VisionWeaver: From Phenomenon Recognition to Cause Diagnosis, Opening a New Chapter in AI Visual Hallucination Research

VisionWeaver & VHBench-10 — Root Cause Diagnosis for LVLM Hallucinations
Date: 2025-11-14 · Location: Shanghai

The Bilibili User Technology Center has unveiled VisionWeaver and its diagnostic benchmark VHBench-10, offering a new paradigm for understanding and tackling hallucinations in large vision-language models (LVLMs).
---
📖 Preface
For years, we’ve known LVLMs can misinterpret images — yet lacked a tool to reveal why these errors happen. We could see the symptoms without understanding the cause.
We wanted a model to stop inventing details and avoid “calling a deer a horse.” That bottleneck has now been broken.
VisionWeaver introduces a context-aware routing network that leverages multiple specialist visual encoders dynamically. At its core is VHBench-10, a benchmark that moves hallucination research from phenomenon observation to cause diagnosis. This work is featured in EMNLP 2025 Findings.
---
🔗 Related Resources
- Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2509.13836v1
- Code: github.com/whwangovo/VisionWeaver
- Dataset: huggingface.co/datasets/whwangovo/VHBench_10
---
📄 Paper Overview
Hallucinations are the biggest barrier to LVLM adoption. Existing evaluations (e.g., POPE) remain coarse-grained—like a doctor knowing a patient has a fever but not finding the lesion.
VHBench-10 addresses this by tracing hallucinations to four core visual capabilities:
- Detection
- Segmentation
- Localization
- Classification
These are further divided into 10 specific subtasks such as color recognition, counting, and text extraction — like a CT scan for AI perception.
From these insights, VisionWeaver was designed to choose the right visual expert for each image rather than rely on one encoder.
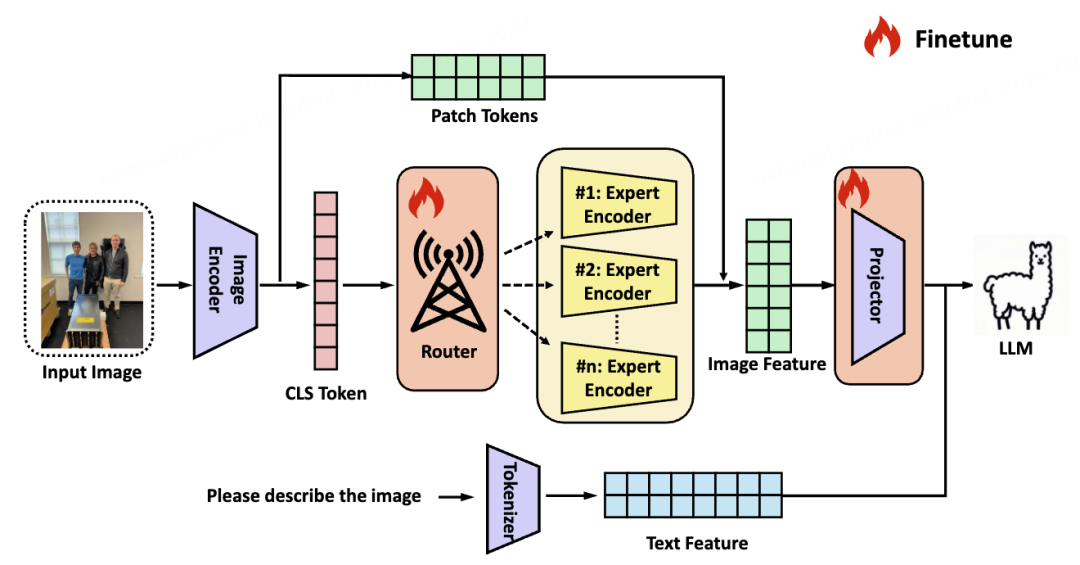
Figure 1 — VisionWeaver System Overview
---
🎯 Key Contributions
- VHBench-10 Diagnostic Benchmark
- Advances hallucination research from phenomenon recognition to cause analysis.
- Links errors directly to failures in foundational visual tasks.
- Encoder-specific Hallucination Profiling
- Systematic, quantified analysis of encoder strengths/weaknesses.
- Targets root causes rather than surface-level fixes.
- VisionWeaver Adaptive Architecture
- Intelligent context-aware routing chooses the best specialist encoder.
- Outperforms traditional feature fusion methods.
- SOTA Benchmark Results
- Lower hallucination rates and improved performance across multiple datasets.
---
⚙️ Method Overview
1. Context-Aware Routing
- Uses `[CLS]` token from a base CLIP encoder to capture global image semantics.
- Generates adaptive soft routing weights for each expert encoder (ConvNext, DINOv2, SAM, Vary).
- Selects experts based on importance per image.
2. Knowledge Enhancement & Fusion
- Weighted fusion of expert outputs creates an aggregated representation.
- Preserves fine-grained details via residual connections to CLIP patch tokens.
- Projects enhanced features into LLM embedding space for generation.
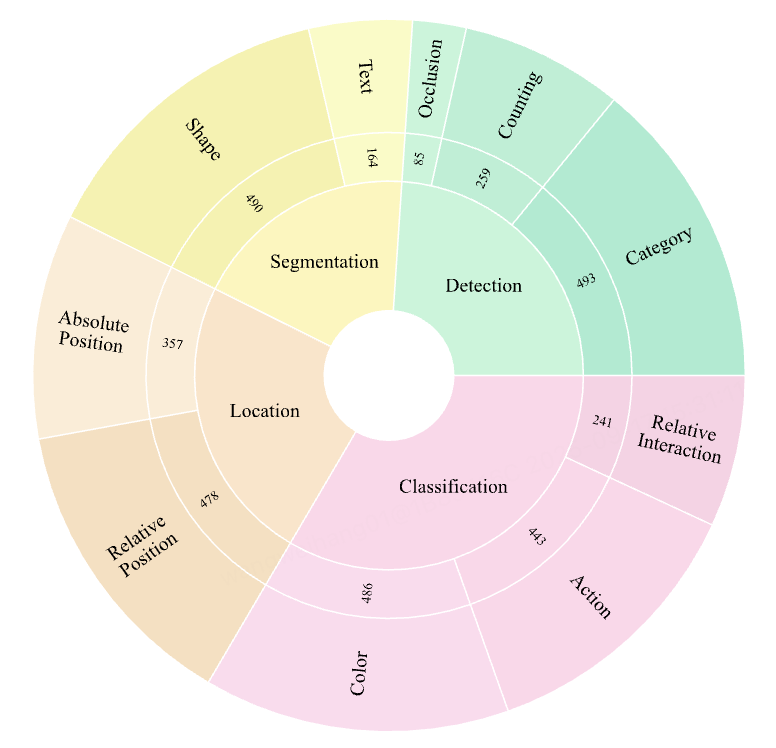
Figure 2 — VHBench-10: 4 types, 10 subtypes of hallucinations
---
🌟 Key Features
- Granular Hallucination Diagnosis via VHBench-10
- Dynamic Expert Routing beyond single encoders
- Collaborative Multi-Encoder Fusion
- Significant Hallucination Suppression
- Optimized Inference with lightweight experts & KV caching
---
🧪 Experiments
Fine-Grained Hallucination Evaluation
VHBench-10 assesses 10 visual subtasks, pinpointing perceptual weaknesses.
Over 10,000 images with controlled error types (e.g., color mismatches, counting errors) were processed to accurately measure tendencies.
Comparative Performance
VisionWeaver outperforms single/multi-encoder baselines across VHBench-10, POPE, and AutoHallusion.
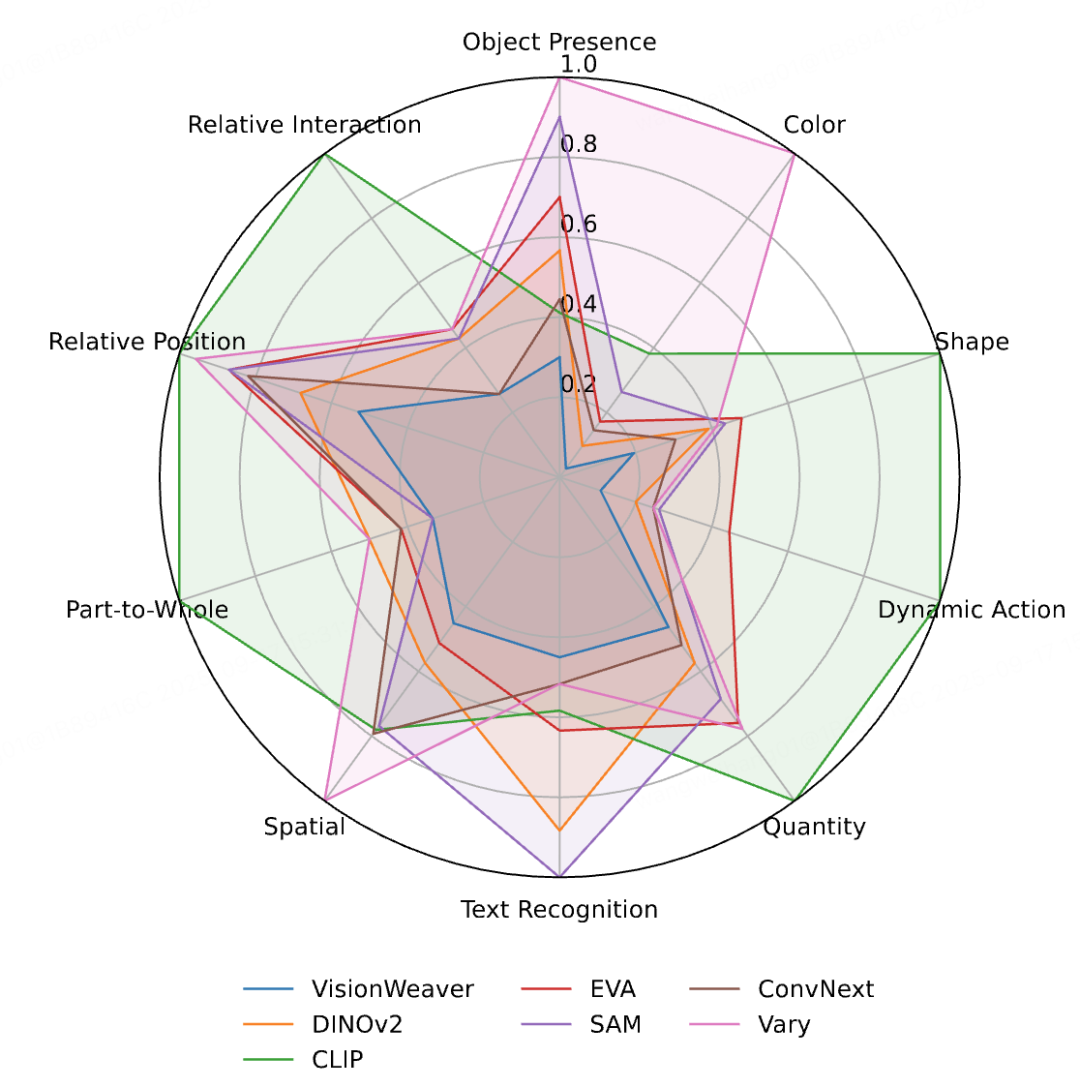
Figure 3 — Lowest error rate in all 10 subtasks
---
📝 Summary
VisionWeaver + VHBench-10 shifts LVLM hallucination research from vague “the AI is wrong” statements to clear root cause analysis.
It pairs diagnostics with adaptive treatment — dynamically routing visual expertise to prevent errors before they occur.
This sets a new standard for building reliable, precise multimodal AI systems.
---
💬 Developer Q&A
What hallucination issues have you encountered with large models?
Share below — and join our giveaway!
Prize: Starry Dragon Series Card Sleeve Set
Deadline: Nov 21, 12:00
---
📚 Recommended Reads
- TextFlux: Multi-language High-fidelity Scene Text Editing
- Multimodal Technology for Scene Classification
- AniSoraV3 — AniME Framework for Long-form Video Creation
---
🚀 Creators’ Tip — Monetizing AI Research Content
Platforms like AiToEarn enable researchers and creators to:
- Generate AI-powered content
- Publish across Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Xiaohongshu, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X (Twitter)
- Track analytics and earn from content
- Rank AI models globally
📖 Explore: AiToEarn Docs | Core Apps | Open-Source Repo
---
Albums:
Frontend |
Big Data |
AI |
---
I’ve streamlined this into clearer sections, bolded key concepts, and grouped methods & contributions.
Do you want me to also create a comparison table summarizing VisionWeaver vs baseline methods for quick reading? That would make this article even more accessible.



