Understanding Organic Social in Google Analytics
Learn how Google Analytics tracks organic social traffic, distinguishes it from paid, and uses GA4 features and UTM parameters for accurate insights.
Understanding Organic Social in Google Analytics
Organic social in Google Analytics is a powerful indicator of how well your unpaid social activity drives traffic to your site. If you want to know what is organic social in Google Analytics, how it’s tracked, and how to use those insights to strengthen your marketing strategy, this guide provides the details you need to make data-backed decisions.
---
What is "Organic Social" in Google Analytics?
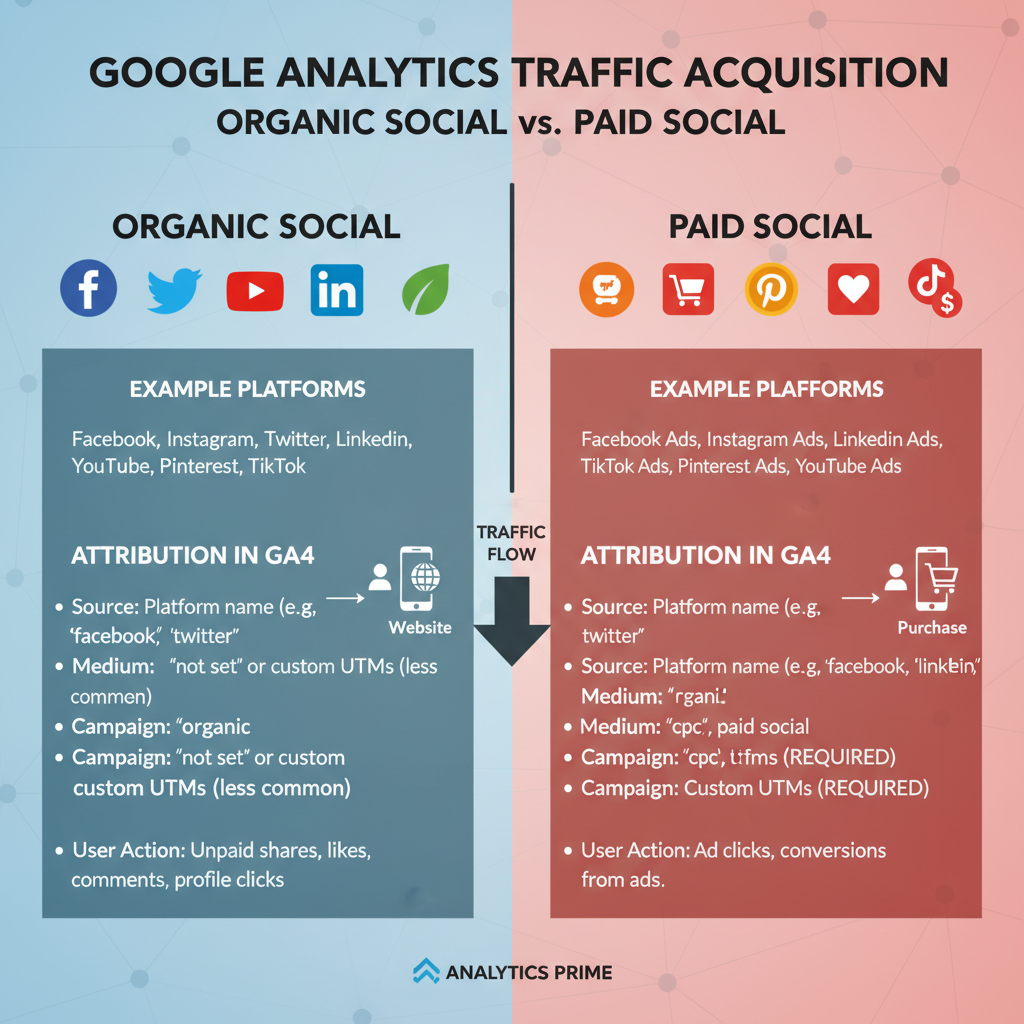
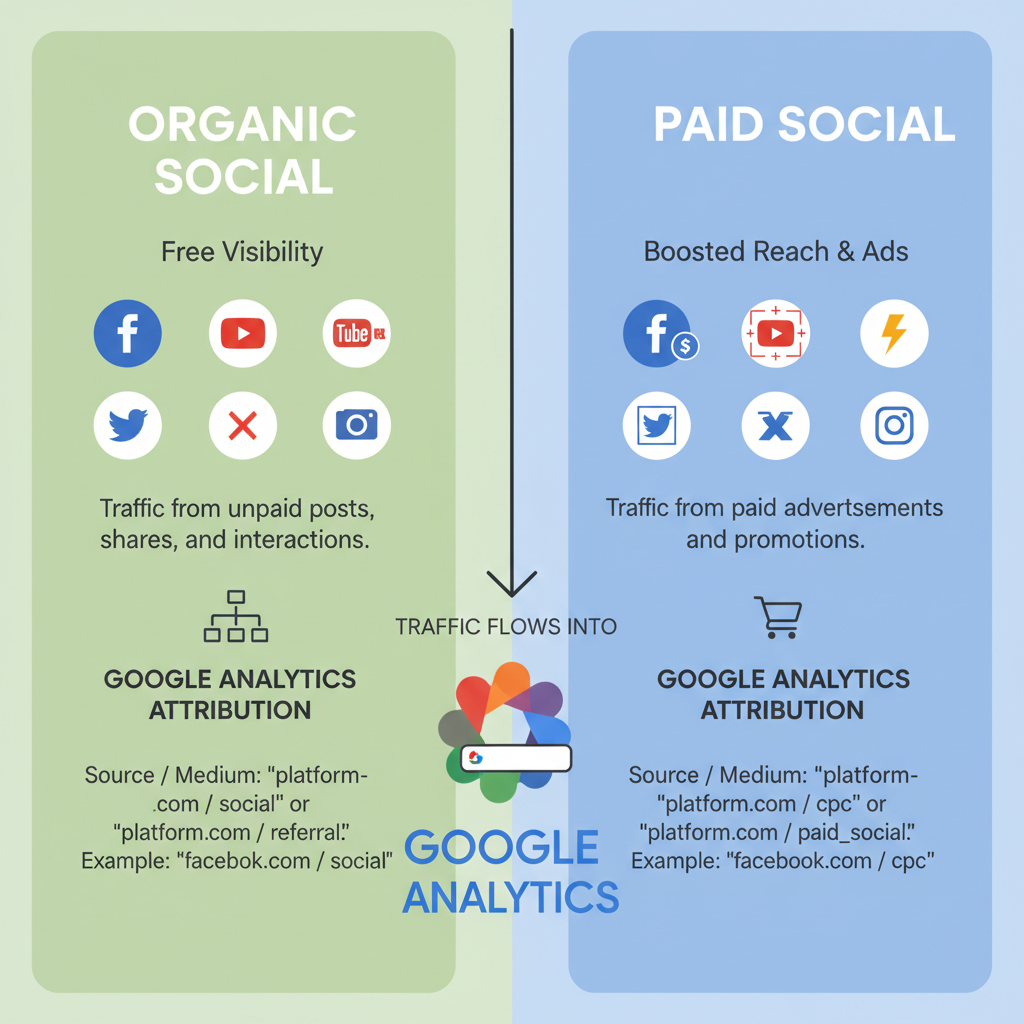
In Google Analytics (GA), organic social refers to traffic generated through unpaid social media activities: posts, shares, likes, comments, follower links, and bio URLs. It completely excludes any clicks from paid advertisements on social platforms.
For example, someone clicking on your business’s tweet link — where you didn’t pay to boost the tweet — counts as organic social traffic.
---
Organic Social vs. Paid Social Traffic
Understanding the distinction between organic and paid traffic is vital:
- Organic social: Generated naturally without any advertising spend.
- Paid social: Comes from sponsored posts, display ads, or promoted listings.
Google Analytics separates these channels to help marketers measure ROI accurately.
| Traffic Type | Source | Cost Involved | Typical Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Social | Unpaid posts on social platforms | No direct ad spend | Twitter link in a profile bio, Facebook post shared by followers |
| Paid Social | Sponsored or promoted social media content | Yes | Facebook Ads campaigns, Instagram sponsored post clicks |
---
How Google Analytics Classifies Channels
GA uses Default Channel Grouping rules to categorize traffic automatically:
- Organic Social:
- Source matches known social domains.
- No paid campaign indicators present.
- Paid Social:
- Identified via UTM parameters (`utm_medium=paid social`) or known ad referral types.
In GA4, you can customize channel groupings far beyond the limitations of Universal Analytics (UA).

---
Examples of Organic Social Sources
Organic social traffic often comes from:
- Facebook (non-boosted posts & shares)
- Twitter (X)
- Instagram (bio links, unpromoted stories)
- YouTube (unsponsored video descriptions)
These sources appear in GA’s Referral and Social reports whenever unpaid links drive clicks.
---
How GA Detects and Categorizes Social Referral Traffic
Google Analytics confirms organic social traffic by:
- Checking if the referring domain is a known social network.
- Ensuring no paid parameters exist (such as `utm_medium` for paid).
- Assigning the traffic to the Organic Social channel.
Universal Analytics uses the Social Network list, while GA4 relies on Channel Group logic.
---
Importance of UTM Parameters for Accurate Attribution
UTM tagging differentiates organic and paid campaigns.
Example:
https://yourwebsite.com/blog-post?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=organic_social&utm_campaign=springlaunchUse:
- `utm_source`: Example — `twitter`, `linkedin`.
- `utm_medium`: `organic_social` or `paid_social`.
- `utm_campaign`: Campaign name.
Without proper tagging, reports may mix up traffic types.
---
GA4 vs. Universal Analytics in Social Reporting
GA4 changes social reporting by:
- Utilizing event-based tracking instead of session-based.
- Adding custom channel grouping options.
- Combining reports into Traffic Acquisition.
- Offering enhanced filtering by medium (`organic`, `paid`).
UA sticks to fixed social domains and session-driven channel grouping.
---
How Organic Social Data Can Inform Marketing Strategy
Analyzing organic social data lets you:
- Identify high-engagement platforms.
- Pinpoint content formats that perform best.
- Focus resources on successful channels.
- Improve audience targeting.
Leveraging this insight maximizes reach without increasing ad spend.
---
Interpreting Organic Social Metrics
Metrics to track for organic social include:
| Metric | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Sessions | Indicates the volume of unpaid social traffic |
| Engagement Rate | Reveals the depth of visitor interaction |
| Conversion Rate | Shows goal completions from organic social visitors |
---
Common Mistakes When Analyzing Organic Social Traffic
Avoid these issues:
- Tagging errors that misclassify paid traffic as organic.
- Ignoring differences in platform engagement styles.
- Looking at organic social data in isolation.
- Missing attribution paths where organic social is an assist channel.
---
Creating Custom Channel Groupings for Precise Tracking
In GA4:
- Go to Admin > Data Settings > Channel Groupings.
- Define rules for `source` or `medium`.
- Separate organic social using:
- Medium contains `organic_social`.
- Source matches your chosen social regex.
In UA, do this via View Settings to refine grouping.
---
Summary: Benefits of Monitoring Organic Social Traffic in Google Analytics
Monitoring organic social traffic in GA helps you understand unpaid social’s performance, align content with high-impact channels, and measure ROI accurately. By mastering classification rules and using precise UTM tags, you gain a clear view of how organic social adds value to your marketing.
Take action: Review your GA4 channel groupings today, ensure UTM parameters are consistent, and start optimizing strategies based on your organic social performance data.