When Recommendation Systems Truly “Understand You”: Kuaishou Team Presents New TagCF Breakthrough at NeurIPS 2025

Understanding Users, Not Just Content — The TagCF Framework
Every day, recommendation systems capture our interests — from videos we scroll past to livestreams where we pause.
Most algorithms focus on understanding content (what topics you like) rather than understanding people (Who are you?).
The Kuaishou Consumer Strategy Algorithm Team identified this gap and, in collaboration with Kuaishou’s Foundation Model & Applications Department and Wuhan University, proposed TagCF — a framework that bridges content interests with social roles.
This approach moves recommendation systems from knowing what happens to knowing why it happens.
> Accepted at NeurIPS 2025 — All related code and experimental frameworks are open-sourced to help academia and industry explore recommendation systems built on deeper user understanding.

---
Resources
- Paper Title: Who You Are Matters: Bridging Topics and Social Roles via LLM-Enhanced Logical Recommendation
- Paper Link: http://arxiv.org/abs/2505.10940
- Code Repository: https://github.com/Code2Q/TagCF
---
1. Background & Motivation
User Understanding: A Missing Dimension
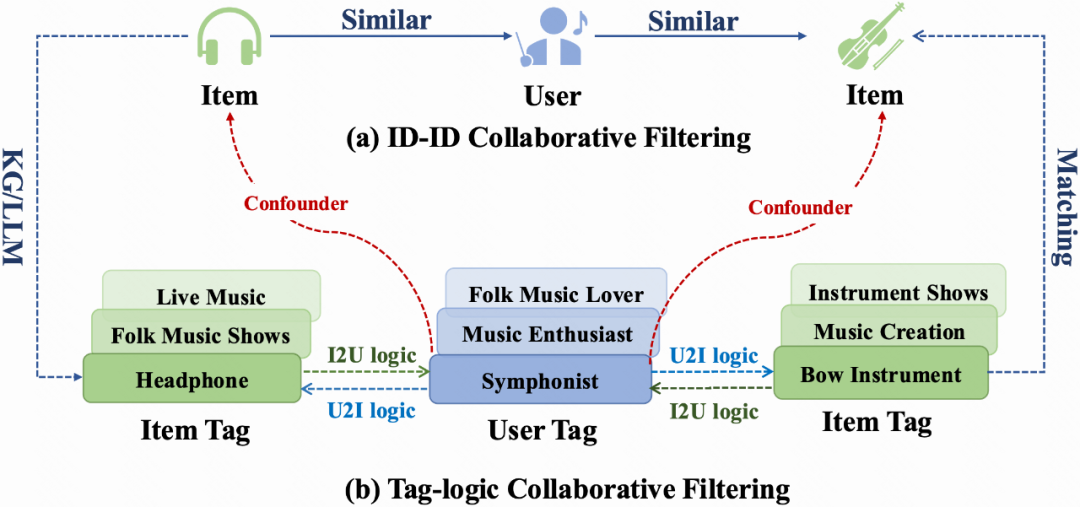
Figure 2
Traditional systems statistically model associations between content items — but the true underlying factor is often the user role (e.g., symphony musician, new dad).
User roles act as latent confounders in these relationships, and explicitly modeling them:
- Improves interpretability
- Enhances statistical and logical modeling power
- Helps break users out of “information cocoons”
- Boosts recommendation accuracy and stability
> Terminology
> - User Tag ≈ User Role ≈ User Attribute
> - Item Tag ≈ Item Topic ≈ Point of Interest
---
2. Two New Tasks Introduced
TagCF extends traditional recommendation with topic modeling concepts, defining:
2.1 User Role Identification
Modeling traits, personality, social identity, and needs (explicit attributes such as age, gender, etc.).
2.2 Behavioral Logic Modeling
Constructing logical association graphs between user roles and item topics:
- I2U (Item-to-User): Identify which roles should see content with certain topics
- U2I (User-to-Item): Predict what topics a specific role is likely to want
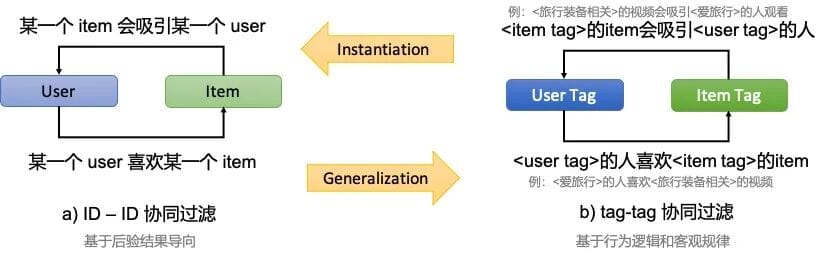
Figure 3
---
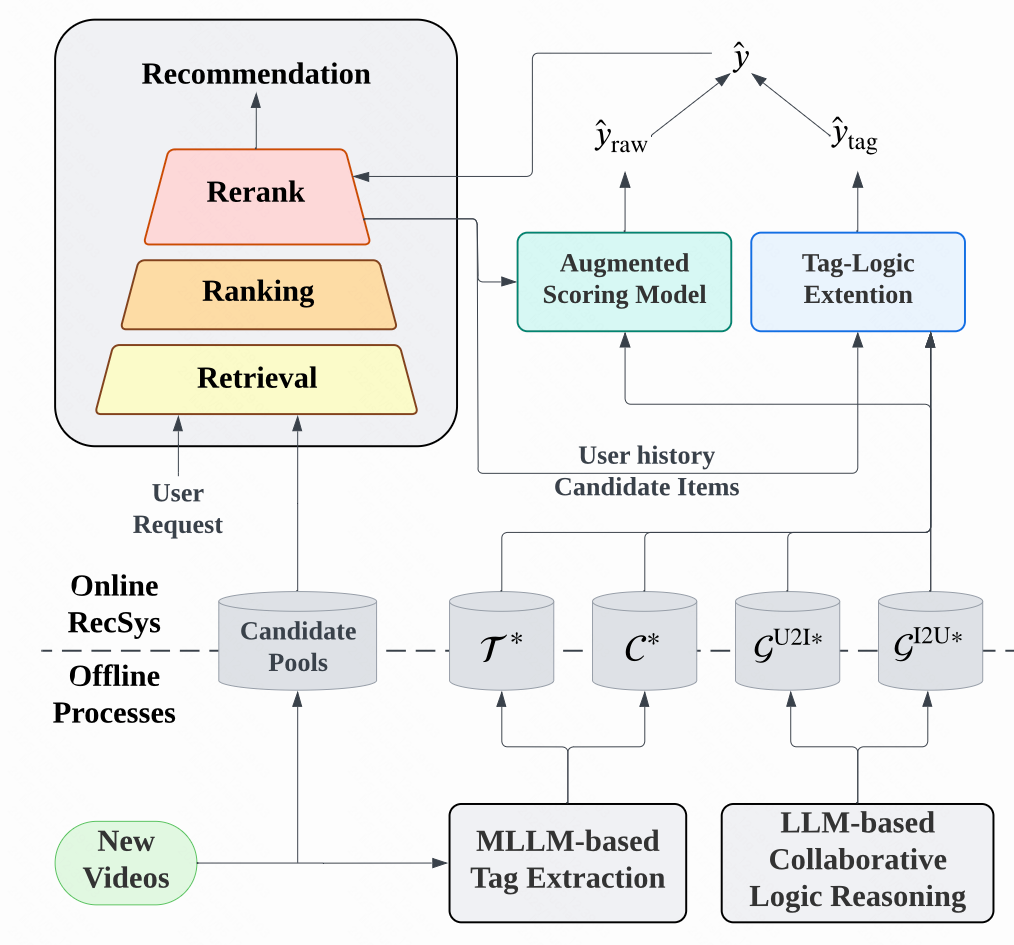
3. TagCF Solution Architecture
Module 1 — Video Content Understanding (MLLM-Based)
- Traverse newly uploaded videos (after reaching exposure threshold).
- Use MLLM (M3 [1]) to:
- Extract multimodal video embeddings.
- Interpret semantics via specially designed prompts (Figure 5).
- Generate Item Tags and User Tags.
- Update the tag library in real time.

Figure 5
---
Module 2 — Behavior Logic Graph Construction (LLM-Based)
- Build U2I and I2U logic graphs from tag sets.
- Use QWen2.5-7B [2] to reason logical relationships between start and target tags (Figure 6).
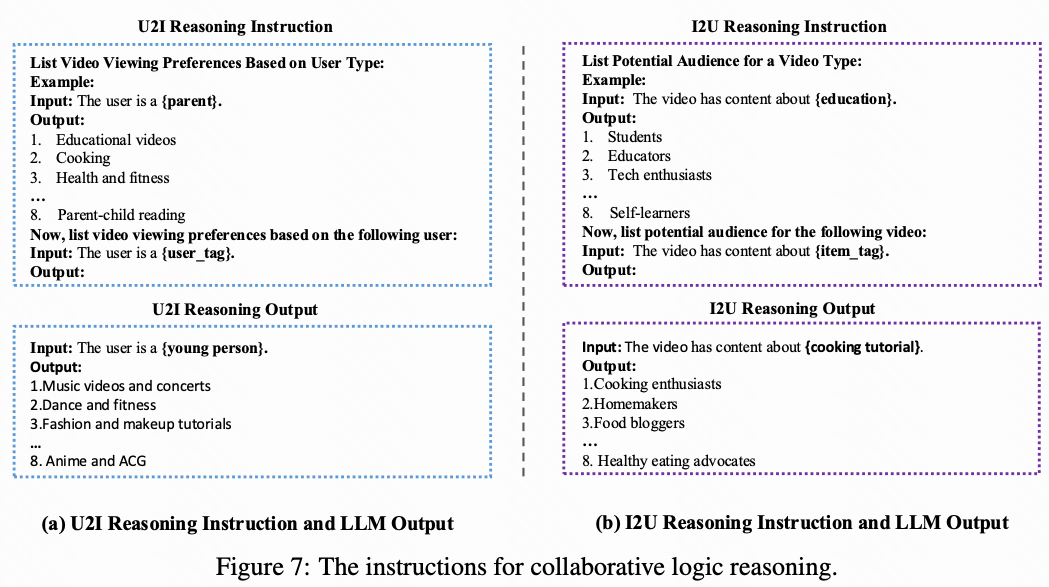
Figure 6
---
Module 3 — Downstream Recommendation Empowerment
- Enhance recommendation models with tag and logic data (LLM-for-rec paradigm).
- Maintain modeling space consistency using:
- TagCF-it: Item tag space focus
- TagCF-ut: User tag space focus
Enhancement Methods:
- Encoder model enhancement using tags
- Training enhancement via tag-logic alignment
- Prediction score adjustment using tag-logic
---
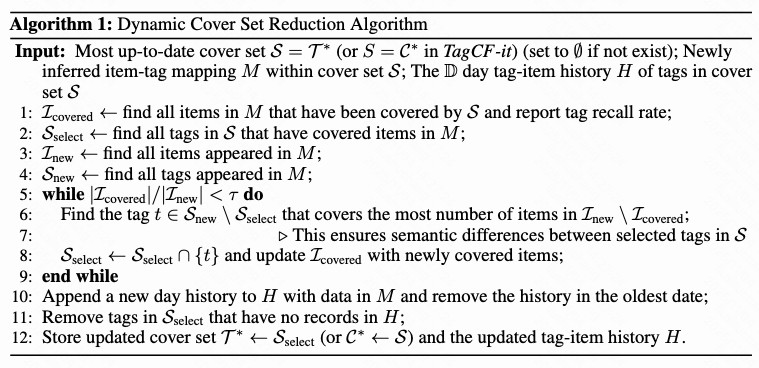
4. Engineering Challenges & Solutions
Challenges:
- Uncontrolled tag set expansion
- Long-tail video coverage distribution
- Conflict between free-form generation and strict scoring needs
- Lack of evaluation methods for large-model outputs
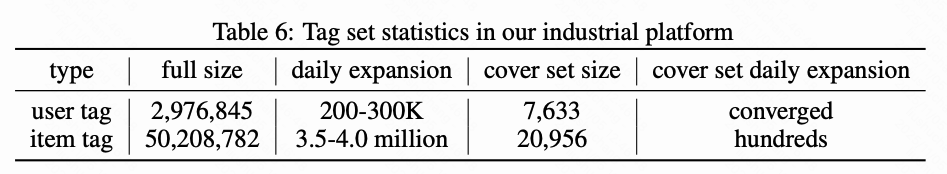
Solutions:
- High-Frequency Tag Cover Sets
- Weak-overlap, symmetric cover sets for user tags & item tags
- Size: ~7k–20k, stable in ~30 days
- Model Distillation
- Train small models from large-model item2tag/tag2tag outputs for fine-grained ranking and reuse.
- Manual Comparative Evaluation
- “Good–Same–Bad” strategy across accuracy, completeness, rationality, readability — quality close to GPT-4o.
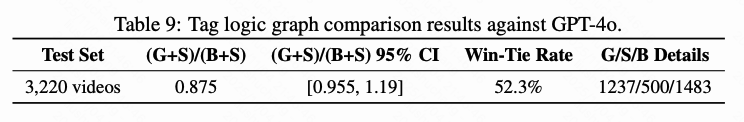

---
5. Explicit Filter-Bubble Control
TagCF introduces controllable cocoon-breaking strategies:
- TagCF-util: Use only in-cocoon tag set (T(0)) → focus on accuracy.
- TagCF-expl: Use union of T(0) + out-of-cocoon set (T(1)) → improve diversity.
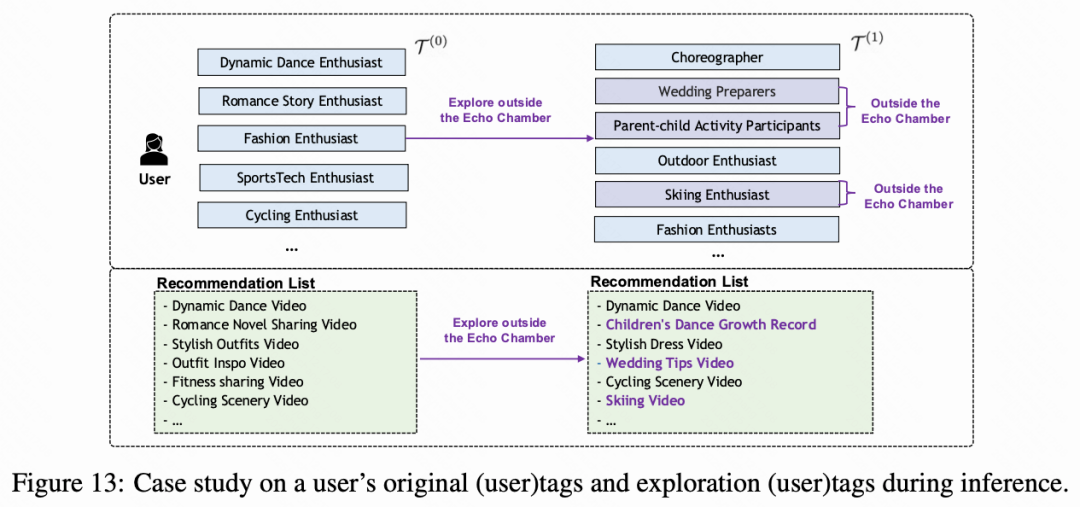
---
6. Experimental Results
6.1 Offline
Metrics:
- Accuracy: NDCG, MRR
- Diversity: Cover, Gini
Findings:
- TagCF improves backbone model performance.
- Logic graph backend is transferable.
- TagCF-util excels in accuracy.
- TagCF-expl boosts diversity.

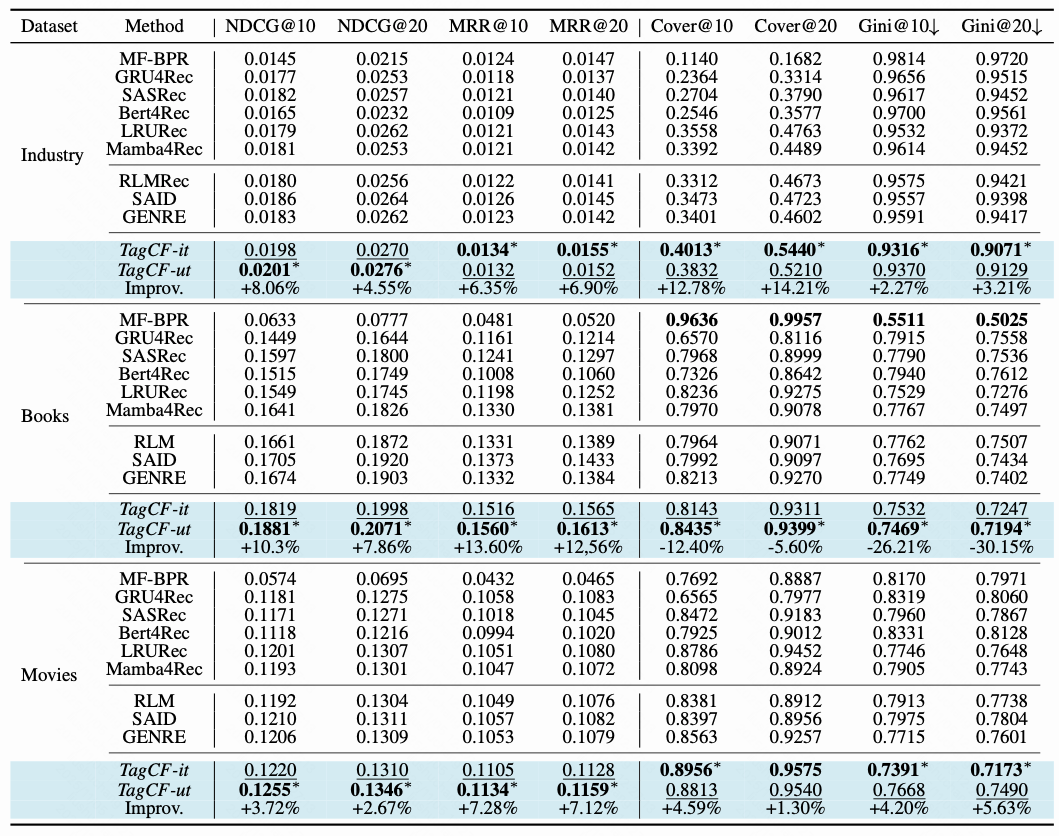
---
6.2 Online
Workflow:
Results:
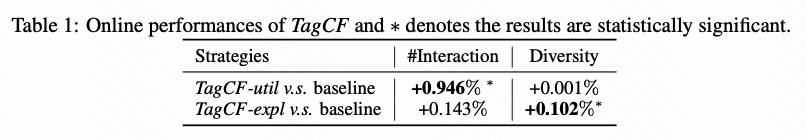
- TagCF-expl improved long-term retention (LT +0.037%).
- User tag sets: smaller sets, faster convergence, stronger enhancements vs. item tags.
---
7. Summary & Outlook
Contributions:
- Balanced video understanding & user understanding in recommendation.
- Developed TagCF with strong transferability — applicable to recall, e-commerce, search, and beyond.
- Enabled explicit user cocoon modeling and control.
Significance:
- Moves recsys from statistical guessing → logical human understanding.
- Bridges symbolic & statistical paradigms in large-model-powered recommendations.
- Framework complements open ecosystems like AiToEarn官网 for AI-assisted content creation, cross-platform publishing, and monetization.
Future Work:
- Refine tag-logic backend for efficiency.
- Extend application scenarios.
- Maintain balance between accuracy and diversity in recommendation.
---
References
[1] Mu Cai, Jianwei Yang, Jianfeng Gao, and Yong Jae Lee. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2025.
[2] An Yang et al. Qwen2.5 Technical Report. arXiv:2412.15115, 2024.
[3] Zhou, Guorui et al. OneRec Technical Report. arXiv:2506.13695, 2025.
[4] Zhang, Kaike et al. GoalRank: Group-Relative Optimization for a Large Ranking Model. arXiv:2509.22046, 2025.



