Why Can’t LLMs Handle Complex Tasks? Overview of ReAct and Reflexion Techniques
# Advanced Prompt Engineering: ReAct & Reflexion Frameworks for LLMs
In **Artificial Intelligence** — particularly in the application of **large language models (LLMs)** — models perform remarkably well on many tasks but still face clear limitations in complex scenarios. Tasks requiring **multi-step reasoning**, **real-time information retrieval**, and **dynamic decision-making** remain challenging.
## Common Limitations of LLMs
- **Fact hallucination**: Generating plausible but inaccurate information.
- **Lack of real-time data**: Unable to access new information post-training cutoff.
- **Insufficient planning ability**: Struggles to decompose and strategize for complex tasks.
- **Error propagation**: One wrong inference can derail the entire output.
Researchers have proposed prompt engineering frameworks to address these issues. Two notable ones are:
- **ReAct** (**Reasoning + Acting**)
- **Reflexion** (**Self-Reflection**)
By embedding reasoning, action, and reflection mechanisms, these frameworks **significantly enhance LLM performance** in knowledge-intensive, decision-making, and programming tasks.
This article explains **ReAct**, its mechanics, and applications, then discusses **Reflexion** as a self-reflective extension, before exploring their combination.
---
## ReAct Framework: Coordinating Reasoning and Action
### Core Concept
Proposed by **Yao et al., 2022**, ReAct combines *Reasoning* and *Acting* to mimic human decision-making:
- **Reasoning**: Internal thought traces (similar to Chain-of-Thought) for task decomposition and strategic planning.
- **Acting**: Executable actions (e.g., search queries, calculations) to retrieve real-time external information.
ReAct operates on a **Think → Act → Observe → Think again** loop, merging internal reasoning with external tool use.
### Problems Solved
- **CoT-only approaches**: Cannot interact with the world, prone to hallucinations.
- **Act-only approaches**: Lack planning, underperform on multi-step tasks.
ReAct **reduces hallucinations** by verifying facts during actions and decomposes problems using reasoning steps.
### How It Works
1. Select and rewrite examples into "Thought–Action–Observation" trajectories.
2. Add them as **few-shot prompts** to the LLM.
3. LLM follows this loop until completion.
---
### Sample ReAct Trajectory
**Task**: Clean a greasy frying pan
Thought: The pan is greasy; soap alone may not work well. First, remove excess grease.
Action: Scrape off solid grease with a spatula.
Observation: Most solid grease removed.
Thought: Use hot water + dish soap next.
Action: Soak in hot soapy water for 10 minutes.
Observation: Remaining grease loosened.
Thought: Finish by scrubbing, rinsing, and drying.
Final Answer: Pan cleaned successfully.
---
## Practical Applications of ReAct
### 1. Knowledge-Intensive Question Answering
Avoid hallucinations by retrieving real-time data.agent.run("Who won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics? What were their main contributions?")
### 2. Complex Decision-Making
Dynamic planning for multi-step tasks.agent.run("Plan a weekend family trip for three from Beijing to Tianjin with a budget of 3000 RMB")
### 3. Data Analysis and Computation
Integrate calculators and analysis tools.agent.run("Calculate quarterly sales growth rates for 2023 and forecast Q1 2024 sales")
### 4. Customer Service
Fetch information to solve real-time issues.agent.run("A user reports they cannot log in, error code AUTH-001, please provide a solution")
### 5. Programming Assistance
Automate code generation, debugging, and technical advice.agent.run("Create a React component implementing a user login form with email and password validation")
---
## Implementing ReAct Agents with LangChain
1. **Initialize LLM and tools**
2. **Create agent** using `initialize_agent`
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
llm = ... # Initialize LLM
tools = [...] # Define tools
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent_type="react")
**Tip:** Frameworks like **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)** can integrate with ReAct pipelines for publishing AI-generated content across platforms (**Douyin, WeChat, YouTube, Instagram**, etc.), enabling monetization while leveraging intelligent reasoning.
---
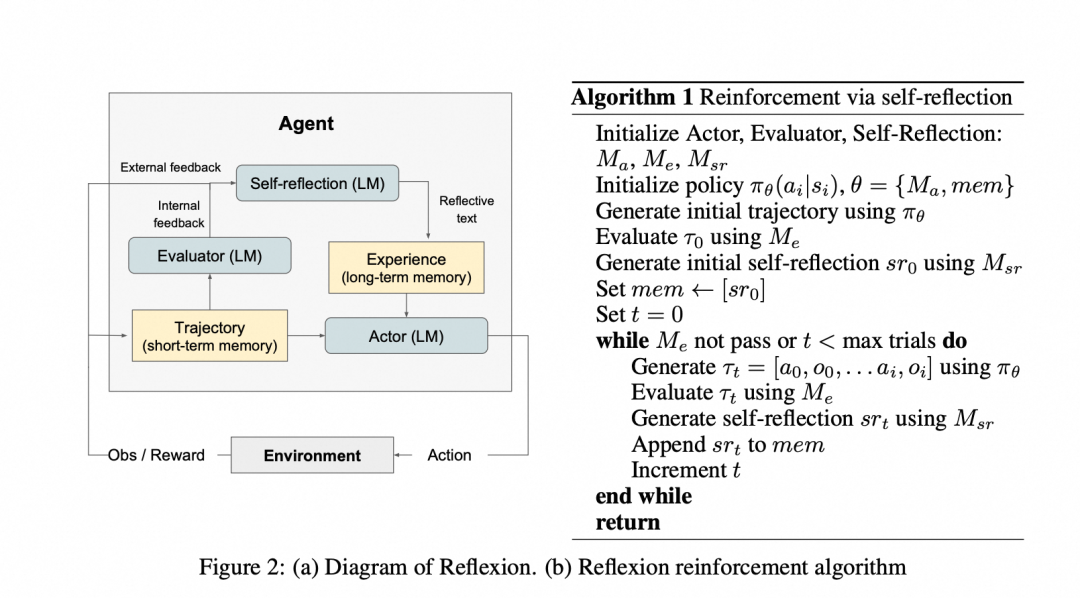
## Reflexion: Self-Reflection for LLMs
### Core Concept
Proposed by **Shinn et al.**, Reflexion extends ReAct with reinforcement learning via **language-based feedback**, simulating human self-reflection.
**Components:**
- **Actor**: Generates actions (*via ReAct or CoT*).
- **Evaluator**: Scores the action trajectory (success/failure).
- **Self-Reflection**: Produces improvement suggestions stored in memory.
**Workflow**: Action → Evaluation → Reflection → Iteration
---
### Example Reflexion Process
**Initial Attempt**:
- **Thought**: Clean quickly with cold water.
- **Action**: Rinse with cold water; dry.
- **Observation**: Grease remains.
- **Evaluation**: Failure.
- **Reflection**: Use hot water, dish soap, baking soda next time.
**Improved Attempt**:
- **Thought**: Use hot water & degreaser.
- **Action**: Search "greasy pan cleaning steps".
- **Observation**: Steps found; execute.
- **Evaluation**: Success.
---
## Differences: ReAct vs Reflexion
| Feature | ReAct | Reflexion |
|-----------------------|--------------------------------------|-------------------------------------|
| Core Process | Reasoning–Action–Observation loop | Adds Evaluation + Reflection steps |
| Goal | Real-time dynamic task solving | Long-term improvement via memory |
| Best For | Immediate reasoning tasks | Iterative optimization tasks |
**Integration:** Reflexion can use ReAct as its **Actor** component, combining:
- **ReAct:** Dynamic reasoning.
- **Reflexion:** Reflective learning & memory.
---
## Performance Highlights
- **Decision-Making (AlfWorld)**: Reflexion > ReAct, near full task success.
- **Reasoning (HotPotQA)**: Surpasses CoT after few iterations.
- **Programming (HumanEval)**: Outperforms SOTA in multiple languages.
---
## Future Directions
1. **Improved Memory Management**: Smarter storage/retrieval/forgetting.
2. **Evaluator Accuracy**: Reduce misjudgments.
3. **Multimodal Integration**: Add vision, speech channels.
4. **Personalization**: Adapt strategies to user preferences.
5. **Explainability**: More transparent reasoning.
---
### In Practice
Pairing these frameworks with distribution tools like **[AiToEarn官网](https://aitoearn.ai/)** allows creators to:
- Generate high-quality, reflective AI output.
- Publish across major global/social channels.
- Track analytics and monetize effectively.
---
**References:**
- *ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models*
- *Reflexion: Language Agents with Verbal Reinforcement Learning* ([PDF](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.11366))
---


