What Does Media Upload Mean in Digital Platforms
Learn what media upload means on digital platforms, including file types, technical steps, size limits, and best practices for efficient transfers.
Understanding Media Upload in Digital Platforms
In today’s connected world, the term media upload is central to how we share, store, and distribute content online. Whether it’s posting a photo on Instagram, adding a video to YouTube, or uploading documents to a corporate intranet, media uploading is the backbone of digital content exchange. This guide explores what does media upload mean, the types of media, technical processes, best practices, platform-specific methods, and emerging trends to help you manage uploads efficiently and effectively.
In simple terms, media upload refers to the process of transferring multimedia files — such as images, videos, audio, and documents — from a local device (computer, smartphone, tablet) to an online platform or server for viewing, sharing, or processing.
---
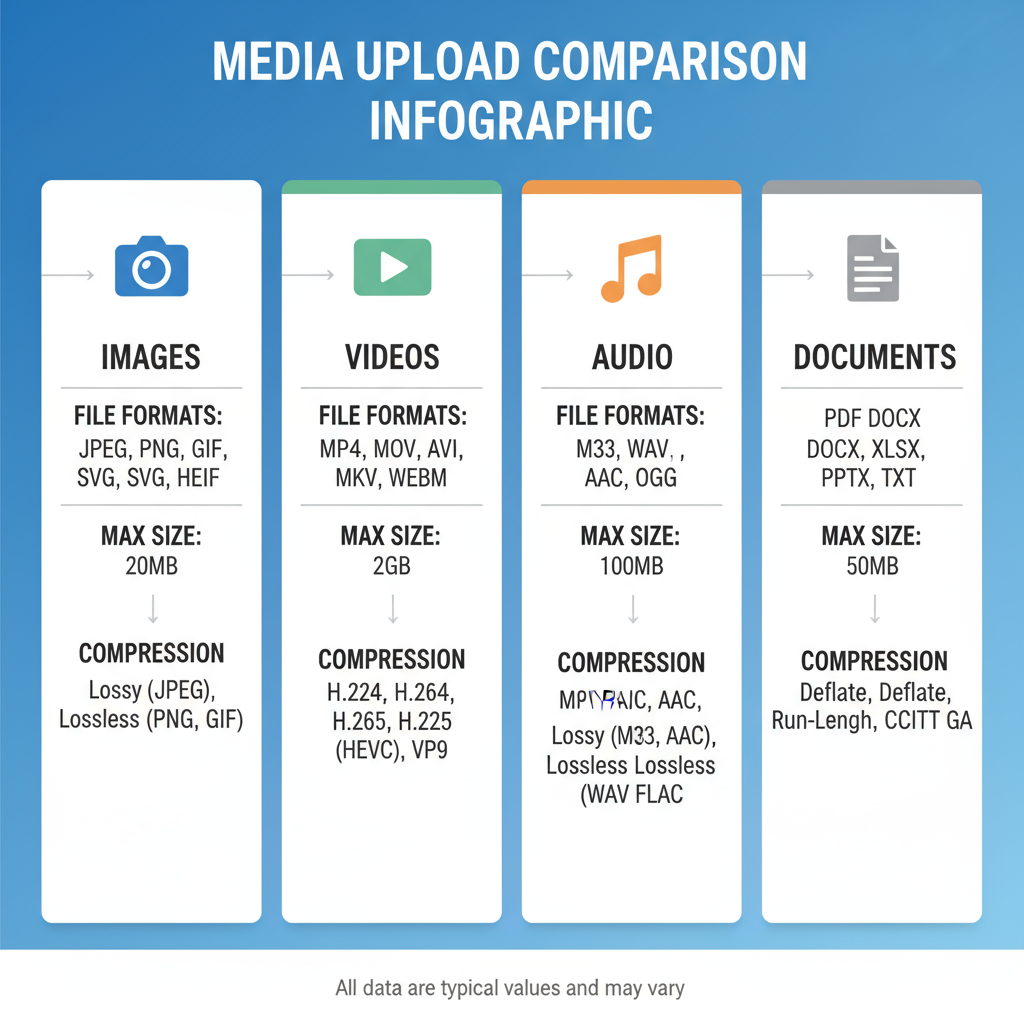
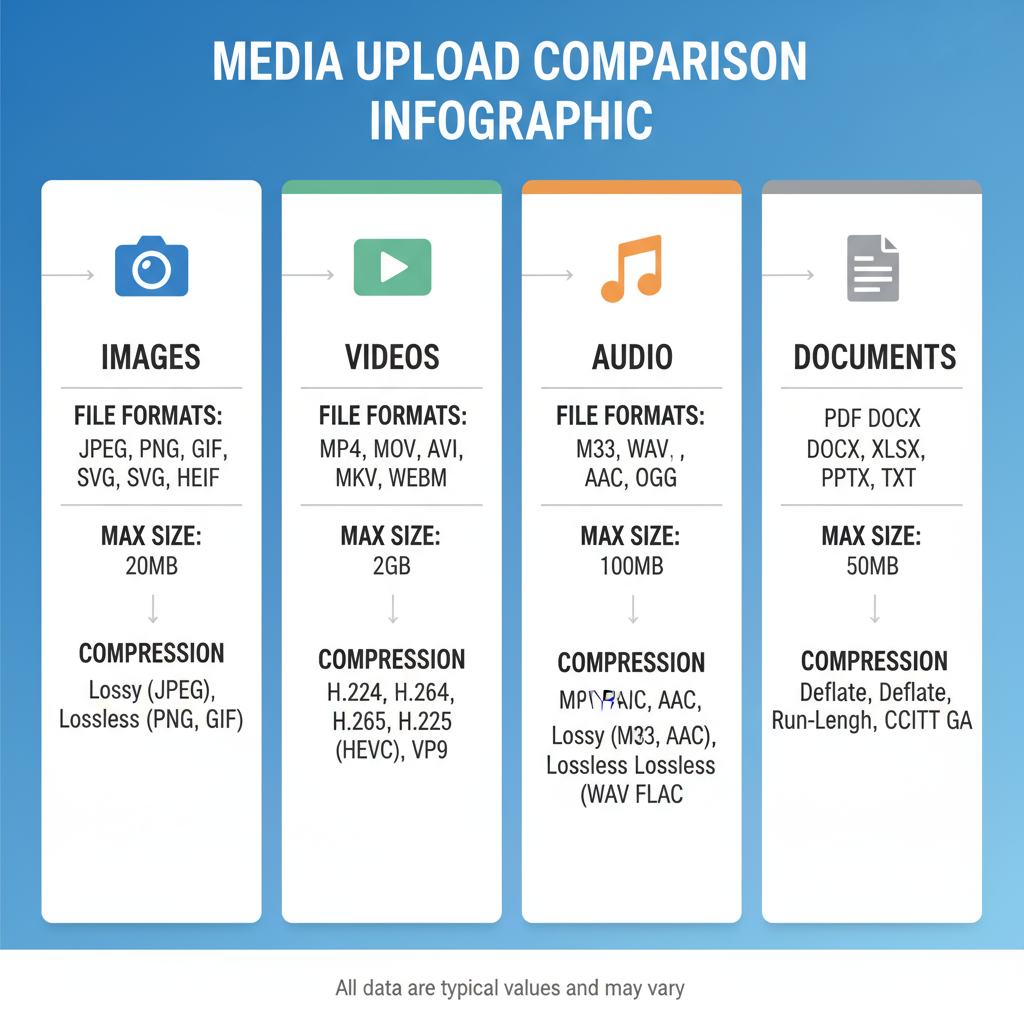
Common Types of Media for Upload
Every platform supports different media types. Understanding these will help you choose the right file when you need to upload:
- Images – JPEG, PNG, GIF, and increasingly WebP formats.
- Videos – MP4, MOV, AVI, and web-friendly formats like WebM.
- Audio – MP3, WAV, AAC.
- Documents – PDF, DOCX, XLSX, and text files.
| Media Type | Common Formats | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Image | JPEG, PNG, WebP | Profiles, galleries, marketing projects |
| Video | MP4, MOV, WebM | Tutorials, entertainment, product demos |
| Audio | MP3, WAV | Podcasts, music streaming |
| Document | PDF, DOCX | Reports, manuals, presentations |
---
The Technical Process Behind Uploading
At the core of every upload is a transfer operation from your local device to a remote server or cloud storage.
Step-by-Step:
- Selection – User chooses a file from the device.
- Initiation – Platform’s upload function begins transfer.
- Encoding/Processing – File may be encoded or compressed for speed.
- Transmission – Sent over HTTPS or other secure protocol to the server.
- Storage – Server saves the file in a directory or database.
- Confirmation – Platform reports upload success.
Example of a basic HTML upload form:
Upload
---
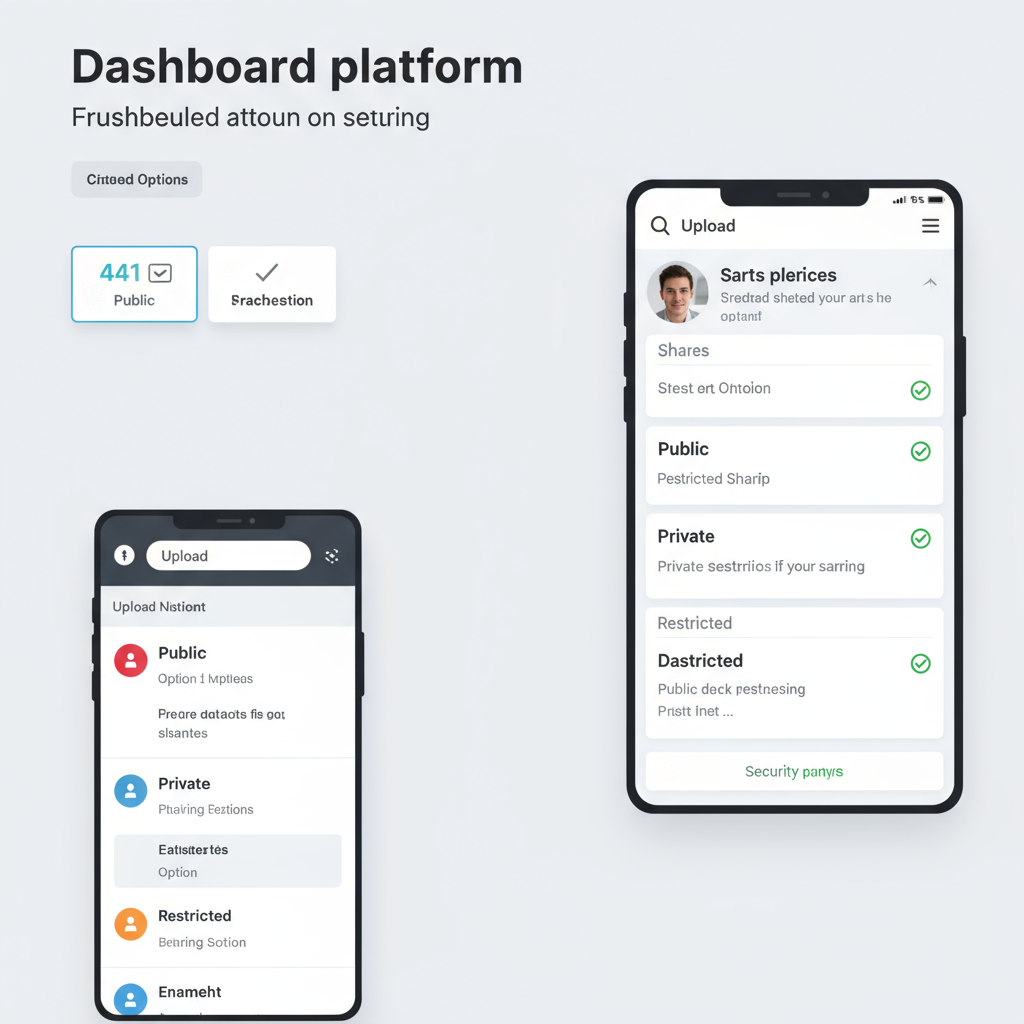
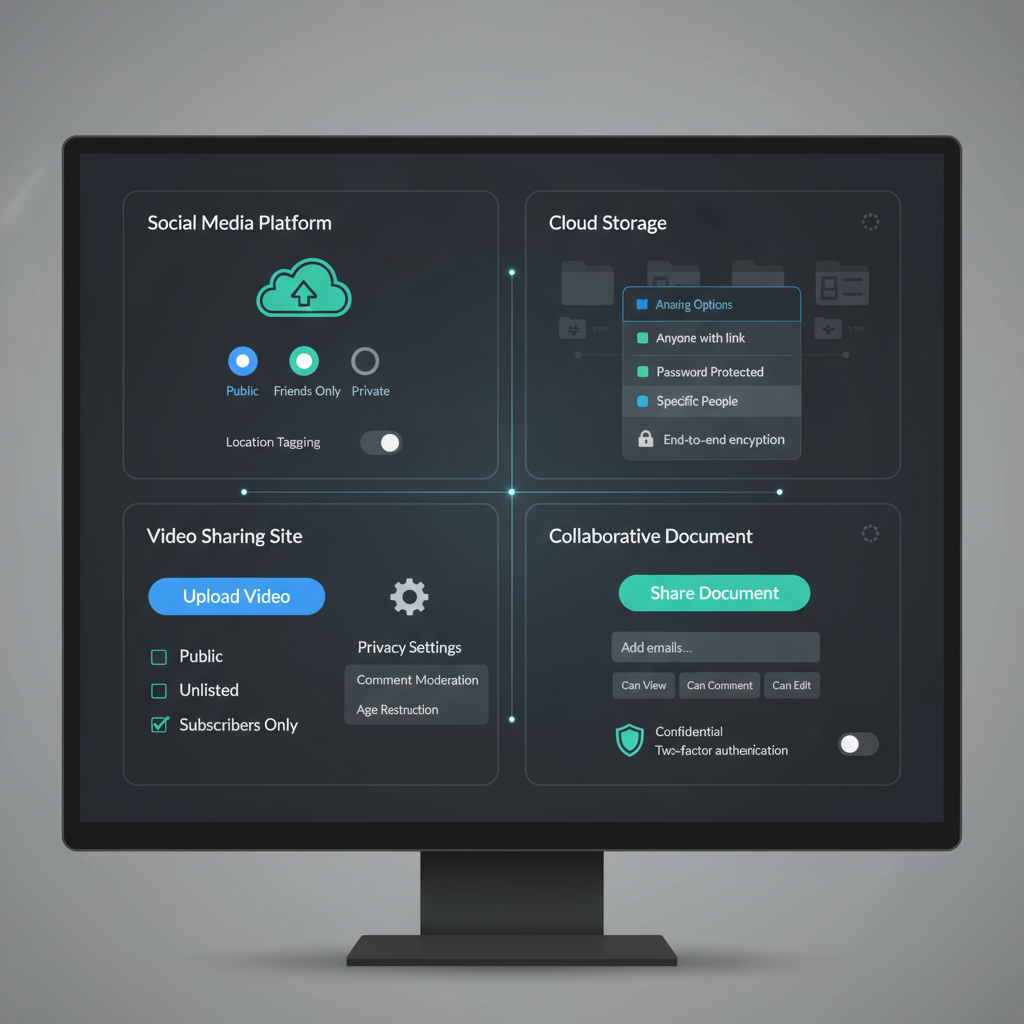
Public, Private, and Restricted Uploads
Different platforms handle accessibility in distinct ways:
- Public Uploads – Anyone can view, share, or download.
- Private Uploads – Only the uploader can view; may require authentication.
- Restricted Uploads – Available to specific authorized users or groups.
These distinctions matter for security, privacy, and user engagement, especially in professional and business environments.
---
File Formats, Size Limits, and Compression Standards
Platforms often impose size limits to manage storage costs and performance. Typical constraints:
- Images: 5–10 MB
- Videos: 1–5 GB
- Audio: 100 MB
- Documents: 100 MB
Compression tools such as JPEG compression for images or H.264 for videos are standard to reduce file size without noticeably compromising quality.
Some systems also transcode formats upon upload, e.g., converting a MOV file to MP4 for compatibility.
---
Common Platforms and Their Upload Mechanisms
Different platforms handle uploads in unique ways:
| Platform | Upload Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media (Instagram, Facebook) | Mobile app & web interface | Instant previews, auto-compression |
| CMS (WordPress, Drupal) | Admin dashboard uploader | Integrates media library management |
| File-Sharing (Google Drive, Dropbox) | Drag-and-drop, sync apps | Version control, permission settings |
| Video Platforms (YouTube, Vimeo) | Web upload, API | Automated transcoding & streaming optimization |
---
Security and Privacy Considerations
Uploading media isn’t just a technical process — security is paramount.
- Encryption – Use HTTPS to secure data during transfer.
- Access Control – Define permissions for who can view/download the content.
- Data Retention – Be aware of platform policies and data expiration timelines.
- Malware Scanning – Protect systems by scanning uploaded files for malicious content.
---
Troubleshooting Failed or Slow Uploads
Understanding why uploads fail or slow down helps maintain productivity:
- Check Internet Connectivity – Slow or unstable connections hinder uploads.
- File Size – Reduce file size or split content into smaller segments.
- Browser/Device Issues – Clear cache, try a different browser or device.
- Platform Limits – Verify your account status allows uploads and meets platform criteria.
- Try Alternative Methods – Use dedicated upload apps, APIs, or command-line utilities.
---
Best Practices for Optimizing Media for Uploads
Optimizing media before upload ensures better performance, compatibility, and accessibility:
- Naming Conventions – Use clear, descriptive names (e.g., `product_photo_2024.jpg`).
- Metadata – Embed titles, descriptions, and tags for SEO and discovery.
- Resolution & Dimensions – Fit within platform’s ideal specs to avoid distortion.
- Compression – Balance quality and size for user experience.
- Formats – Choose web-friendly formats to ensure broad compatibility.
---
Future Trends in Media Uploading
The future of media uploading is being shaped by technological innovations:
- AI Optimization – Tools that auto-compress, tag, and categorize uploads intelligently.
- Instant Sharing – 5G and faster networks enable near-instant uploads globally.
- Decentralized Storage – Blockchain-based and IPFS systems for distributed file hosting.
- Edge Processing – Handling compression and encoding on the user’s device before transfer to minimize bandwidth consumption.
---
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
If you’ve ever wondered what does media upload mean, now you know it’s much more than just clicking “upload.” It’s a coordinated process that involves knowing your media type, understanding the platform’s mechanism, applying best practices for optimization, and safeguarding privacy.
By mastering media uploads, individuals and businesses can share content faster, safer, and smarter — keeping audiences engaged and information accessible in the fast-paced digital environment.
Ready to improve your upload workflow? Apply these tips now to optimize speed, security, and reach for your media.