1/2 vs 9/16 Inches: Measurement Conversion and Comparison
Learn how to convert and compare 1/2 vs 9/16 inch measurements to decimals and millimeters, with practical tips for woodworking and construction accuracy.
Introduction to Fractional Inch Measurements and Their Importance
Fractional inch measurements, such as 1/2 and 9/16, are essential in woodworking, construction, metalworking, and countless DIY projects. In U.S. customary units, tape measures and rulers are marked with fractions like 1/16, 1/8, and 1/4, making it fundamental to understand how to read and convert them accurately. Mastering these conversions—both to decimal inches and millimeters—helps ensure precise cutting, drilling, fitting, and assembly, reducing costly errors and rework.
Even a fraction of an inch can make the difference between a perfect fit and a frustrating redo. Knowing exactly what each measurement represents equips you to work with greater accuracy and professional results.
---
Understanding What 1/2 Inch Represents
The fraction 1/2 inch equals half an inch. In decimal form:
1 ÷ 2 = 0.5 inchesTo convert inches to millimeters (mm):
mm = inches × 25.4Applying the formula:
0.5 inches × 25.4 = 12.7 mmSummary:
- Fraction: 1/2 inch
- Decimal (inches): 0.5
- Millimeters: 12.7
On a ruler or tape measure, 1/2 inch is typically the longest mark between the zero and the next whole inch, making it easy to spot.
---
Decoding 9/16 Inch
The fraction 9/16 inch involves a simple division:
9 ÷ 16 = 0.5625 inchesConverting to millimeters:
0.5625 inches × 25.4 = 14.2875 mmRounded values:
- Decimal (inches): 0.5625
- Millimeters: ≈ 14.29
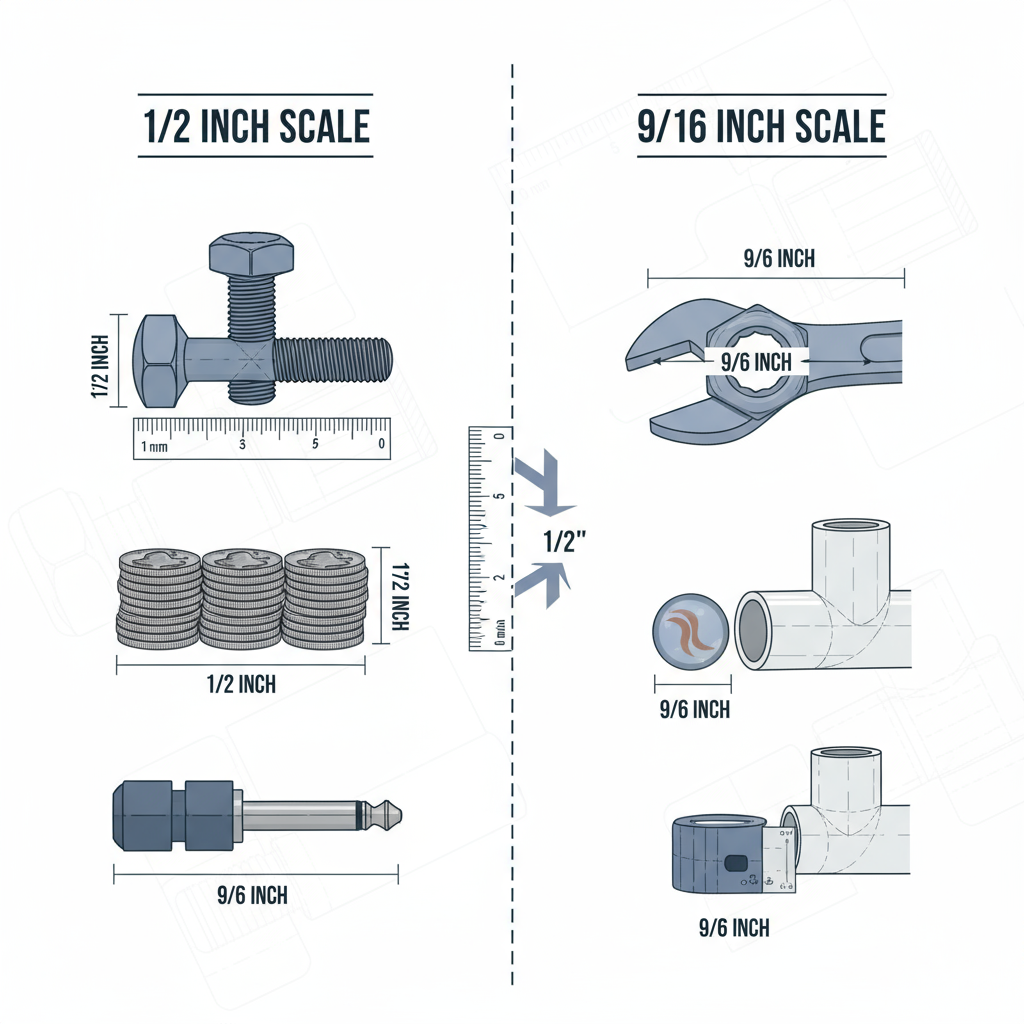
On standard tape measures, 9/16 inch appears as the ninth mark after zero when counting increments of sixteenths.
---
Comparing 1/2 Inch vs 9/16 Inch
A clear side‑by‑side comparison:
| Fraction | Decimal (inches) | Millimeters | Difference from 1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 0.5 | 12.7 | — |
| 9/16 | 0.5625 | 14.29 | +0.0625 inches (~1.59 mm) |
Size Difference Insight:
- Inches: 9/16 is 0.0625 inches larger than 1/2.
- Millimeters: Approximately 1.59 mm bigger.
This small variance is critical in precision work such as joinery, metal fitting, or mechanical assemblies.
---
Practical Applications of 1/2 and 9/16 Inch
Woodworking:
Mortises and tenons require precise sizing—choosing the right fraction determines whether parts fit snugly or bind.
Construction:
Structural framing, spacing, and alignment depend on exact fractional measurements to maintain strength and aesthetics.
DIY Projects:
Hole diameters for bolts or dowels must match specifications to ensure smooth assembly without forcing parts.
---
Common Errors When Reading Fractions on Tools
- Miscounting increments: Confusing 8/16 with 9/16 can create costly measurement errors.
- Ignoring line thickness: Pick a consistent side of each mark when measuring.
- Mixing units: Careless switching between inches and millimeters leads to mismatches.
- Poor lighting: Dim workspaces make small lines hard to distinguish.
---
Tips for Accurate Fractional Measurement
- Start from the zero edge: Confirm your tool’s hook is accurate.
- Use fine marking tools: Sharp pencils reduce ambiguity.
- Verify before cutting: “Measure twice, cut once” saves materials and effort.
- Highlight key fractions: Annotate project plans with decimal and metric equivalents.

---
Choosing Between Digital Calipers and Tape Measures
Digital Calipers:
- Ideal for small dimensions.
- Can display inches, millimeters, and fractions instantly.
- Great for quick conversions on site.
Tape Measures:
- Best for large scales.
- Require manual fraction reading.
- Durable and portable for varied environments.
Usage Tip: Use calipers for precision under several inches; tape measures for broader dimensions.
---
Converting Fractions to Millimeters
Working collaboratively—especially across regions—requires a common measurement language. Millimeters remove fractions, making communication clearer.
Formula:
mm = inches × 25.4Examples:
- 1/2 → 12.7 mm
- 9/16 → 14.29 mm
- 5/8 → 15.875 mm
Millimeters provide exactness in design drawings, machining, and quality control.
---
Summary and Key Takeaways
For consistent, accurate work:
- Convert fractional inches to decimals and millimeters before executing precision tasks.
- Double‑check measurements, especially when switching between tools or units.
- Choose calipers for short distances and tape measures for longer runs.
- Remember the critical difference: 1/2 inch = 12.7 mm, 9/16 inch = 14.29 mm, with a variance of ~1.59 mm.
By mastering fractional inch reading and conversion, you elevate the quality and precision of any project—whether building furniture, framing a house, or machining components. Start applying these skills today to work smarter and with greater confidence.