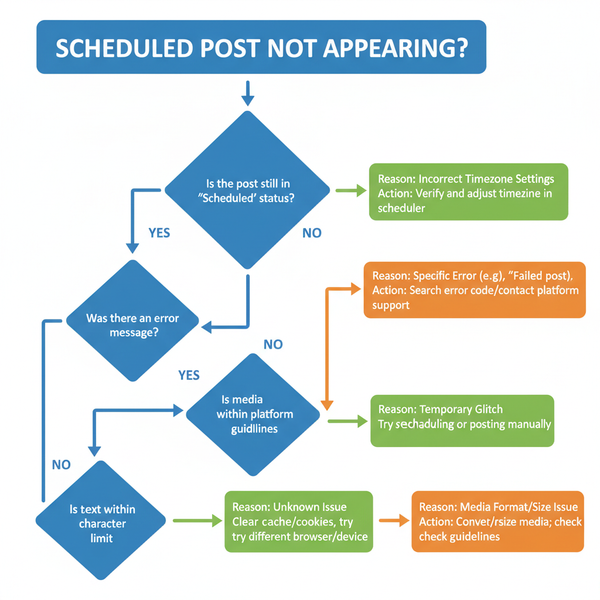
What Does UTM Mean in Marketing and How to Use Parameters
Learn what UTM parameters mean in marketing, how they work with analytics, and best practices for consistent campaign tracking across channels.

Introduction to UTM Parameters in Marketing
If you have ever wondered "What does UTM mean in marketing?", you are not alone. UTM parameters are a fundamental tracking tool in digital marketing, empowering teams to accurately measure the impact of campaigns across multiple channels. By adding small but powerful tags to your URLs, you can uncover exactly where your traffic originates and how visitors engage with your content — without relying on guesswork.
UTM tracking plays a vital role in analytics and attribution, letting you pinpoint the specific sources, mediums, and campaigns that drive conversions. This data-driven approach ensures your marketing strategy is firmly grounded in measurable insights.

What Does UTM Mean? A Breakdown of the Acronym
The term UTM stands for Urchin Tracking Module.
It comes from "Urchin," a web analytics package that Google acquired in 2005 — the foundation for Google Analytics. Although the software evolved, the UTM naming convention persisted and is now the industry standard.
These modules are snippets of code appended to URLs to transmit campaign information to analytics platforms.
For example, here’s a URL using UTM parameters:
https://example.com/landing-page?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=spring_saleHow UTM Parameters Work With Analytics
When someone clicks a UTM‑tagged link, your analytics tool reads the embedded parameters and categorizes the traffic accordingly. This allows you to distinguish between:
- Paid social vs organic social visitors
- Email newsletter clicks vs transactional email clicks
- Traffic from different ad creatives or campaigns
In Google Analytics, these show up as Source, Medium, and Campaign in the "Acquisition" reports.
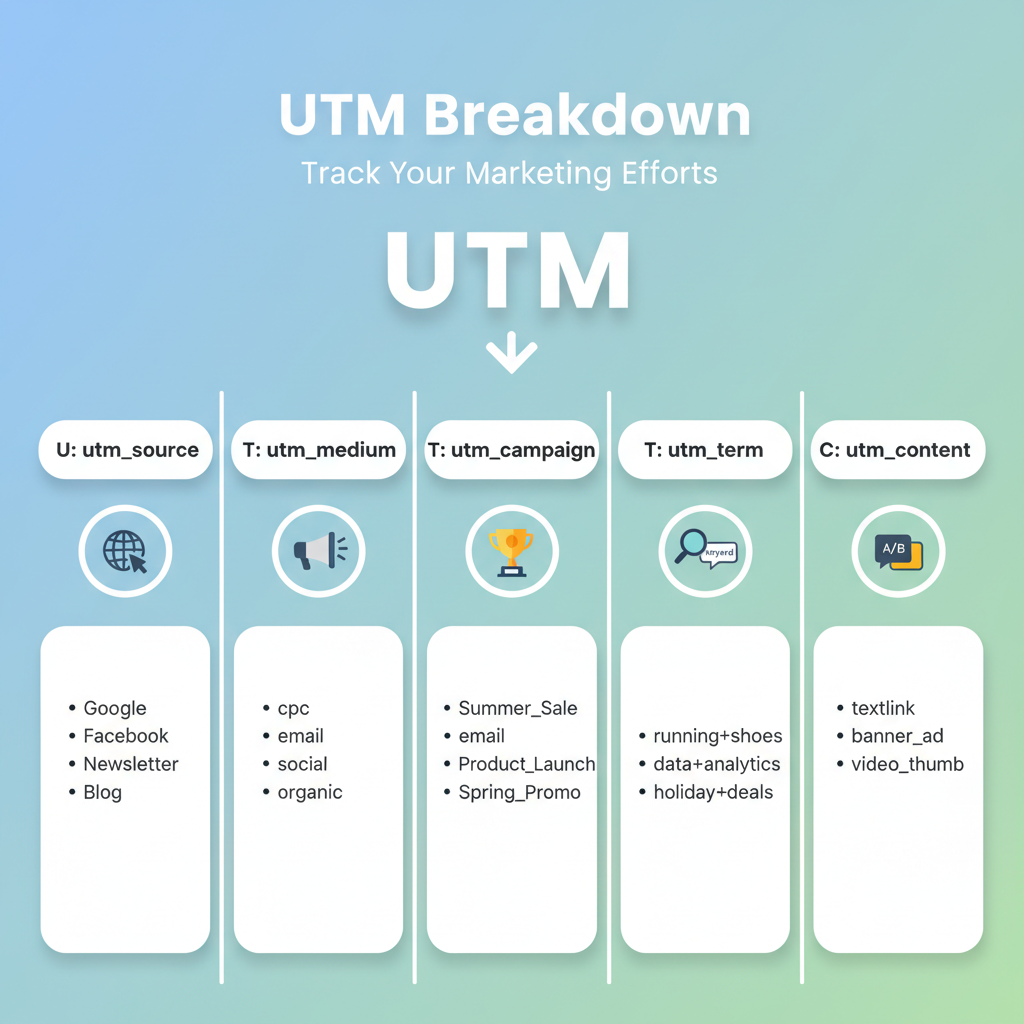
Common UTM Parameters Explained
There are five primary UTM parameters recognized by Google Analytics:
| Parameter | Purpose | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| utm_source | Identifies where the traffic is coming from | facebook, newsletter, google |
| utm_medium | Specifies the marketing channel | cpc, email, social |
| utm_campaign | Names the specific promotion or campaign | spring_sale, launch_event |
| utm_term | Tracks paid search keywords | buy+shoes, seo+services |
| utm_content | Distinguishes between similar links or creatives | banner_ad, text_link |
Creating UTM Codes: Manual vs Free Builders
Manual Creation
UTM parameters can be manually appended to URLs. You start with a `?` after the base URL, then add `parameter=value` pairs separated by `&`.
Example of manual creation:
https://example.com/?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=product_launchUsing Free UTM Builders
Tools like Google’s Campaign URL Builder make the process easier by offering a simple form. Fill in the fields, and it generates a fully tagged URL.

Pros: Saves time, reduces errors
Cons: Requires solid naming conventions for accuracy
Importance of Consistent Naming Conventions
Consistency is critical in UTM tagging. Inconsistent naming — such as `Facebook` in one tag and `FB` in another — fragments your reporting.
Tips for consistency:
- Document a standard naming guide
- Use all lowercase values
- Replace spaces with underscores or hyphens
- Cross-check with your analytics team before campaign launch
Consistent naming keeps your data clean and easily segmentable.
Best Practices for Adding UTMs to Marketing Channels
Different channels require different tagging approaches:
- Social Media: Tag by platform and post type; e.g., `utm_source=instagram&utm_medium=social`.
- Email: Differentiate newsletters from promo blasts; e.g., `utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=weekly_newsletter`.
- Paid Ads: Match UTMs with ad set names for quick comparison.
- Influencer Marketing: Unique UTMs for each influencer to track ROI.
Note: Never tag internal site links with UTMs — this can overwrite session source data and distort analytics.
Analyzing UTM Data to Measure Performance
With UTM tracking in place, review data in your analytics dashboard. Look for:
- Top‑performing channels by conversion rate
- Cost‑per‑acquisition tied to particular mediums
- Engagement metrics by creative (`utm_content`)
Use this intelligence to refine your marketing strategy — cut spending on low‑return campaigns and double down on channels delivering strong ROI.
Good vs Bad UTM Tags
| Good Tag | Why It's Good | Bad Tag | Why It's Bad |
|---|---|---|---|
| utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=black_friday_2024 | Clear, detailed, consistent | utm_source=G&utm_medium=click&utm_campaign=sale | Ambiguous source, inconsistent medium, vague campaign name |
| utm_source=linkedin&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=ebook_launch&utm_content=text_link | Includes all necessary identifiers | utm_source=ln&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=a | Unknown source acronym, unclear campaign name |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overcomplicating Tags: Stick to essential parameters to keep analysis clear
- Not Testing Links: Always verify UTM‑tagged links before publishing
- Mixing Cases: Analytics sees `Email` and `email` as distinct values
Advanced Tips
Using UTM with Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager (GTM) can capture UTM parameters and send them to custom dimensions or pixels, enabling unified tracking across multiple platforms.
Offline‑to‑Online Tracking
Embed UTMs in QR codes on printed materials like flyers or packaging. Scans direct users to tagged URLs, attributing visits to offline sources.
Example:
https://example.com/offers?utm_source=flyer&utm_medium=qr&utm_campaign=store_openingThis technique bridges offline campaigns with online analytics.
Summary and Actionable Checklist
UTM parameters are essential for marketers aiming to track, analyze, and fine‑tune campaigns. Solid implementation delivers clear, accurate data you can trust.
Checklist for Implementing UTM Tagging:
- Learn the five key parameters
- Create a consistent naming convention
- Use reputable UTM builder tools
- Apply UTMs to every external marketing link
- Test tags before launch
- Monitor analytics reports regularly
- Optimize strategy based on results
By adopting systematic UTM tagging, you gain precise visibility into campaign performance — enabling smarter decisions and better ROI.
Start refining your UTM strategy today to unlock deeper insights into your marketing efforts.