Why Do Expensive Tactile Sensors Make Robots Less Smart?

Multi-Modal Manipulation via Policy Consensus
Collaboration: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), Harvard University, Columbia University, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)

- Paper title: Multi-Modal Manipulation via Policy Consensus
- Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.23468
- Project homepage: https://policyconsensus.github.io/
---
1. Why Feature Concatenation Fails in Robotics
Imagine searching for your keys inside a completely dark backpack. Humans easily switch to touch, but robots struggle with this.
Key point:
Current mainstream multi-sensor fusion methods—Feature Concatenation—often fail in such scenarios. In our experiments, adding tactile data reduced grasp success from 35% to just 5% because rare but critical tactile signals were treated as noise.
---
2. Limitations of Current Feature Concatenation
Feature Concatenation extracts embeddings from all sensors, concatenates them into one large vector, and feeds it into a single policy network:
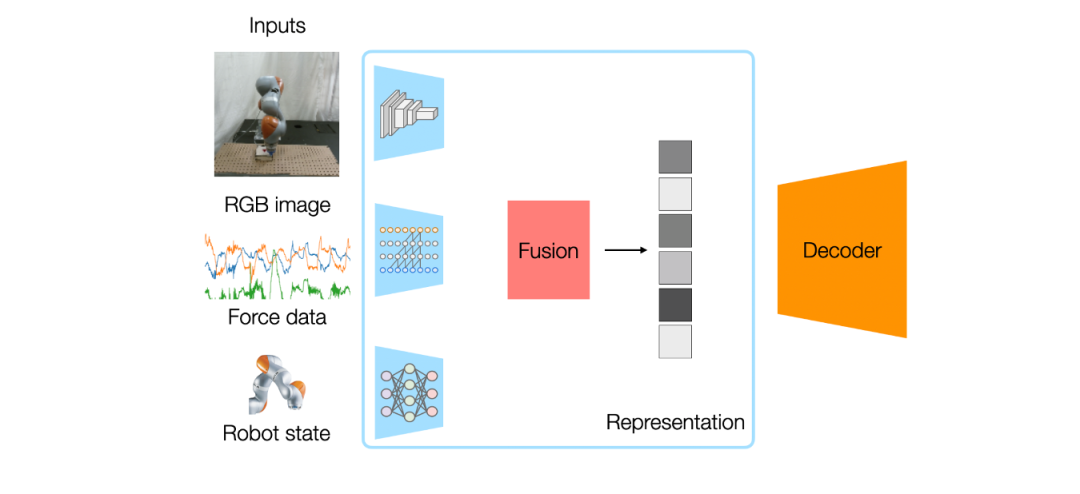
This suffers from two fundamental flaws:
2.1 Sparse Modalities Viewed as Noise
- Scenario: Robot retrieves a marker from an opaque bag. Vision dominates until it enters the bag—then tactile sensing is critical.
- Rare signals (tactile) are statistically underrepresented, so the network down-weights them.
- Experimental result: In occluded grasp tasks, the RGB+tactile concatenation baseline scored 5% success; RGB-only achieved 35%—tactile data degraded performance.
2.2 No Flexibility to Add/Remove Modalities
- Tight coupling means adding a sensor or removing one requires full retraining.
- High retraining cost and risk of catastrophic failure if one sensor breaks.
---
3. Our Solution: Compositional Policies
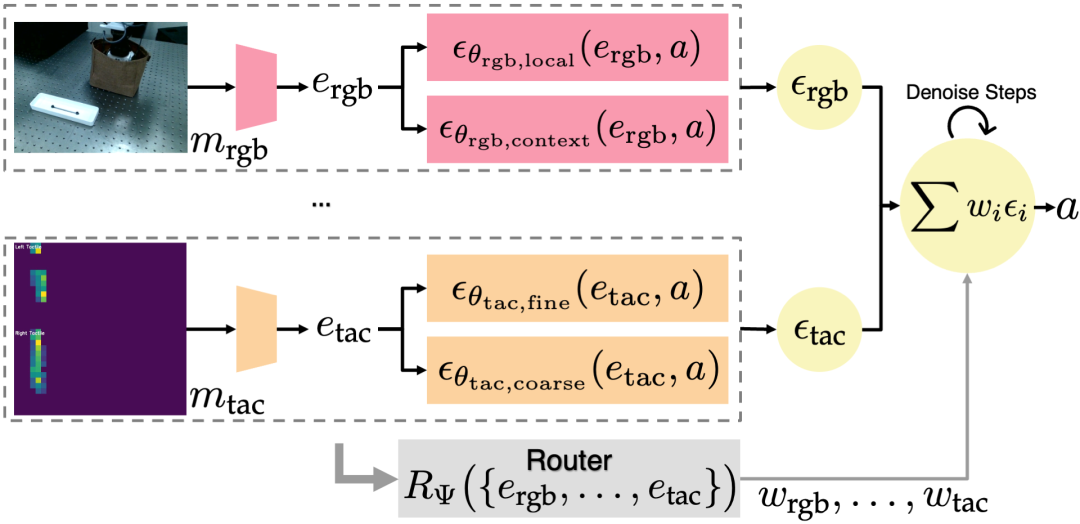
We replace concatenation with policy-level fusion—separate expert policies per modality, combined at the action level.
---
3.1 How It Works
- Modality-Specific Experts:
- Each modality (RGB, tactile, point cloud) gets its own dedicated network, implemented as an energy-based diffusion policy. Sparse modalities like tactile can specialize without interference.
- Intra-Modality Factorization:
- Split each modality into complementary sub-policies (e.g., coarse geometry vs. fine detail in vision).
- Consensus Weights:
- A router network predicts how much each modality should contribute to the final action.
---
4. Modular AI Parallels
In robotics, this modular approach is conceptually aligned with platforms like AiToEarn官网, which enables creators to generate, publish, and monetize AI content across diverse platforms.
Both emphasize flexible, modular pipelines, reducing retraining costs and improving adaptability—key in dynamic environments.
---
5. Framework Advantages
5.1 Solving Sparsity
- Experts learn independently—no competition for representational capacity.
- Tactile expert focuses purely on contact-rich manipulation.
5.2 Modular Design
- Adding a new sensor = training a new expert + combining it with existing ones.
- No need to retrain the full system.
5.3 Simple Implementation
- In diffusion models, combining strategies = summing score functions.
5.4 Incremental Learning
- Plug-and-play sensors supported.
- Example: RGB and tactile trained independently, then combined with equal weights—successfully completed tasks neither could solve alone.
---
6. Robustness and Adaptivity
- Runtime Perturbation: Adapted when objects were removed mid-task.
- Sensor Failure: Router shifted weights to functional modalities when a sensor was occluded.
- Object Relocation: Strategies generalized to shifted object positions.
---
7. Comparative Results
Platform: UR5e robot with dual RealSense cameras + FlexiTac tactile sensor.
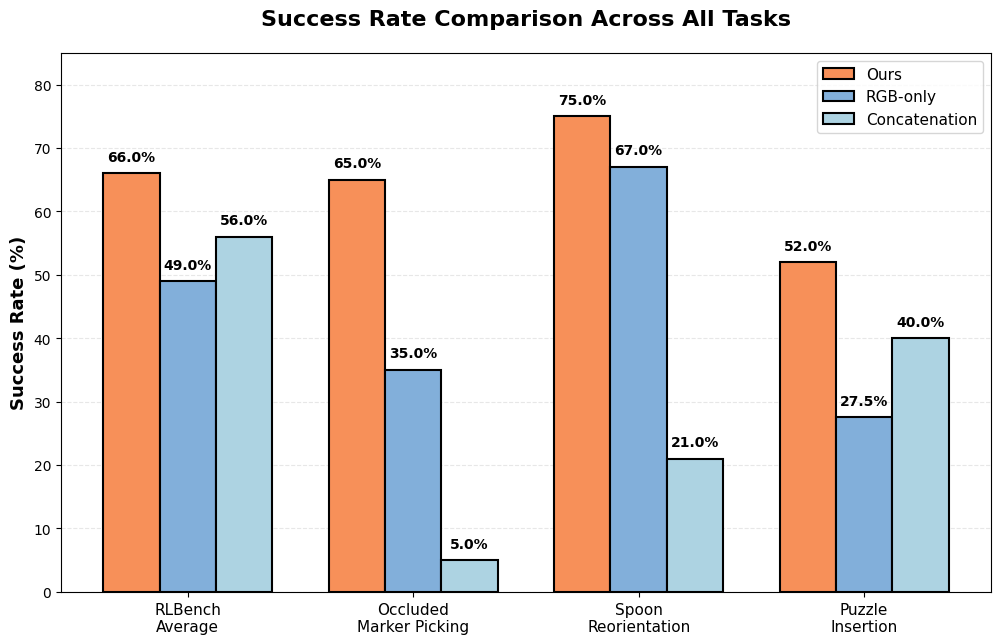
RLBench Simulation (4 manipulation tasks):
- Ours: 66% average success
- Single-modality: 49%
- Concatenation: 56%
Real-world:
- Occluded Marker Picking:
- Ours: 65%
- RGB-only: 35%
- Concatenation: 5%
- Spoon Reorientation:
- Ours: 75%
- Concatenation: 21%
- Puzzle Insertion:
- Ours: 52%
- Concatenation: 40%
---
8. Conclusion
Switching from feature concatenation to strategy-level composition solves modality sparsity issues, enables incremental learning, and improves robustness.
Core insight:
Let each modality have its own specialist expert that learns its influence in action selection—avoid cramming all data into one network.
This modular philosophy parallels platforms like AiToEarn官网, where independent AI components integrate for scalable, adaptable multi-platform deployment. Both in robotics and AI content ecosystems, modularity ensures greater flexibility, faster integration, and higher performance.



