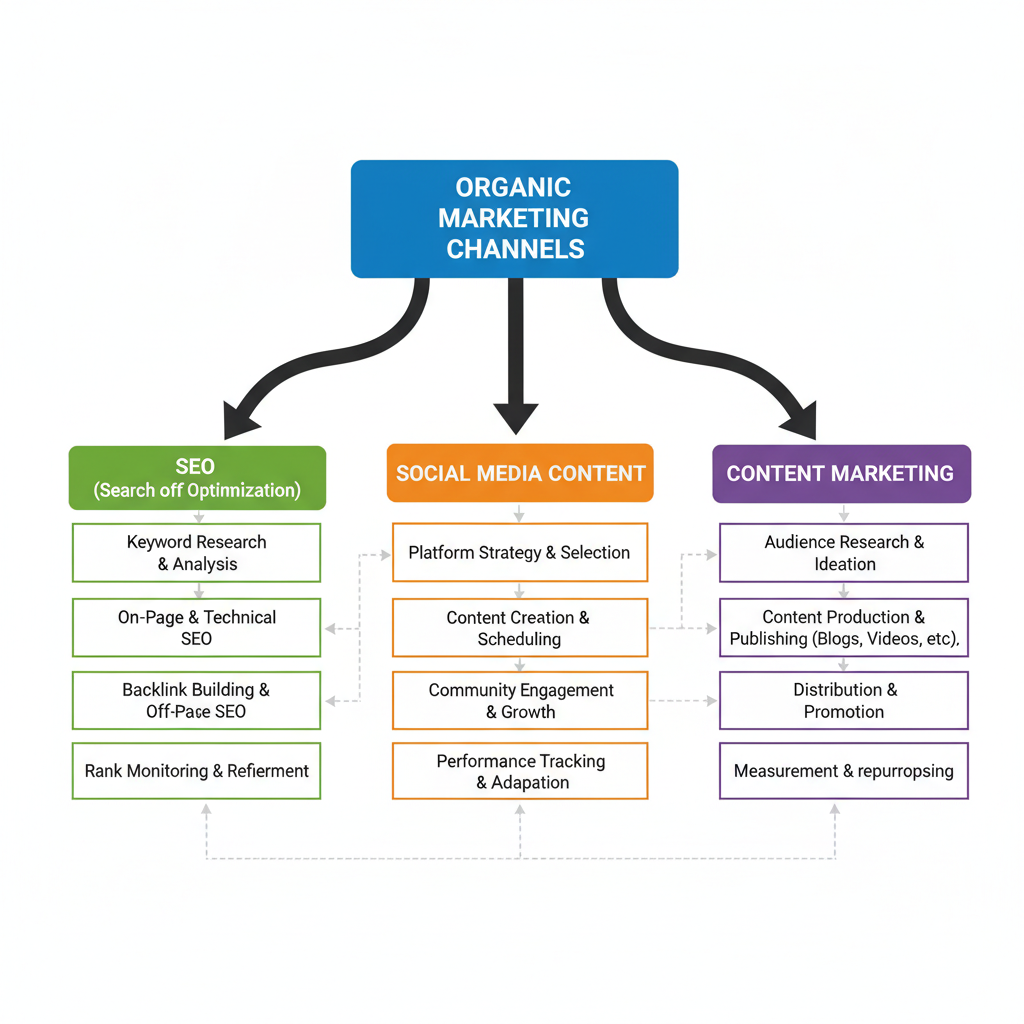
Main Organic Marketing Channels
Strong organic marketing begins with quality content and strategic engagement.
1. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Optimize pages for relevant keywords to rank higher in search results.
2. Social Media Content
Share regular, valuable updates while interacting consistently with followers.
3. Content Marketing
Create blogs, videos, and guides to offer lasting value without direct advertising.
---
Primary Paid Marketing Channels
Paid marketing thrives on precise targeting and budget control.
1. PPC Ads
Pay-per-click search ads on platforms like Google and Bing.
2. Social Media Ads
Sponsored content across Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok, and more.
3. Influencer Promotions
Partner with influencers to tap into a loyal, niche audience.
---
Long-Term Benefits of Organic vs Paid
- Organic: Consistent inbound traffic, brand credibility, authority in your market.
- Paid: Swift brand awareness, rapid customer acquisition, measurable short-term outcomes.
---
When Paid Marketing Delivers Faster Results
Paid methods excel when:
- Launching a new product or service
- Running time-sensitive deals
- Quickly targeting niche demographics
- Testing ideas before committing to a long-term plan
---
When Organic Marketing is More Sustainable
Organic wins when:
- Building durable digital assets (evergreen articles, videos)
- Prioritizing trust and thought leadership
- Needing predictable budget use
- Leveraging evergreen SEO gains
---
Combining Organic and Paid for Maximum Impact
A hybrid strategy uses paid marketing to drive immediate attention while building an organic foundation.
Steps to integrate:
- Run paid ads to boost early traction
- Analyze engagement and identify proven topics
- Invest in long-term organic optimization
- Retarget warm audiences with paid campaigns
---
Tracking KPIs for Both Methods
Measure success with:
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): Understand ad or headline attractiveness
- Conversions: Track completed purchases or desired actions
- Engagement: Monitor likes, shares, comments, watch time
---
Tips to Balance Your Budget Between Organic and Paid
- Use paid ads for launches or rapid scaling
- Increase organic investment as traffic builds
- Assign fixed paid ad spend and flexible organic budget
- Continuously A/B test messaging and targeting
---
Pros and Cons Comparison Table
| Organic Marketing | Paid Marketing | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
---
Summary and Next Steps
In the organic vs paid marketing debate, neither approach alone is a complete solution. Organic marketing lays a durable foundation that builds trust and authority, while paid marketing offers speed and precision. The best results come from a thoughtful blend, guided by data and adjusted according to evolving goals.
To succeed:
- Clarify your business objectives
- Allocate resources strategically
- Track KPIs for continuous improvement
Ready to craft a winning mix? Combine sustainable organic strategies with targeted paid campaigns and watch both short- and long-term results flourish.