Mediaplatform Types, Functions, and Revenue Models
Learn about different types of media platforms, their core functions, and revenue models, from traditional to modern digital ecosystems.

Introduction to Media Platforms
A mediaplatform is any system, service, or technology that enables the creation, distribution, and consumption of content across varying formats and devices. In today’s fast-paced digital era, media platforms have become essential tools for communication, entertainment, marketing, and education. They range from traditional broadcast networks to sophisticated, interactive digital ecosystems that connect billions of people worldwide.
Historically, media platforms operated on a one‑way communication model—television, radio, and print relied on centralized production to distribute materials to largely passive audiences. Driven by digital transformation and high‑speed internet, the concept has evolved into interactive, on-demand, user‑centered experiences that enable real‑time feedback and social interaction.

Modern mediaplatforms are accessible on multiple devices, use complex algorithms to recommend personalized content, and often serve as hubs where communities find, share, and discuss information.
---
Traditional vs. Digital Media Platforms
Traditional
Traditional media platforms include newspapers, magazines, radio stations, and television channels. They use fixed schedules, centralized production, and target the broadest possible demographics. User interaction is minimal and feedback cycles are slow.
Digital
Digital media platforms—streaming services, social media networks, and online news sites—are dynamic and personalized. They enable:
- On-demand consumption at any time
- Algorithm-driven personalization
- Direct engagement via likes, comments, and shares
- Real-time analytics for content optimization
Key Difference: Traditional platforms focus on mass reach, while digital mediaplatforms thrive on data‑driven personalization and user interactivity.
---
Core Types of Media Platforms
Various mediaplatforms fulfill different user needs and business goals. Key categories include:
Social Networks
Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter (X) connect people for sharing short posts, images, videos, and live updates. They foster high community engagement.
Streaming Services
Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify deliver video and audio content over the internet, offering flexibility, diverse libraries, and freedom from schedules.
News Portals
BBC, CNN, and The Guardian curate and distribute global and local news across articles, videos, and live streams.
Content Aggregators
Reddit and Flipboard compile content from multiple sources, allowing users to explore based on interests, trends, or communities.
---
Key Components of Media Platforms
Strong mediaplatforms integrate technological and operational elements for seamless user experiences:
- Content Delivery Infrastructure
- Uses Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and efficient streaming protocols for speed and reliability.
- User Interface (UI)
- Intuitive design enhances navigation, search functionality, and personalized dashboards.
- Algorithms and Recommendation Engines
- Machine learning analyzes user activity to serve relevant and engaging content.
- Monetization Framework
- Enables revenue through ads, subscriptions, or commerce integrations.
- Data Analytics System
- Tracks metrics like view counts, retention, and click‑through rates for informed decision‑making.
---
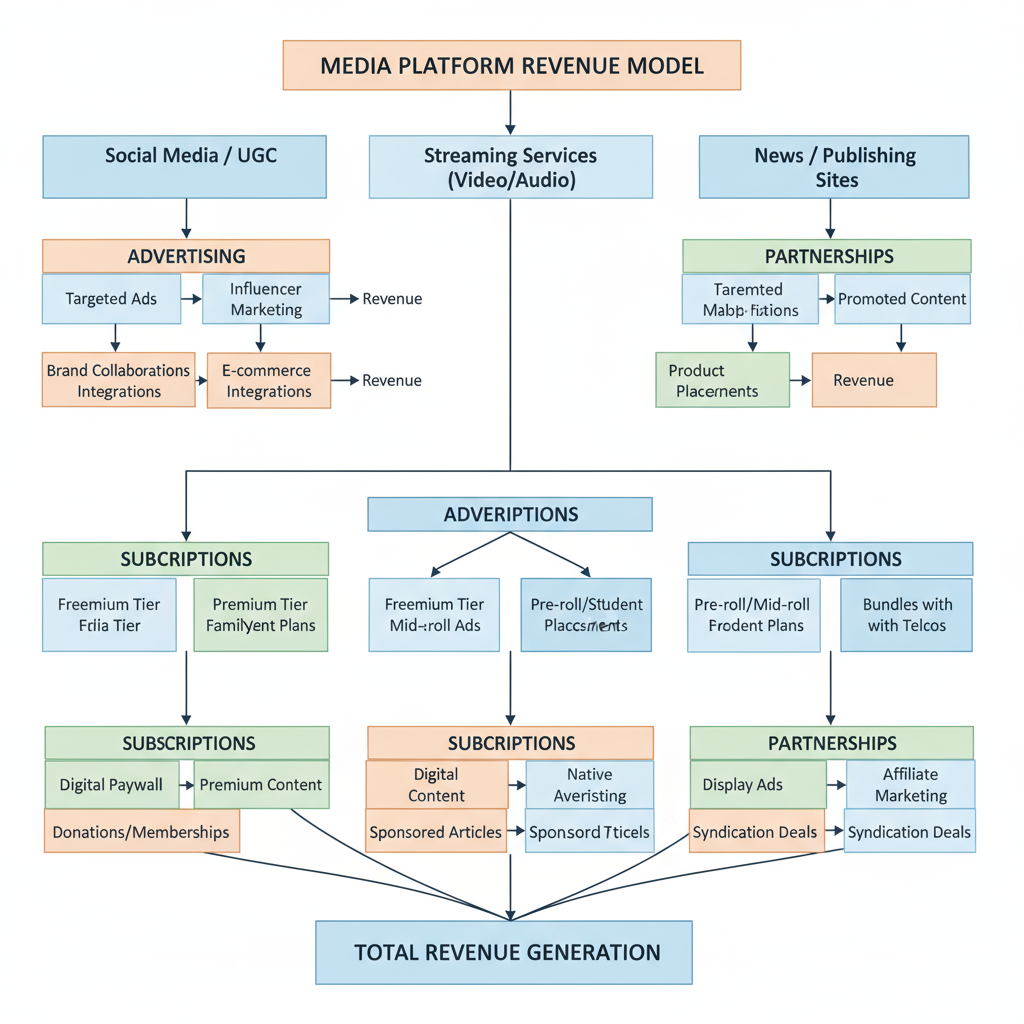
Revenue Models of Media Platforms
Media platforms maintain profitability through a variety of revenue streams:
| Revenue Model | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Advertising | Display, video, or native ads targeted to specific audiences based on demographics and behavior. | Facebook Ads, YouTube Ads |
| Subscriptions | Recurring fees for unlimited access, premium features, or ad‑free experiences. | Netflix, Spotify Premium |
| Pay‑Per‑View | One‑time payment to access exclusive or special content. | Amazon Prime Video Rentals |
| Affiliate & Partnerships | Revenue through collaborative promotions, sponsored content, or affiliate links. | Influencer‑brand deals |
| Freemium | Free basic service with optional premium upgrades or in‑app purchases. | Freemium gaming platforms |
---
User‑Generated Content and Community Building
User‑generated content (UGC)—text posts, videos, images, reviews—offers authenticity and promotes engagement. Advantages include:
- Higher Engagement: Content from peers often outperforms brand‑produced media.
- Authenticity: Builds trust through genuine voices.
- Network Effects: Growing content attracts more users and creators.
TikTok exemplifies a UGC‑driven platform where trends and communities emerge organically.
---
Case Studies of Major Media Platforms
Evolving from a college directory to a multifaceted social tool, Facebook integrates messaging, marketplaces, live streaming, and advertising. Its algorithm prioritizes engagement to drive ad revenue.
YouTube
YouTube combines professional productions with UGC. Monetization stems from ads, Premium subscriptions, and content partnerships.
Netflix
Netflix pioneered large‑scale subscription-based video-on-demand, investing heavily in originals to sustain retention through tailored recommendations.
---
Mobile Optimization and Cross‑Platform Accessibility
With most mediaplatform use happening on mobile devices, optimization is critical:
- Ensure sites and apps are responsive and adaptive.
- Deliver quick load times and leverage features like push notifications.
- Support broad availability on web, mobile, and smart TVs.
- Maintain data synchronization across all user devices.
Tip: Employ a mobile‑first design approach to optimize small‑screen experiences before scaling.
---
Challenges Facing Media Platforms
Key difficulties in the mediaplatform sector include:
- Misinformation – The fast spread of inaccurate data risks credibility.
- Content Moderation – Balancing open speech and community safety is complex.
- Data Privacy – Regulatory compliance (GDPR, CCPA) is essential in handling user information.
- Platform Saturation – Competition fragments user attention, raising acquisition and retention costs.
---
Best Practices for Businesses Using Media Platforms
Businesses can maximize mediaplatform benefits by:
- Building Consistent Brand Identity – Maintain uniform visuals, tone, and voice.
- Strategic Content Planning – Develop calendars for timely and themed campaigns.
- Active Engagement – Respond promptly to messages, comments, and mentions.
- Leveraging Analytics – Track engagement, reach, and conversions for optimization.
- Testing and Iterating – Use A/B testing for formats, styles, and publishing times.
---
Future Trends in Media Platforms
Emerging trends are set to reshape the mediaplatform landscape:
AI‑Driven Personalization
Advanced AI will deliver hyper‑relevant content and ads, increasing both engagement and revenue.
VR & AR Experiences
Immersive technologies will expand storytelling methods in gaming, training, and interactive media.
Decentralized Networks
Blockchain and Web3 concepts could return control of data and monetization to creators.
Interactive & Shoppable Media
Embedding e‑commerce directly in videos or posts will merge entertainment with instant purchasing.
---
Conclusion
A mediaplatform is more than a distribution channel—it's an interconnected ecosystem combining technology, audience behavior, business models, and community. By understanding mediaplatform types, structures, and monetization methods, businesses and creators can tap into vast opportunities while addressing inherent challenges. As technologies evolve, keeping pace with innovations in personalization, immersive formats, and user engagement will be crucial.
Call to Action: Whether you are a brand, a creator, or an aspiring entrepreneur, start leveraging mediaplatforms today to grow your audience, boost engagement, and stay ahead in the competitive digital marketplace.