# Building Lookalike Audiences in BigQuery with Jaccard Similarity and AI-Powered Workflows
**Editor’s Note:** This post is part of a series showcasing how organizations use **Google Cloud’s** unique data science capabilities compared with other cloud platforms.
Google Cloud offers **end-to-end vector embedding generation and search**, customizable with task-optimized models and hybrid search — delivering highly relevant results for both semantic and keyword queries.
---
## Overview
**Zeotap’s Customer Intelligence Platform (CIP)** helps brands understand and predict customer behavior to improve engagement.
Partnering with **Google Cloud** enables Zeotap to deliver a privacy-first, secure, and compliant platform built on **BigQuery**.
With BigQuery ML, Zeotap empowers digital marketers to:
- Build AI/ML models directly in BigQuery
- Predict customer behavior
- Personalize marketing experiences at scale
For creators and data-driven marketers aiming to expand beyond analytics into **AI-generated content** for multiple channels, open-source platforms such as **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)** combine AI generation, publishing, analytics, and model ranking — enabling monetization across **Douyin, Instagram, YouTube, X (Twitter)**, and more.
---
## Problem: Sparse Data in Lookalike Audience Modeling
**Lookalike audience extensions** in Zeotap identify new customers similar to existing high-value segments.
However, **incomplete first-party data** reduces effectiveness — advertising algorithms struggle to detect key traits needed for matching.
**Solution:** Zeotap integrates [multigraph algorithms](http://papers.adkdd.org/2021/papers/adkdd21-selvaraj-multigraph.pdf) with quality datasets to enhance precision for lookalike models.
---
## Our Approach with BigQuery ML + Vector Search
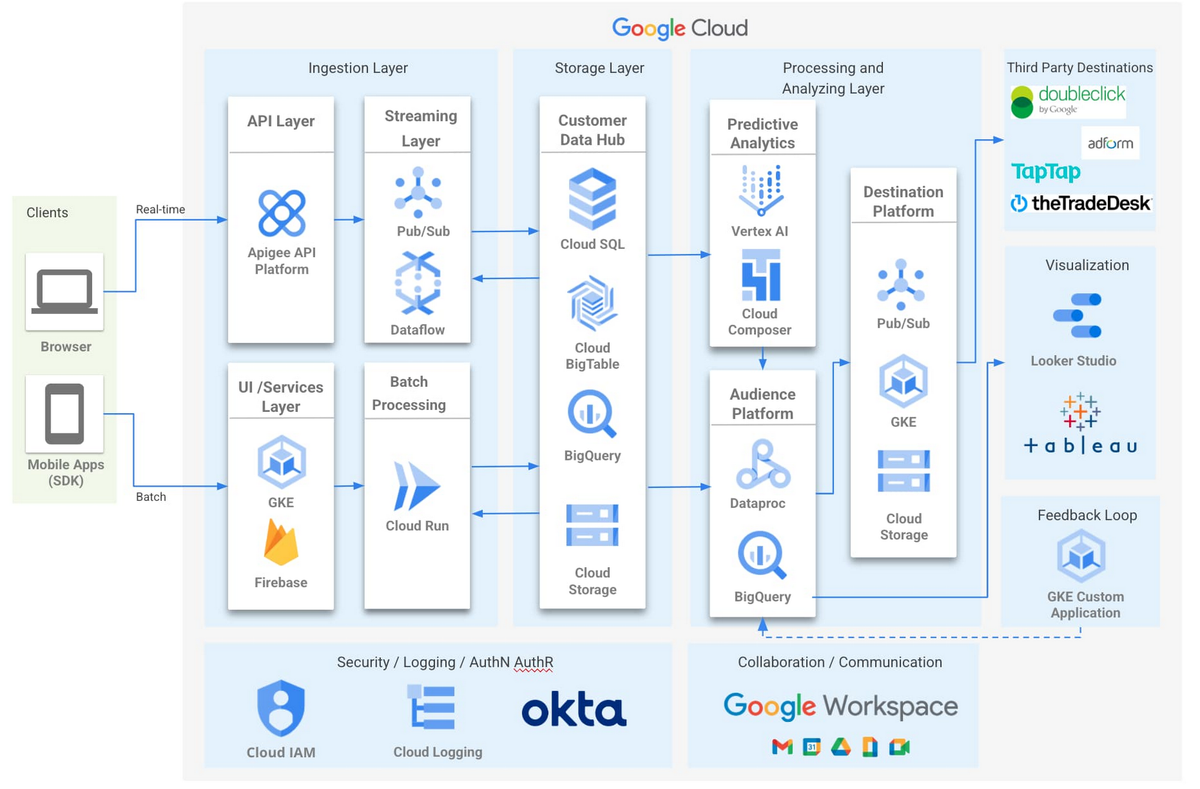
We solved an **end-to-end lookalike audience problem** entirely inside **BigQuery** by:
1. Converting **nearest-neighbour** search into a simple **inner join**
2. Addressing **cost, scalability, and performance** constraints
3. Implementing **Jaccard similarity** for low-cardinality categorical columns
> _Note: High-cardinality workflows are outside this scope._
---
## Jaccard Similarity Explained
**Why Jaccard?**
It measures set overlap efficiently and is ideal for **low-cardinality features**.
**Formula:**
\[
\frac{|A \cap B|}{|A \cup B|}
\]
**Meaning:**
> _Of all unique attributes in either user profile, what percentage are shared?_
Unlike Euclidean or Cosine similarity, it ignores attributes absent in both sets — aligning with **Occam’s razor** for simplicity.
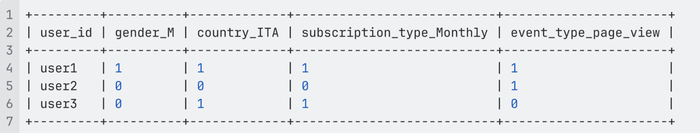
### Example Table
| Users | Interests | Vector `[Movie,Sport,Music,Books,Travel]` | Intersection X∩Y | Jaccard Similarity |
|-------|--------------|-------------------------------------------|------------------|--------------------|
| X | Movie, Sport | [1,1,0,0,0] | - | - |
| Y | Movie, Sport | [1,1,0,0,0] | 2 | 2 / 2 |
---
## Implementation Blueprint
### Step 1: Generating Embeddings
Use [one-hot encoding](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/standard-sql/bigqueryml-syntax-one-hot-encoder?hl=en) and [multi-hot encoding](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/standard-sql/bigqueryml-syntax-multi-hot-encoder?hl=en) in BigQuery for low-cardinality features.
---
### Step 2: Workaround for Unsupported Jaccard Distance
**BigQuery Vector Search supports:**
- Euclidean
- Cosine
- Dot Product
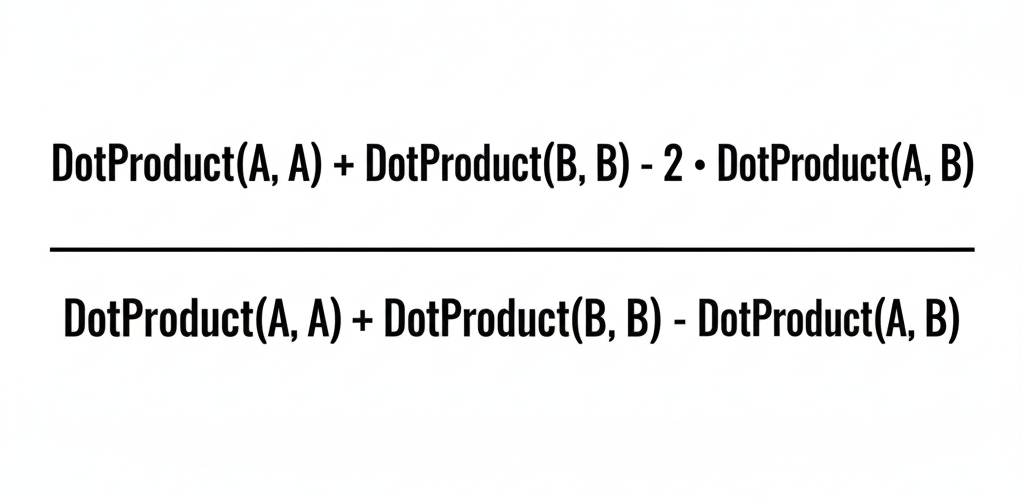
Since Jaccard is not native, express **Jaccard Distance** as:
\[
J_d(A,B) = 1 - \frac{|A \cap B|}{|A \cup B|} = \frac{|A \cup B| - |A \cap B|}{|A \cup B|}
\]
Rewriting with dot product + [Manhattan norm](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/standard-sql/bigqueryml-syntax-lp-norm?hl=en):
- **Manhattan norm for binary vector = dot product with itself**
- Enables Jaccard distance computation via supported **dot product search**
---
### Step 3: Building the Vector Index
**Index Types in BigQuery:**
- [IVF](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/vector-index#ivf-index) — Inverted File Index
- [TREE_AH](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/vector-index#tree-ah-index) — Tree + Asymmetric Hashing ([ScaNN algorithm](https://github.com/google-research/google-research/blob/master/scann/docs/algorithms.md))
**Choice:** TREE_AH for **large batch queries** (millions of records) due to reduced latency & cost.
---
### Step 4: Rare Feature Strategy for Pre-Filtering
**Goal:** Reduce search space before expensive computations.
Process:
1. Identify **omnipresent** features
2. Retain only **rare/discriminative** features in search index
Result:
- Reduced search space by **~78%**
- Achieved via **pre-filters** in BigQuery `VECTOR_SEARCH`
- Added a "flag" column to the index for filtering
_If a filter column isn’t indexed, BigQuery applies **post-filtering** — less efficient._
---
### Step 5: Batch Strategy
**Challenge:** Complexity grows with `(M × N)`
- M = pool of base users
- N = query users
**Solution:**
- Batch query users (e.g., 500K per batch)
- Run vector search over full base set M
- Grid search to find optimal batch size
---
## Key Outcomes
- Overcame **lack of native Jaccard support** by combining dot product & Manhattan norm
- Delivered **custom lookalike models** with a single SQL script
- Avoided external vector databases — saving cost & complexity
- Process scaled to **118M+ user-encoded vectors** for a single client
---
## Built with BigQuery Advantage for ISVs & Data Providers
**Built with BigQuery** enables companies to:
- Deploy SaaS on Google Cloud’s secure, scalable infrastructure
- Access advanced AI/ML without building from scratch
- Integrate multiple data sources
- Leverage ecosystem tools
---
## Complementary AI Content Platforms
Platforms like **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)** fit naturally into these solutions, enabling:
- AI content generation
- Multi-channel publishing
_(Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X)_
- Model performance ranking via [AI模型排名](https://rank.aitoearn.ai)
- Open-source, global reach
- Efficient monetization pipelines
---
## Next Steps
- Learn more about [Built with BigQuery](https://cloud.google.com/solutions/data-cloud-isvs)
- Explore [AiToEarn文档](https://docs.aitoearn.ai/) for integrating AI content workflows
- Optimize your vector searches, rare feature selection, and batching for scale
---