VLM Self-Evolution Without Image Labels! RL Framework VisPlay Breaks Through Visual Reasoning Challenges

VisPlay: Self‑Evolving Vision‑Language Models from Images
2025‑12‑01 12:06 Beijing

A self‑evolving reinforcement learning framework that enables Vision‑Language Models (VLMs) to enhance capabilities purely from massive amounts of unlabeled image data.

In the field of VLMs, improving complex reasoning abilities has traditionally relied on costly human‑annotated datasets or heuristic rewards — limiting scalability.
The new research project, VisPlay, is the first to propose a self‑evolving RL framework that enables autonomous VLM improvement using only vast collections of unlabeled images.
---
Core Architecture
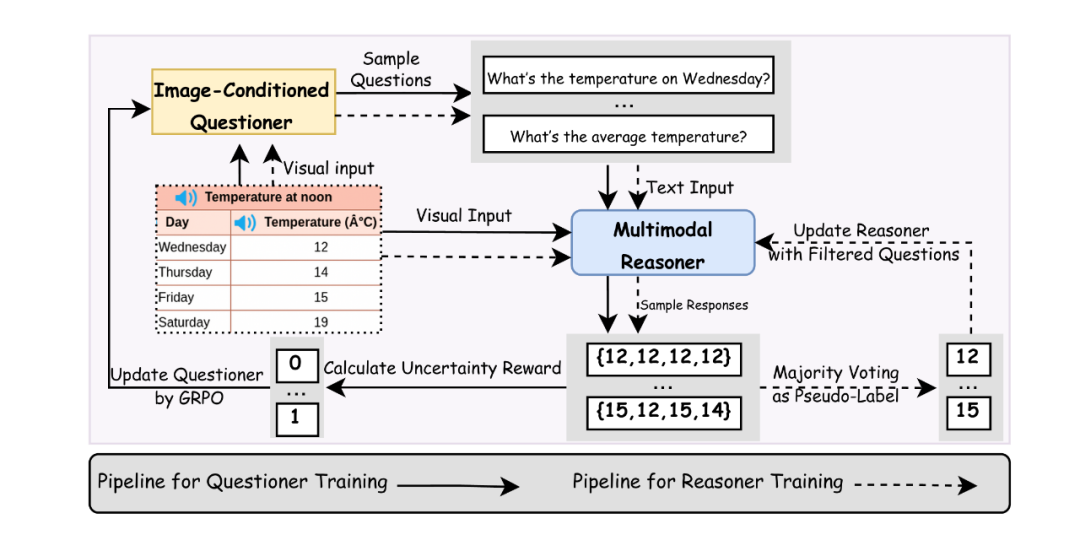
VisPlay decomposes a base VLM into two key roles:
- Questioner – Generates diverse and challenging image‑based questions.
- Reasoner – Produces high‑quality, verifiable answers to these questions.
This is paired with the GRPO algorithm and custom reward mechanisms that balance question complexity with answer quality.

Reference Links:
- Title: VisPlay: Self‑Evolving Vision‑Language Models from Images
- Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.15661
- GitHub: https://github.com/bruno686/VisPlay
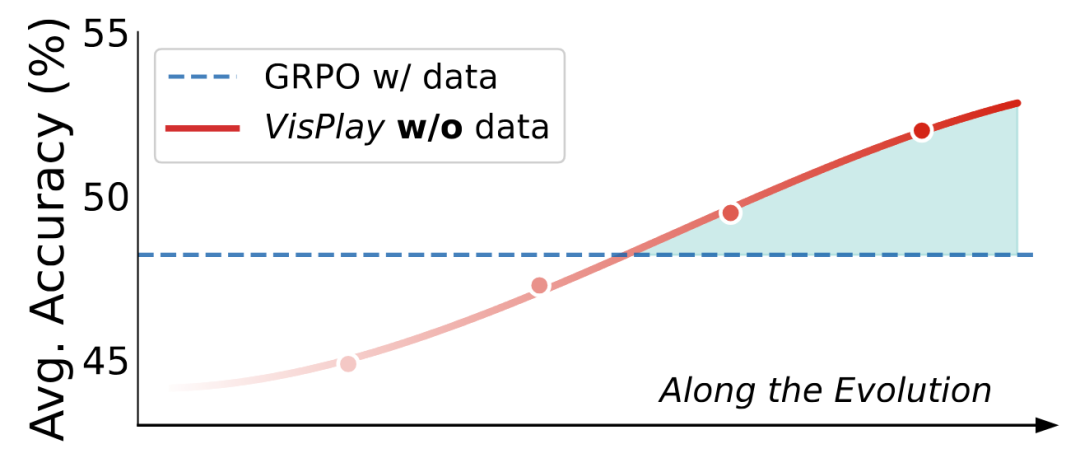
Key Outcome: VisPlay delivers sustained improvements in leading models like Qwen2.5‑VL and MiMo‑VL, excelling in visual reasoning, compositional generalization, and hallucination reduction — all at low cost and with scalability in mind.
---
Introduction: Tackling the Data Bottleneck
The “Data Dilemma” in VLM Reasoning
While VLMs have advanced significantly in perception tasks, progress is slower in complex visual reasoning. Mainstream methods — like SFT or RL — rely heavily on high‑quality labeled data.
- Supervised Fine‑Tuning (SFT): Needs costly, large‑scale annotation.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): Requires precise reward signals, often tied to intensive human labeling or task‑specific rules.
As models scale, annotation costs and time constraints hinder development, making self‑evolving learning strategies an attractive solution.
---
VisPlay Framework
Overview
A collaboration between University of Illinois Urbana‑Champaign, Washington University in St. Louis, University of Maryland, and National University of Singapore introduced VisPlay, enabling VLMs to self‑train from unlabeled images.
---
Components
1. Image‑Conditioned Questioner
- Generates challenging yet answerable questions.
- Uses two novel rewards:
- Difficulty Reward: Promotes deeper reasoning complexity.
- Diversity Reward: Ensures variety in Q&A, preventing narrow focus and improving generalization.
Outcome: Reduces redundancy, improves question quality, and fosters capability growth.
---
2. Multimodal Reasoner
- Produces “Silver Responses” — pseudo‑labeled answers — to the Questioner’s queries.
- Uses answer accuracy as a training signal to refine reasoning ability.
---
Experimental Results
Benchmarks
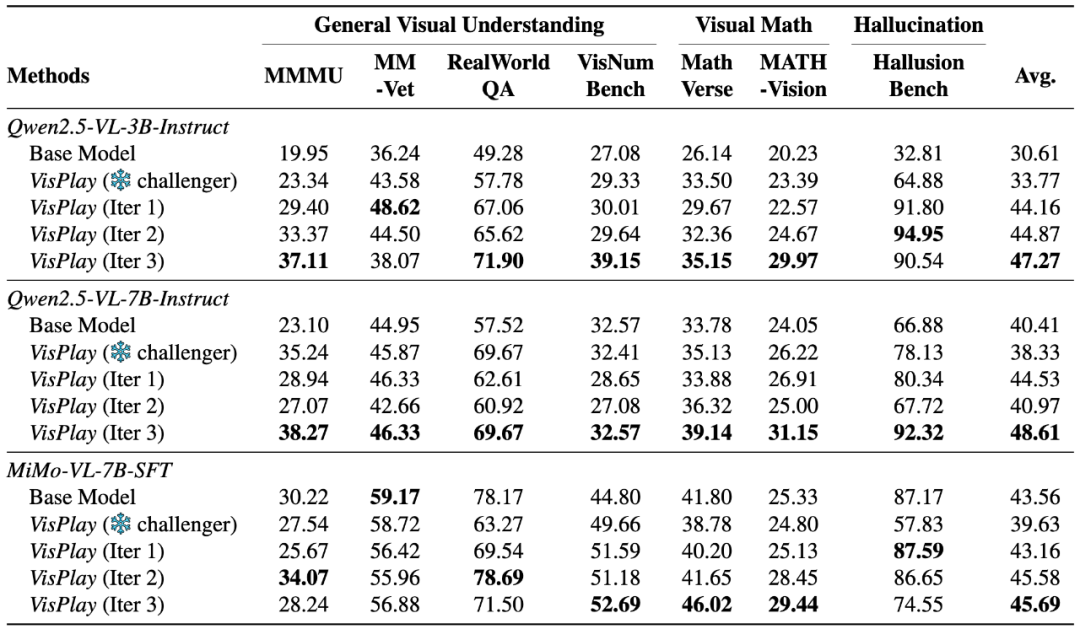
VisPlay was evaluated across eight major datasets including:
- General Visual Understanding: MM‑Vet
- Cross‑Modal Reasoning: MMMU
- Visual Mathematical Reasoning: MathVerse
- Hallucination Detection: HallusionBench
---
Findings
1. Stable, Continuous Improvement
- Demonstrated consistent accuracy gains across all tested models and datasets.
2. Strong Compositional Generalization
- Handled complex, unseen reasoning combinations with robustness.
3. Effective Hallucination Suppression
- Self‑evolved Q&A pairs improved detection and correction of incorrect associations, reducing hallucination rates.
---
Conclusion:
VisPlay proves self‑evolution from vast, unstructured images is feasible for enhancing VLM reasoning — paving the way for autonomous, multimodal AI systems.

---
Broader Context
Beyond AI research, platforms like AiToEarn官网 are applying autonomous generation principles to content creation. They enable:
- Cross‑platform publishing (Douyin, Bilibili, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, X)
- Integrated analytics and model ranking (AI模型排名)
- Monetization of AI‑generated work efficiently and at scale.
---



