What Does a Tweet Look Like Structure and Examples
Learn the structure, key elements, and examples of tweets on X, plus tips on formatting, visuals, and interaction to boost engagement.
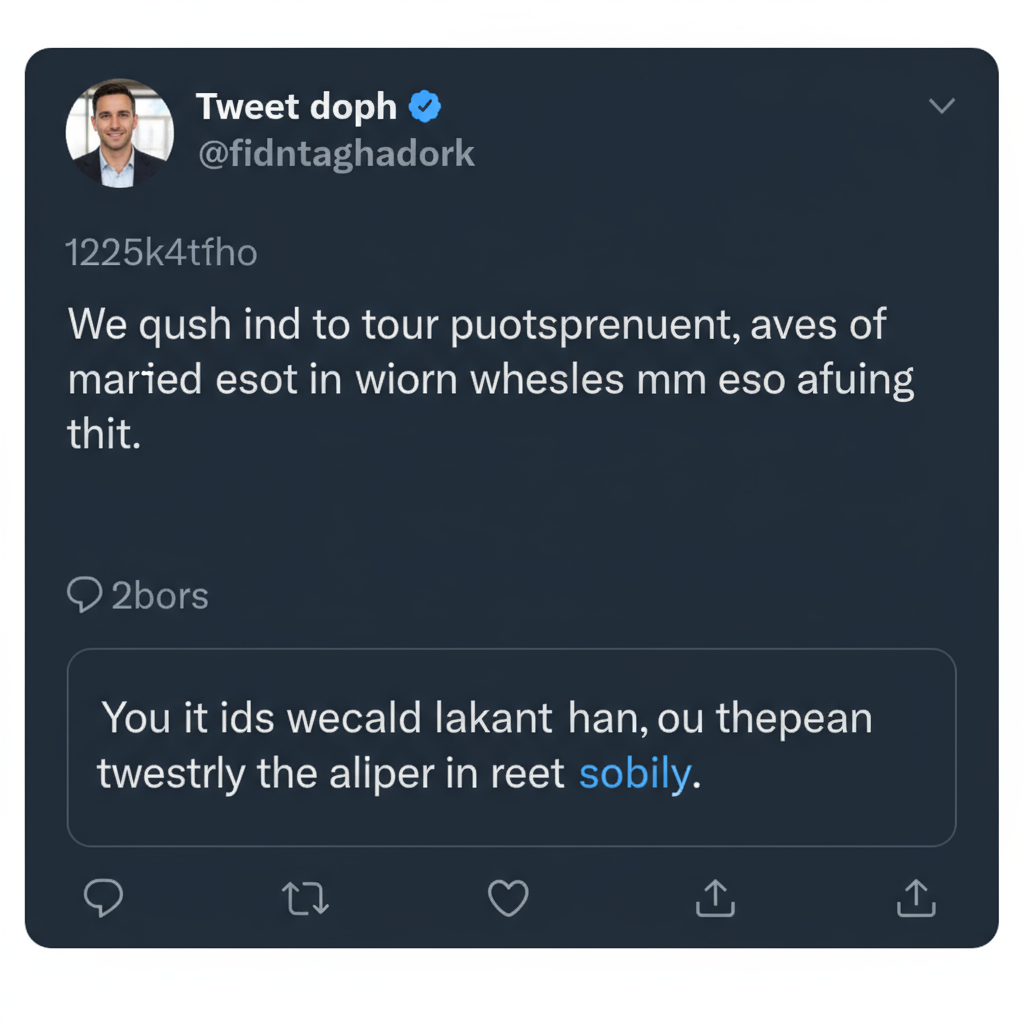
Introduction to Twitter/X and What a Tweet Looks Like
Twitter, recently rebranded as X, is one of the most influential social media platforms, enabling users to share bite-sized updates called tweets. These posts can blend text, images, videos, and interactive elements, making them a powerful vehicle for real-time conversations.
If you’ve ever wondered what does a tweet look like, this guide will walk you through its structure, visual features, interaction tools, and formatting tips, helping you identify and create effective tweets.
---
Basic Anatomy of a Tweet
A tweet’s structure is consistent across devices, so users can quickly scan and interact with content. Common components include:
- Profile Picture – Small, circular avatar identifying the user.
- Handle and Display Name – The handle starts with `@` and uniquely identifies the account; the display name is user-selected.
- Timestamp – Indicates when the tweet was posted.
- Tweet Text – The main body; may include hashtags, mentions, emojis, and hyperlinks.
- Action Icons – Reply, Retweet, Like, and Share icons beneath the text.
This uniform layout supports quick recognition and enhances the platform’s fast-paced communication style.
---
Character Limit and Content Display
When Twitter launched, users were restricted to 140 characters; in 2017, the limit expanded to 280 characters for most languages.
Today, X also offers subscribers long-form tweets of up to 4,000 characters. In standard timelines, posts beyond 280 characters display a “Show more” link.
Tips for working within the limit:
- Keep sentences concise and impactful.
- Use line breaks for readability.
- Place your most important information first.
---
Visual Elements Within Tweets
Including visual media in tweets greatly improves engagement. Common options:
- Images – Single or multi-image layouts (up to 4 images per tweet).
- GIFs – Looping, low-size animations.
- Videos – Include a preview thumbnail with a play button overlay.
- Polls – Allow followers to vote directly.
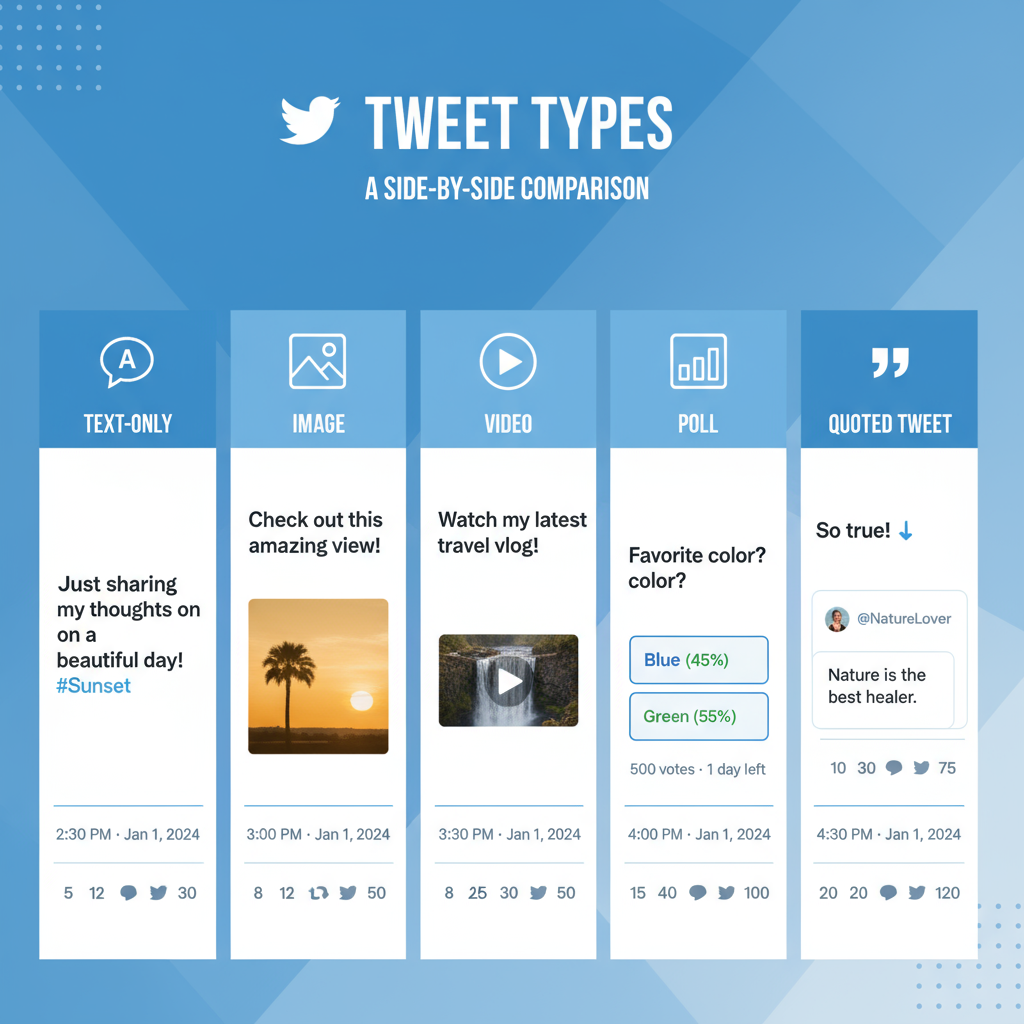
Image layout examples:
- One image spans the tweet’s width.
- Two images display side-by-side.
- Three or four images use grid formats for variety.
Polls appear in place of media, featuring voting buttons and time limits.
---
Interaction Tools
Beneath each tweet, you’ll find engagement icons:
- Reply – Leave a public comment or join a conversation.
- Retweet – Share the tweet with followers; can be plain or with your own comment (Quote Tweet).
- Like – Represented by a heart icon, showing approval.
- Share – Copy the tweet’s link, bookmark it, or send via direct message.
These tools transform tweets from static messages into interactive, viral content.
---
Formatting Tips for Clarity and Engagement
To optimise your tweet’s look and performance:
- Use whitespace for easy scanning.
- Add emojis to convey tone or highlight points.
- Include hashtags to boost discoverability.
- Mention relevant accounts to increase visibility and interaction.
- Add a call-to-action (CTA) to drive clicks, replies, or retweets.
Example:
🔥 Big news!
Our app just launched 🚀
Check it out: example.com/app
#TechLaunch #Startup---
Examples of Tweet Types
Understanding various tweet formats makes it easier to create tailored posts.
| Tweet Type | Description | Example Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Text-only | Contains only text—no media or links. | "Good morning everyone! 🌞 #PositiveVibes" |
| Media Tweet | Includes one or more images, a GIF, or a video. | Text caption + attached media. |
| Thread | A series of connected tweets by the same author. | Main tweet + replies from the same account to continue text. |
| Quote Tweet | Shares another tweet with your commentary above it. | Your comment above the embedded tweet. |
---
Accessibility Features
X includes features to make tweets usable for a wider audience:
- Alt text for images – Describes visuals for screen readers.
- Captions for videos – Helps hearing-impaired users.
- High contrast mode – Improves visibility for visually impaired users.
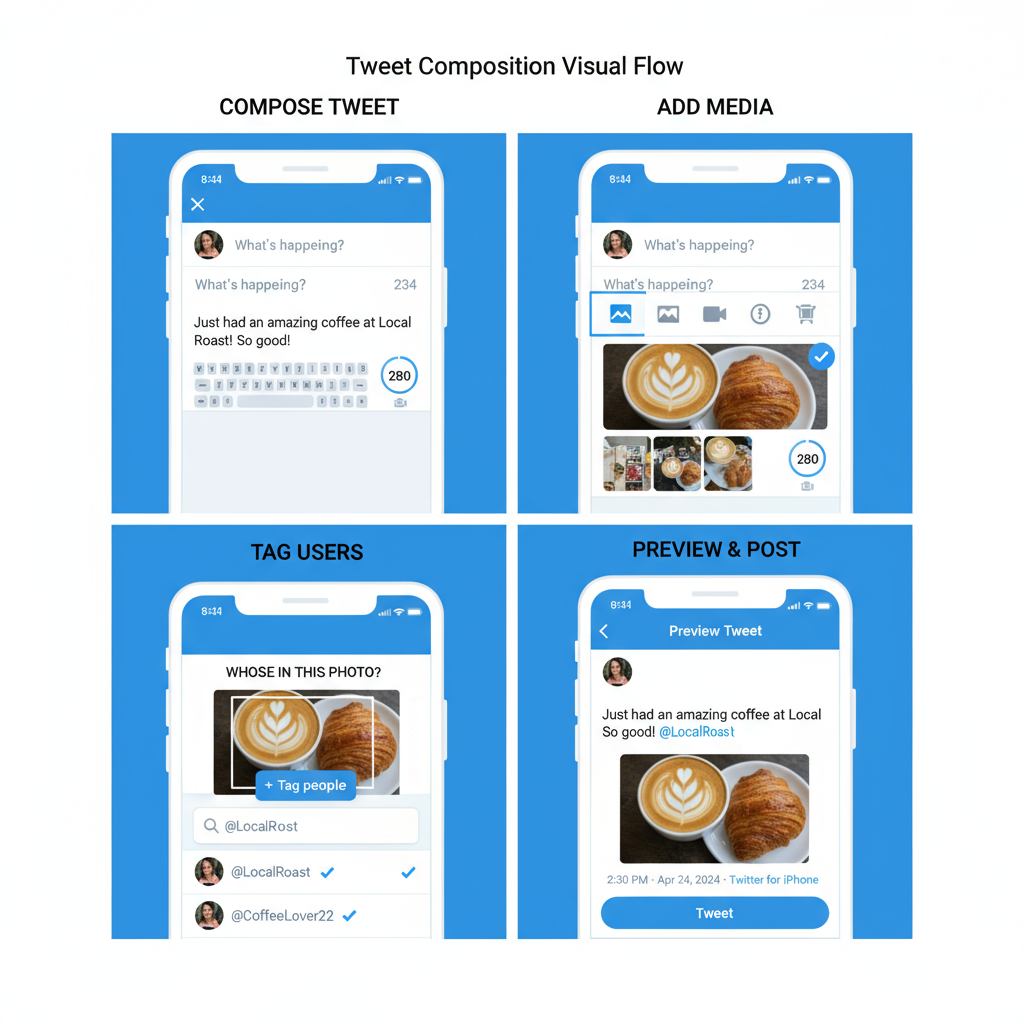
Adding alt text is simple: when uploading media, click “Add description” and write a short, clear depiction of the image content.
---
Tweets in Timelines vs. Direct Links
The context influences how tweets are displayed:
- In Timelines – Compact preview, possible text truncation, mixed with other content.
- In Direct Links – Full presentation, expanded media, and replies underneath.
Direct links also show detailed engagement stats and conversational context.
---
Mobile vs. Desktop Layout Differences
While tweet structure is the same, device variations affect presentation:
- Mobile – Vertical, narrower media display; actions via tap menus.
- Desktop – Wider media display; hover actions; can view multiple columns.
Some features, such as tweet editing (for Premium users), may have interface differences between devices.
---
Best Practices for Visually Appealing Tweets
Boost the impact of your tweets by following these guidelines:
- Select high-quality, relevant visuals.
- Balance text and imagery so neither overwhelms the other.
- Maintain a consistent brand voice to strengthen identity.
- Post at peak engagement times by analysing audience activity.
- Engage quickly to sustain audience interest.
---
Summary and Next Steps
You now know exactly what a tweet looks like—from its core elements and character limits to visual formats, accessibility options, and best posting practices. Think of a tweet as more than just text; it’s a crafted piece of microcontent designed to inform, entertain, and spark conversation.
Experiment with different formats, visuals, and timing to see what resonates with your followers. Open your X timeline today and start creating tweets that capture attention and inspire engagement.


