What Is Social Media Accounts? Definition, Types, Uses
Learn what a social media account is, platform types, key uses, and how to create, manage, and secure profiles for personal branding and business growth.
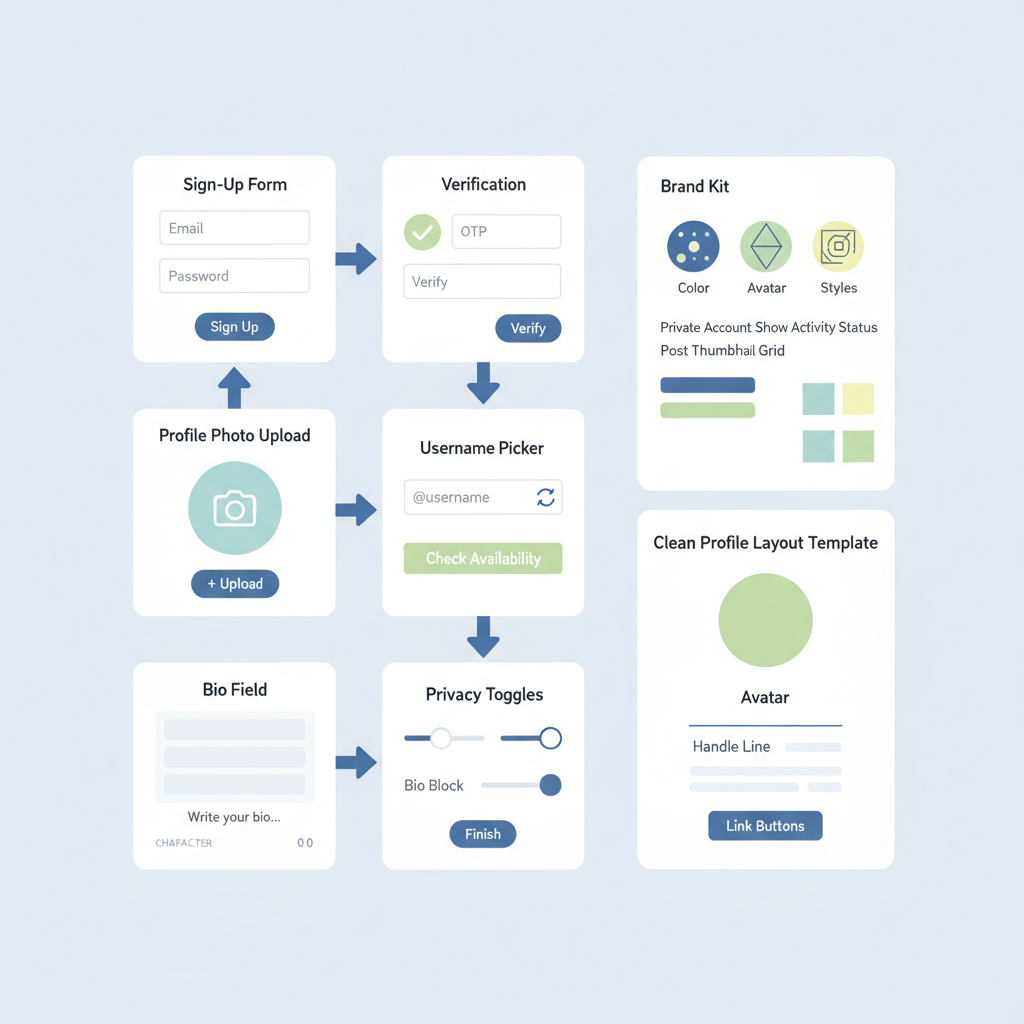
If you’re searching for what is social media accounts, this guide offers a clear definition, practical steps, and best practices to help you build secure, effective profiles for personal branding and business growth.
Introduction to Social Media Accounts
If you’ve ever wondered “what is social media accounts” in practical terms, think of them as your gateway identity on digital platforms where people connect, share, and discover content. A social media account represents a unique profile tied to a user (individual, brand, organization, or community) that enables posting, messaging, following, and participation in platform-specific features. Whether it’s posting photos on Instagram, building thought leadership on LinkedIn, or chatting in communities on Reddit, your account is the foundational unit that carries your presence, permissions, and reputation.
In this guide, you’ll learn what social media accounts are, why they matter, the types available, how to create and manage them effectively, and how to secure them for long-term success. We’ll also explore future trends shaping the way accounts operate, from AI-driven tools to decentralized identity.
Definition of a Social Media Account
A social media account is a registered identity on a social networking platform that grants access to user-specific features, such as creating profiles, posting content, engaging with others, customizing settings, and accessing analytics. It typically includes:
- Credentials: A unique username, email or phone number, and a password.
- Profile: Display name, bio, avatar, cover image, links, and media.
- Permissions: Posting, commenting, messaging, admin rights for pages or groups.
- Connections: Followers, friends, subscriptions, or communities.
- Data: Saved preferences, activity logs, and content history.
It’s helpful to distinguish related terms:
- Account: Your authenticated identity and access to platform features.
- Profile: The public-facing info linked to your account (bio, posts, media).
- Page: A specialized entity for brands, businesses, or public figures (often managed by multiple accounts).
- Handle: The unique public username (e.g., @BrandName) used for mentions and discovery.
If you’re researching “what is social media accounts,” note that platforms differ in policies and capabilities, but the account is always the anchor for identity, content, and interactions.
Purpose and Importance of Social Media Accounts
Social media accounts serve multiple purposes:
- Personal expression: Share life updates, photos, opinions, and hobbies.
- Community participation: Join groups, comment on threads, and direct message friends.
- Professional branding: Demonstrate expertise, network, and find job opportunities.
- Business growth: Reach audiences, run ads, build loyalty, and drive sales.
- Customer support: Offer assistance, answer questions, and manage feedback in real time.
- Research and listening: Monitor trends, sentiment, competitors, and conversations.
Importance stems from their role as a primary digital touchpoint:
- Discoverability: Accounts and handles make you searchable.
- Credibility: Verified profiles and consistent branding build trust.
- Ownership: Control of messaging and content distribution.
- Analytics: Track performance, optimize campaigns, and prove ROI.
- Portability: Cross-link accounts across platforms to diversify reach.
Common Types of Social Media Platforms
Different platforms emphasize distinct modes of interaction. Understanding the platform types helps you decide where to create accounts aligned with your goals.
| Platform Type | Examples | Primary Use | Core Content Format | Typical Account Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Networking | Facebook, LinkedIn | Personal + professional connections | Posts, articles, events | Profiles, pages, groups, messaging |
| Microblogging | X (Twitter), Mastodon | Real-time updates, commentary | Short posts, threads | Handles, lists, spaces, API access |
| Photo/Video Sharing | Instagram, TikTok, Snapchat | Visual storytelling, entertainment | Photos, short videos, stories/reels | Highlights, filters, stickers, music |
| Community/Forum | Reddit, Discord | Topic-based discussion | Threads, channels, long-form posts | Roles, moderation tools, bots |
| Video Platforms | YouTube, Twitch | Long-form video and live streaming | Videos, livestreams, shorts | Channels, subscriptions, monetization |
| Messaging-first | WhatsApp, Telegram | Direct and group communication | Text, voice, media attachments | Contacts, broadcast lists, communities |
Creating and Managing a Social Media Account
Getting started is easy, but strategic setup pays dividends.
Steps to Create
- Choose a platform aligned with your objective (personal networking, brand awareness, customer support).
- Register using email or phone; select a unique username (handle).
- Complete your profile: avatar, cover image, bio, website, location.
- Configure privacy and security settings (two-factor authentication, session alerts).
- Follow relevant accounts and import contacts to seed your network.
- Post an introduction and set content expectations.
Naming and Branding Tips
- Keep handles consistent across platforms for recall (e.g., @AcmeCo).
- Use readable formats: lowercase, hyphens or underscores, avoid ambiguous numbers.
- Include keywords in your bio to improve discoverability.
Example Bio Template
Display Name: Acme Outdoor Gear
Handle: @acmeoutdoors
Bio: Premium hiking and camping gear | Tips, reviews, and trail stories
Link: acmeoutdoors.com
Location: Colorado, USA
Contact: hello@acmeoutdoors.com
Hashtags: #Hiking #Camping #GearTips
Posting Cadence: 3x/week
Tone: Helpful, adventurous, trustworthyContent and Workflow Management
- Use a content calendar to schedule posts and maintain consistency.
- Batch-create visuals and copy to streamline production.
- Employ social management tools for scheduling, engagement, and reporting.
- Establish guidelines for voice/tone, community rules, and escalation paths.
Minimal Content Calendar (YAML)
week: 2025-10-06
platforms:
- instagram
- tiktok
- linkedin
posts:
- date: 2025-10-07
platform: instagram
type: reel
topic: "Fall hiking essentials"
assets: ["reel.mp4", "caption.txt"]
status: scheduled
- date: 2025-10-09
platform: linkedin
type: article
topic: "Sustainable materials in outdoor gear"
assets: ["article.md", "cover.jpg"]
status: draftFeatures and Tools of Social Media Accounts
Accounts gain access to platform-specific features that influence content strategy and engagement:
- Posting formats: Text, images, carousels, stories, reels, shorts, live streams.
- Discovery: Hashtags, trends, keywords, sounds, and recommended feeds.
- Engagement: Likes, comments, shares, mentions, replies, duets/remixes.
- Messaging: DMs, group chats, voice/video calls, communities.
- Organization: Lists, folders, highlights, pinning posts, playlists.
- Commerce: Product tags, storefronts, affiliate links, checkout.
- Analytics: Reach, impressions, engagement rate, follower growth, retention.
- Monetization: Ad revenue, tipping, subscriptions, brand partnerships.
- Admin tools: Role-based access, moderation controls, content approvals.
- Integrations: APIs, link in bio, chatbot plugins, UTM tracking.

To illustrate structured data behind an account, here’s a simplified JSON metadata example:
{
"account_id": "123456789",
"handle": "@acmeoutdoors",
"display_name": "Acme Outdoor Gear",
"verified": false,
"profile": {
"bio": "Premium hiking and camping gear",
"avatar_url": "avatar.jpg",
"links": ["https://acmeoutdoors.com", "https://shop.acmeoutdoors.com"]
},
"settings": {
"privacy": "public",
"two_factor": true,
"session_alerts": true,
"comment_filter": ["spam", "abuse"]
},
"roles": [
{"user": "jane@acme.com", "role": "admin"},
{"user": "sam@acme.com", "role": "editor"}
],
"analytics": {
"followers": 21450,
"avg_engagement_rate": 0.035,
"last_30_days_posts": 12
}
}Personal vs Business Social Media Accounts
Understanding the differences helps you choose the right setup.
Personal Accounts
- Focus: Individual expression, friends and family, personal interests.
- Features: Basic analytics (varies), privacy controls, casual posting.
- Pros: Authenticity, easier to build trust, flexible content.
- Cons: Limited advanced tools, may lack monetization options.
Business Accounts
- Focus: Branding, marketing, customer service, sales.
- Features: Advanced analytics, ads, product tags, role-based access.
- Pros: Professional presence, scalable tools, measurable outcomes.
- Cons: Requires strategy, content resources, and consistent management.
Many platforms allow converting personal to business profiles to unlock features such as insights and ad accounts. If your goal is growth and commerce, start with or switch to business.
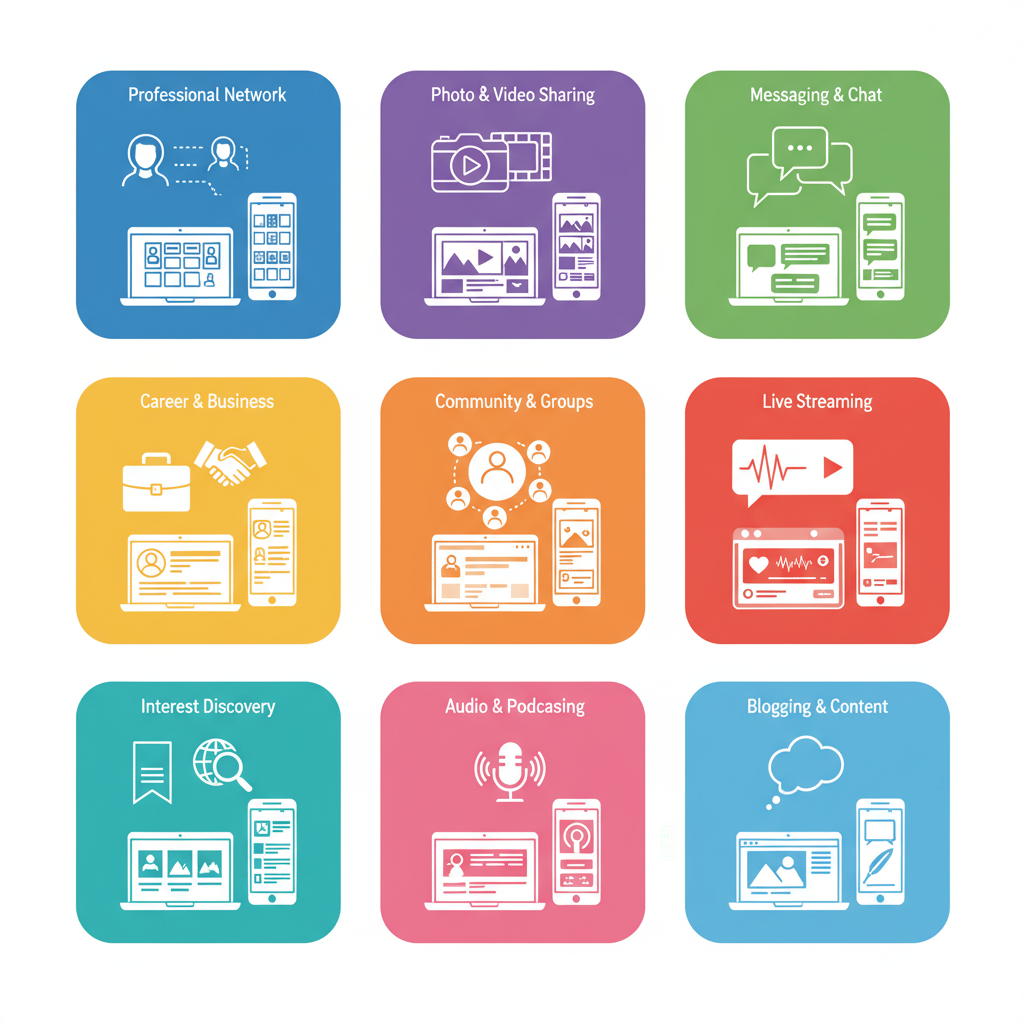
Benefits and Challenges of Using Social Media Accounts
Social media accounts offer powerful benefits, but they also come with responsibilities and risks.
Benefits
- Reach: Access global audiences without gatekeepers.
- Engagement: Two-way communication fosters loyalty and community.
- Speed: Real-time updates, rapid feedback loops, trend participation.
- Data: Analytics inform content strategy and ROI.
- Cost-effectiveness: Organic reach and targeted ads can be budget-friendly.
- Authority: Thought leadership and social proof drive credibility.
- Commerce: Integrated shopping and affiliate tools convert attention to sales.
Challenges
- Algorithm volatility: Changes can reduce reach or shift best practices overnight.
- Content fatigue: Constant creation can strain teams and quality.
- Reputation risk: Public missteps, negative comments, and crises.
- Security threats: Phishing, account takeovers, impersonations.
- Privacy concerns: Data collection and platform policies.
- Fragmentation: Managing multiple accounts across many platforms.
- Compliance: Legal and regulatory obligations for marketing, disclosure, and data.
If you’re exploring “what is social media accounts” from a risk perspective, remember that robust governance and security policies are as important as content strategy.
Best Practices for Account Safety and Privacy
Security and privacy are foundational. Adopt these practices to protect your accounts and your audience.
- Strong passwords: Use a unique, randomly generated passphrase per account.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Prefer app-based or hardware keys over SMS.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Assign least privileges and avoid shared logins.
- Regular audits: Review admins, connected apps, and active sessions monthly.
- Backup codes: Store securely offline for recovery.
- Device hygiene: Keep OS and apps updated, enable disk encryption.
- Phishing awareness: Verify links, domains, and unexpected messages.
- API and integrations: Grant minimal scopes and rotate tokens periodically.
- Privacy settings: Choose appropriate visibility and comment filters.
- Content moderation: Automate spam filtering and document escalation paths.
- Legal compliance: Follow disclosures (e.g., #ad), GDPR/CCPA obligations, and platform policies.
Example of a simple password policy snippet to share with your team:
- Min length: 14 characters
- Composition: Uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols
- No reuse across platforms
- Rotation: When compromise suspected
- Storage: Password manager onlyFuture Trends in Social Media Account Usage
The landscape is evolving quickly. Keep an eye on these trends to future-proof your strategy.
- AI-assisted creation: Generative tools streamline copy, visuals, and captions while suggesting post timing and audience segments.
- Personalization engines: Accounts will see more granular controls over feed curation, allowing better alignment with interests and brand safety.
- Decentralized identity: Federated platforms and protocols (e.g., ActivityPub) enable portable handles and cross-network interactions.
- Interoperability: Unified inboxes and scheduling across platforms reduce fragmentation and improve workflow efficiency.
- Privacy-first design: More options for anonymous or limited profiles, end-to-end encrypted messaging, and transparent data controls.
- Social commerce maturity: Native checkout, shoppable content, and creator storefronts become standard capabilities for business accounts.
- Verified authenticity: Enhanced verification and anti-impersonation tools will protect brand reputation and reduce scams.
- Community-led moderation: Shared governance models and tools to empower trusted members will improve safety and trust.
- Micro-communities: Niche groups and premium subscriber models will favor depth over breadth.
- Algorithm transparency: Greater clarity about ranking signals helps accounts craft content that serves audiences rather than gaming systems.
As these trends converge, understanding “what is social media accounts” expands beyond registration and posting—it encompasses identity portability, safety by design, and intelligent automation that augments human creativity.
Final Thoughts
A social media account is more than a login; it’s a dynamic identity and a strategic asset. By defining your purpose, choosing the right platforms, mastering tools and features, and prioritizing safety, you can build accounts that deliver value—whether for personal expression or business outcomes. Keep iterating with data, stay agile with platform changes, and prepare for a future where accounts are smarter, more secure, and more interoperable than ever.
Summary and Next Steps
Ready to put this into action? Start by auditing your current profiles, updating security settings, and aligning your content plan with clear objectives. If you found this guide helpful, share it with your team and subscribe for more practical tips on social media account strategy and safety.



