---
# **AI’s Impact on Employment: Landscape & Trends**
## **Four Interwoven Effects of AI on the Job Market**
The influence of AI on human professions manifests primarily in **enhancement**, **replacement**, **supplementation**, and **creation**.
Today’s generation of GenAI is in a volatile phase of rapid iteration, with all four effects in play — but at different speeds and scales. This makes AI’s impact on employment **complex and uneven**, particularly in these four areas:
### 1. **Enhancement → Efficiency Gains; Replacement Inevitable**
- AI extends efficiency gains from **physical labor** into **mental labor** more than any prior technology.
- Early adopters gain significant productivity advantages and inevitably replace part of the labor of non‑adopters.
- Goldman Sachs:
- GenAI could raise labor productivity in developed markets (e.g., U.S.) by ~15%.
- Possible short-term rise in unemployment by 0.5 percentage points during transition.
- International Labour Organization:
- 25% of jobs worldwide face GenAI risk
- 34% in high-income countries.
### 2. **Replacement Outpaces Creation in the Short Term (But ≠ Mass Unemployment)**
- Industrial adoption and talent development lag behind AI technical advances.
- Enterprises need time to re‑structure workflows; education needs time to re‑skill workers.
- Current corporate strategy:
- Freeze hiring
- Reassign internal roles
- Reduce outsourcing
- Mitigation path: **Workforce retraining** and transition planning.
### 3. **Supplementation in Labor-Short & High-Risk Jobs**
- AI fills gaps in unpopular, high‑risk, or physically taxing roles — crucial in aging societies (e.g., China).
- Example domains:
- Contact centers, telesales, collections (low-pay, monotony)
- High-altitude work, emergency rescue, and dangerous industrial environments
- **Public services** gain breadth and equity when AI supports education, healthcare.
### 4. **Creation of Fully New Roles Is Slow**
- Currently, the main change is **existing jobs + AI skills**, rather than entirely new titles.
- 2024 survey: AI tool skill requirement rose **68% YoY**, concentrated in data/design/content roles.
- New professions usually emerge **after tools mature** and create wholly new tasks.
---
## **Core Categories of New AI Professions**
Analyzing **718 recruitment postings** (as of Sept 15, 2025) from seven AI large model companies — OpenAI, Anthropic, DeepMind, DeepSeek, Kimi, Zhipu, Tongyi — reveals roles grouped into:
- **Enablers**
- **Collaborators**
- **Governors**
- **Promoters**
- **Supporters**
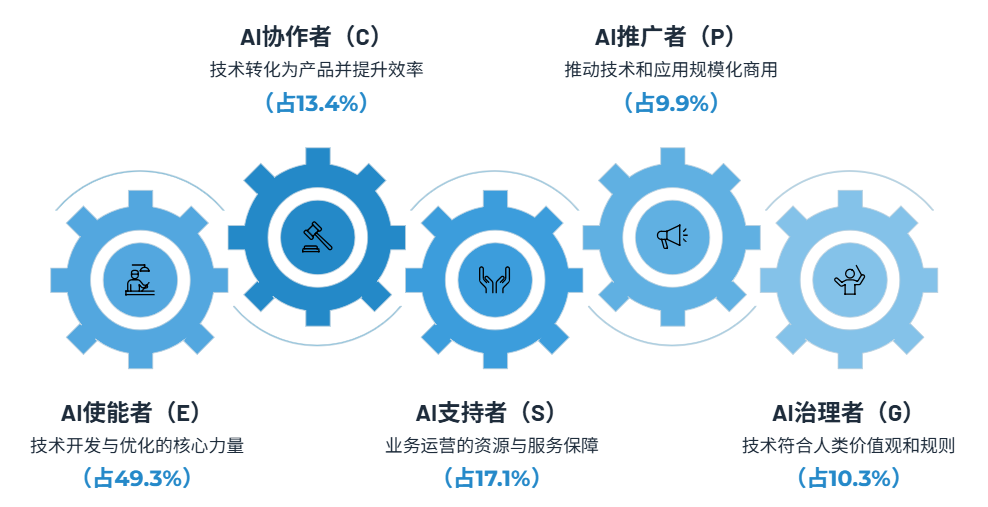
*Figure 1: Five core AI job categories and recruiting proportions*
---
### **1. AI Enablers**
Core **lifeblood** roles that develop, operate, and optimize AI tech to move it from theory into application.
**Examples:**
- AI research scientists
- Algorithm engineers
- Data engineers
- Data center engineers
- AI deployment managers
> Currently nearly **50%** of all AI job postings, showing the strong demand for foundational technical talent.
**Case Study — Frontline Deployment Engineer (FDE, OpenAI)**
- **Team:** Works with product, research, and marketing to deploy models into production.
- **Role:** Embedded at client front lines; solves "last mile" technical challenges; bridges AI potential to productivity.
- **Skills:** Full-stack delivery; understand client needs; refine methodology; coding expertise.
---
### **2. AI Collaborators**
Work at the interface between **people and AI**.
Specialists in maximizing AI tool effectiveness in workflows.
**Examples:**
- Prompt engineers
- AI trainers
- AI product managers
> Current share: **13.4%** — expected to grow with broader AI adoption.
**Case Study — Human-AI Collaboration Lead (OpenAI)**
- **Role:** Designs interaction modes and workflow integrations between people and AI.
- **Skills:** Field research; productivity studies; applied research; problem identification.
**Case Study — Agent Model & Data Product (Kimi)**
- **Role:** Designs and optimizes LLM prompts, contexts, agent capabilities.
- **Skills:** AI product or engineering expertise; deep model & agent knowledge; prompt engineering.
---
### **3. AI Governors**
Ensure AI development aligns with human values, ethics, and law.
**Examples:**
- AI ethics specialists
- Legal advisors
- Auditors
- Alignment engineers
- Safety engineers
**Case Study — Alignment Science Research Engineer/Scientist (Anthropic)**
- **Role:** ML experiments to control AI behavior; scalable oversight and alignment stress tests.
- **Skills:** ML research; familiarity with safety tech; reinforcement learning; large model experience.
---
### **4. AI Promoters**
Drive AI adoption in markets through promotion and customer enablement.
**Examples:**
- AI marketing managers
- Account managers
- Customer success
- GTM strategists
- User growth specialists
**Case Study — AI Success Architect (Anthropic)**
- **Role:** Strategic partner for enterprise API adoption; expand use cases.
- **Skills:** Customer-facing technical experience; API & integration knowledge; large model optimization.
---
### **5. AI Supporters**
Provide operational resources and support infrastructure.
**Examples:**
- AI finance managers
- HR managers
- Project managers
- Technical support engineers
**Case Study — GenAI Prototype Technical Project Manager (DeepMind)**
- **Role:** Plan/deliver technical prototype projects for GTM; ideate, design, test, iterate.
- **Skills:** Technical knowledge; PM expertise; creative problem-solving.
---
## **Four Shifts in AI Career Patterns**
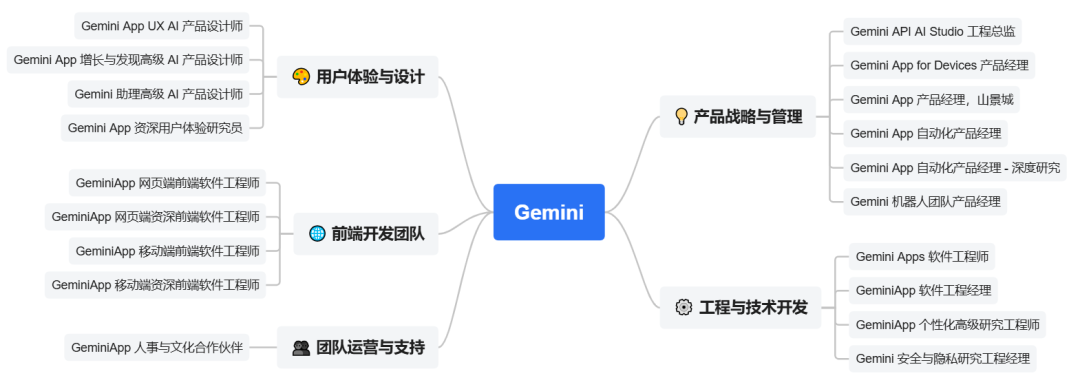
1. **Deep Specialization** — Jobs subdividing into micro‑technical fields (e.g., multimodal engineering, GPU kernels).

*Figure 2: AI software engineer subdivisions*
2. **Cross-Disciplinary Integration** — R&D + deployment; multi‑tech + multi‑business expertise; blend of technical and non‑technical skills.
3. **Human–AI Collaboration** — Roles designed to ensure safe, reliable joint work (e.g., AI Reliability Engineers).
4. **Rapid Rise & Fall of Certain Jobs** — Roles like *Prompt Engineer* & *Data Annotator* shifting to outsourcing/gig work as skills become baseline.
---
## **Future Career Growth: 3 Directions**
### **1. AI-Native**
- Immediate emergence in tech firms building AI.
- Current postings: ~84% technical roles; algorithms dominate.
- Non‑tech (product, governance) set for future growth.
### **2. Services Sector**
- Largest potential for employment expansion (China’s ~56% GDP vs US’s ~80% service sector).
- **AI + Services** → personalized HR, human–AI collaborative creative roles (livestreaming, AI digital humans).
- AI complements eldercare, community services.
### **3. One-Person Businesses & Gig Workforce**
- AI + platforms enables **task-based** work models.
- Flexible employment rising (China: 12.2% → 15.2% postings in 2023–2024).
- AI accelerates solo entrepreneurship across design, dev, content.
---
## **Adaptation Strategies Across Stakeholders**
### **Individual**
- Embrace AI & lifelong learning.
- Build AI literacy to be an **“AI super‑user”**.
- Explore flexible work & creative economy opportunities.
- Microsoft & LinkedIn: 75%+ see AI skills as central to competitiveness.
### **Enterprise**
- **Human‑centric AI transformation**: Use AI to augment, not replace.
- Involve employee representatives in risk assessment of AI systems.
- Example — Germany’s Deutsche Telekom **AI Declaration** with labor unions.
- Facilitate internal reskilling and career transitions (e.g., IKEA’s AI chatbot freeing staff for design advisor roles).
### **Society**
- Encourage AI innovation via subsidies, tax benefits, international cooperation.
- Support traditional enterprises in reskilling.
- Update social safety nets (e.g., unemployment insurance, transition funds).
- Explore **Universal Basic Income** pilots to equitably share AI productivity gains.

---
**Original text:** 《AI时代新职业发展趋势初探》 — *中国人力资源社会保障*, 2025年第10期.

---
## **Recommended Reading**
- 闫德利 — [《AI导致硅谷十万大裁员?》](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MjM5OTE0ODA2MQ==&mid=2650994060&idx=1&sn=5dec83c26db9412c0a64c58147902b1a&scene=21#wechat_redirect)
- 艾伦·麦克法兰 — [《我们很可能正走向一个“无工作社会”|腾研对话海外名家》](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MjM5OTE0ODA2MQ==&mid=2650993888&idx=1&sn=2b29ea8c352e1893c023f4846eca5787&scene=21#wechat_redirect)




