Average Photo Size in Pixels and File Formats Explained
Learn the difference between photo dimensions in pixels and file size, common resolutions, compression formats, and pixel requirements for printing.
Understanding Average Photo Size in Pixels and File Formats
When discussing average photo size, it's important to clarify whether we're talking about dimensions in pixels or file size in KB, MB, or GB. This distinction matters for anyone working with digital images—whether it's for web design, printing, or professional photography—because both metrics affect quality, loading speed, and storage.
---
Dimensions vs. File Size
Digital image dimensions specify the number of pixels in width and height.
Example: a portrait image might be 1920 × 1080 pixels.
File size tells you how much disk space the image occupies. That same 1920 × 1080 photo could range from 450 KB with heavy compression to 5 MB with minimal compression.
Key Differences
- Dimensions influence visual quality and how large you can print.
- File size impacts storage requirements, upload/download time, and bandwidth usage.
> Large dimensions don't guarantee a large file size—compression techniques can make big images tiny in KB.
---
Digital vs. Physical Image Sizes
Physical print size is measured in inches or centimeters, while digital dimensions are counted in pixels.
For example:
- An image at 3000 × 2000 pixels prints at 10" × 6.7" at 300 DPI (dots per inch).
- The same file can be displayed on a website at smaller pixel dimensions without affecting printing potential.
---
Common Digital Photo Resolutions
Different devices capture images at different resolutions:
| Device Type | Typical Resolution |
|---|---|
| Smartphones (Entry-Level) | 1920 × 1080 (Full HD) |
| Smartphones (Flagship) | 4000 × 3000 (~12 MP) |
| DSLR Cameras (Mid-Range) | 6000 × 4000 (~24 MP) |
| Mirrorless Professional | 7952 × 5304 (~42 MP) |
---
Image Compression Formats and Impact
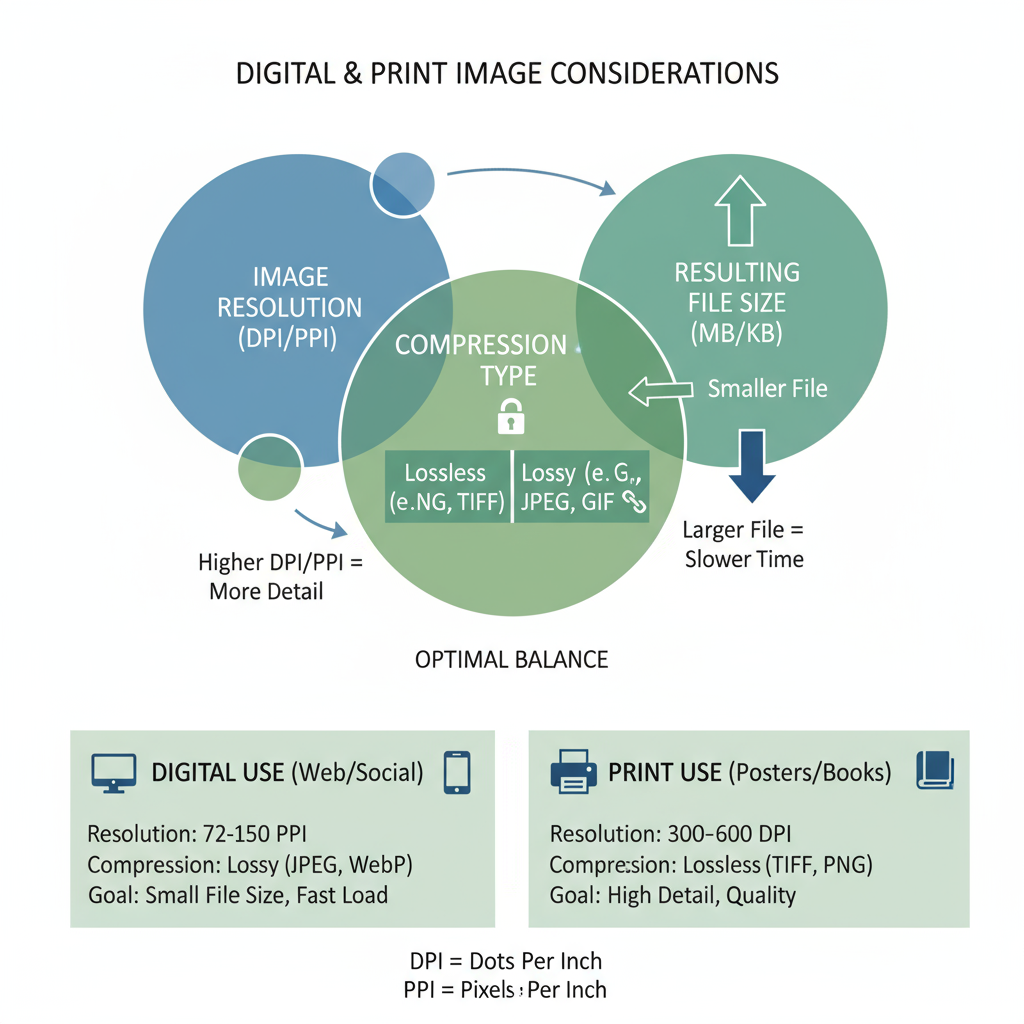
Image formats affect both quality and size:
- JPEG: Lossy compression. Smaller files, slight quality loss—ideal for the web.
- PNG: Lossless compression, transparency support—larger than JPEG.
- RAW: Minimal compression, huge files, maximum detail—perfect for editing.
---
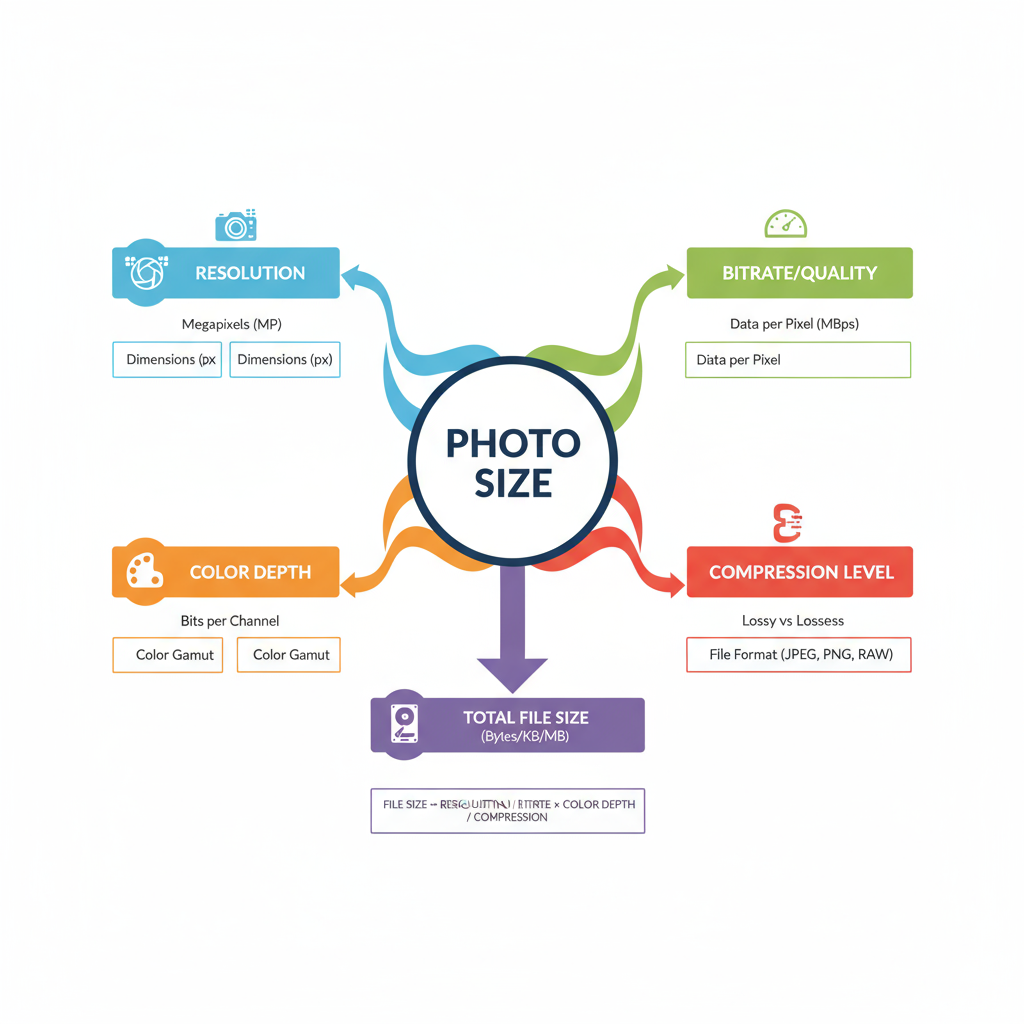
Factors Influencing File Size
Four major factors determine photo size:
- Resolution – More pixels mean bigger files.
- Color Depth – 16-bit images store more data than 8-bit.
- Compression Level – Higher compression reduces size.
- Metadata – Camera info, GPS coordinates, etc.
---
Typical File Sizes by Use Case
| Use Case | Resolution | Format | Average File Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Post | 1080 × 1080 | JPEG | 150 KB – 400 KB |
| Website Banner | 1920 × 600 | JPEG | 200 KB – 500 KB |
| Print (A4) | 2480 × 3508 | JPEG | 2 MB – 5 MB |
| RAW Editing | 6000 × 4000 | RAW | 20 MB – 50 MB |
---
Aspect Ratio and Perceived Size
Aspect ratio determines width-to-height proportions:
- 4:3 – Common in cameras, older monitors.
- 16:9 – Widescreen format, good for video.
- 1:1 – Square composition, popular on Instagram.
Changing aspect ratio can alter perceived image size without changing megapixels.
---
Average Print Sizes and Pixel Equivalents
To print with professional quality, match pixels to the target DPI:
| Print Size (inches) | Resolution Needed @ 300 DPI |
|---|---|
| 4 × 6 | 1200 × 1800 |
| 8 × 10 | 2400 × 3000 |
| A4 | 2480 × 3508 |
| Poster (24 × 36) | 7200 × 10800 |
---
Tips for Optimizing Photo Size
How to balance image quality with efficiency:
- Resize only to the required dimensions.
- Save JPEGs at 80–90% quality for optimal web display.
- Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim for compression.
- Strip metadata before publishing.
- Provide high-DPI (retina) images selectively to avoid excess load.
---
Recommended Resolutions for Popular Platforms
| Platform | Recommended Dimensions |
|---|---|
| Instagram Feed | 1080 × 1080 (square) |
| Facebook Cover Photo | 820 × 312 |
| Blog Featured Image | 1200 × 630 |
| YouTube Thumbnail | 1280 × 720 |
---
Checking and Adjusting Image Size
Tools for resizing and optimizing:
- Adobe Photoshop – Full control over size and format.
- GIMP – Free, open-source alternative.
- Preview (macOS) – Easy resizing and format conversion.
- IrfanView (Windows) – Quick batch resize capability.
- Online editors – Canva, Figma, Pixlr.
Example: Resizing in Python with Pillow
from PIL import Image
## Load image
img = Image.open("photo.jpg")
## Resize to 800x600 pixels
resized = img.resize((800, 600))
## Save as JPEG with specified quality
resized.save("photo_resized.jpg", quality=85)---
Summary and Best Practices
In summary, understanding average photo size means knowing both the pixel dimensions and file size.
Key takeaways:
- Pixels determine resolution, quality, and printable size.
- File size affects speed, storage, and bandwidth.
- Device type, format, and compression settings define end file size.
Best practices for managing photo size:
- Match resolution to intended use—trim excess pixels for the web.
- Use JPEG for general use, PNG for transparency, RAW for high-detail editing.
- Consider aspect ratio in design decisions.
- Test images on final platforms to ensure quality and fast performance.
By mastering these principles, you’ll deliver images that are sharp, efficient, and fit for purpose. Start refining your image workflow today to achieve faster load times and stunning visuals.