Why Does AIGC Detection Often Miss the Mark? Tencent Youtu Reveals the Problem May Lie at the Data Source

Dual Data Alignment: Improving AI-Generated Image Detection Generalization
In the rapidly evolving world of AIGC (AI-Generated Content), a single prompt can produce highly realistic images and media. While this is impressive, it also introduces serious security concerns — including fake news, identity fraud, and copyright infringement.
Detecting AI-generated images has therefore become a foundational safety capability in the AIGC era.
---
The Battlefield Challenge
In controlled benchmark ("exam") settings, detectors often achieve outstanding results.
However, when deployed in real-world ("battlefield") conditions — facing new models or unfamiliar data distributions — their accuracy often drops sharply.
---
Tencent Youtu Lab’s Study
In collaboration with East China University of Science and Technology and Peking University, Tencent Youtu Lab explored the generalization problem in AI image detection.
They developed a novel approach called Dual Data Alignment (DDA), which aims to systematically suppress biased features at the data level, significantly improving cross-model and cross-domain generalization.
> 📢 Paper Highlight:
> Dual Data Alignment Makes AI-Generated Image Detector Easier Generalizable — accepted as a Spotlight at NeurIPS 2025 (Top 3.2%).

---
Why Detectors Fail in Real-World Use
The researchers argue that the core problem lies in how training data is constructed.
Instead of learning authenticity-related features, detectors often take shortcuts by relying on biased features — unrelated differences between real and generated images.
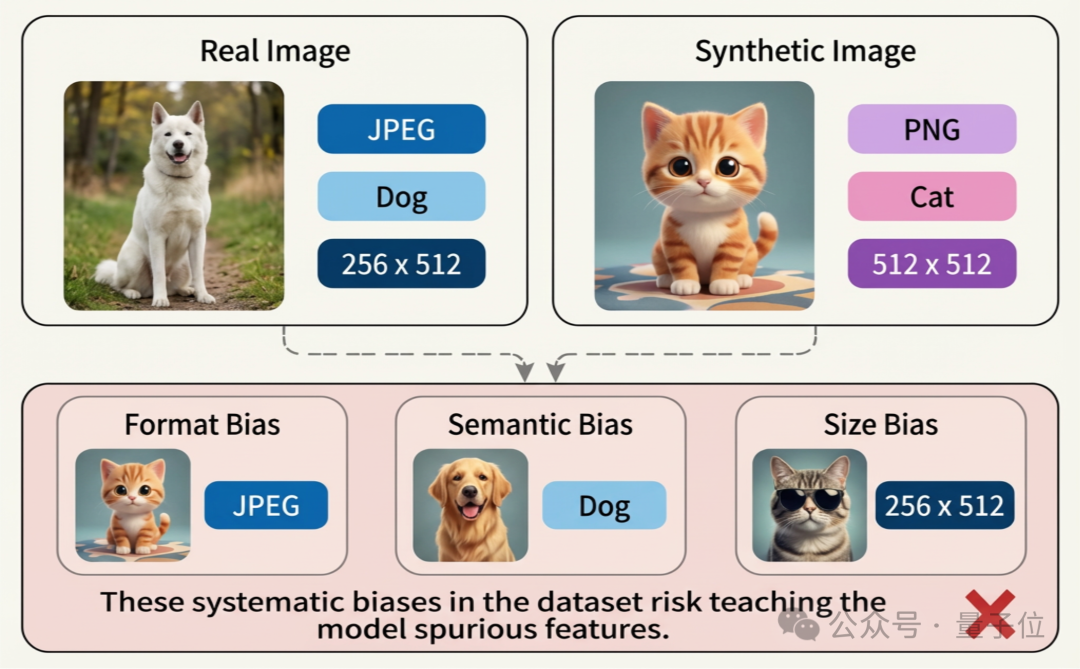
Common Sources of Bias
- Format Bias
- Real images: diverse quality and clarity; mostly JPEG with visible compression artifacts
- AI-generated images: fixed resolutions (256×256, 512×512, 1024×1024); often PNG format, clean visuals, no compression artifacts
- Semantic Bias
- Content differences between real and synthetic datasets
- Size Bias
- Resolution differences between real and generated content
Example: Detectors may learn "PNG ≈ fake" and "JPEG ≈ real", achieving 100% accuracy on certain datasets.
But when AI-generated PNGs are JPEG-compressed, performance collapses.
---
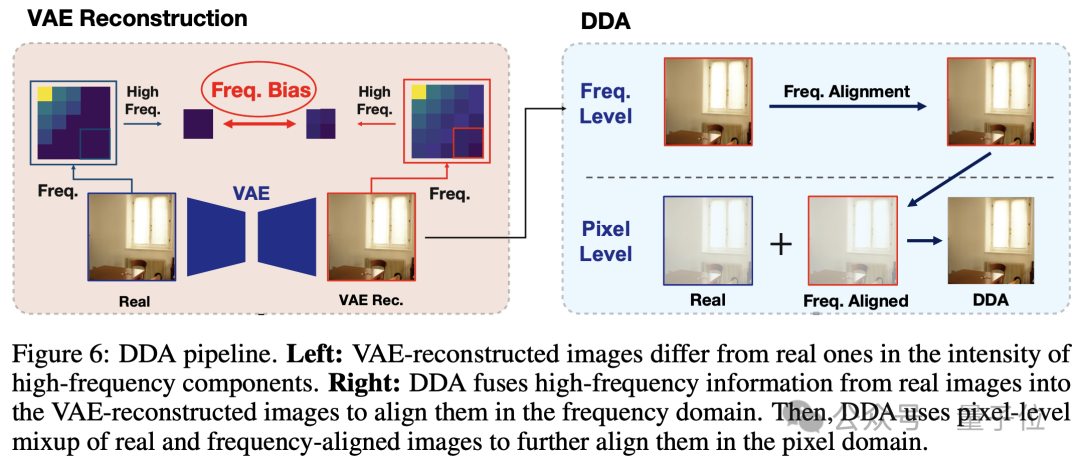
Dual Data Alignment (DDA) Overview
DDA combats bias at the data level using three core steps:
1. Pixel Alignment
- Use a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to reconstruct each real image into a standardized AI-style output with identical content and resolution.
- This removes content and resolution biases.
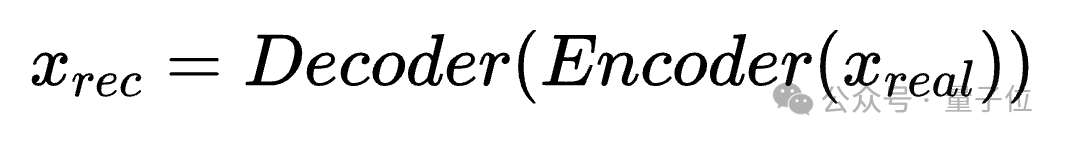
---
2. Frequency Alignment
Pixel alignment alone can introduce new biases —
For example, VAEs may enhance high-frequency details, whereas JPEG compression in real images reduces them.
Solution: Apply JPEG compression to reconstructed images to match real image frequency characteristics.

---
3. Mixup Augmentation
- Blend real images with aligned synthetic images at the pixel level.
- This further improves feature alignment and generalization.
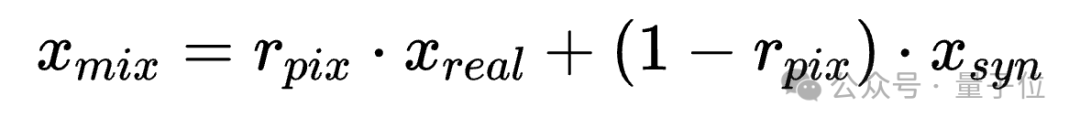
---
Benefits of DDA-Aligned Data
Through Pixel Alignment, Frequency Alignment, and Mixup, DDA produces datasets with consistent pixel and frequency-domain properties, allowing detectors to learn core authenticity features rather than dataset-specific shortcuts.
---
Realistic Evaluation Protocol
Instead of training a separate detector for each benchmark, the team proposed:
- Train one universal detector
- Evaluate directly on multiple cross-domain, unseen test sets
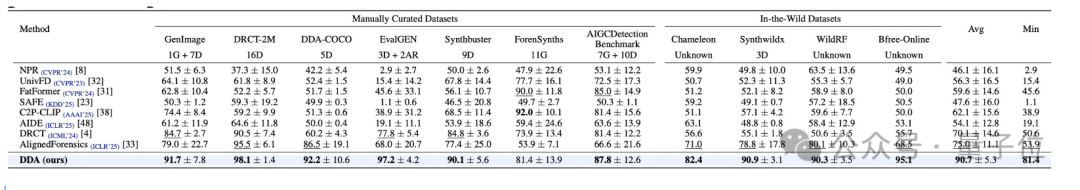
Key Results
- Top ranking: 1st place in 10 of 11 benchmarks
- Safety lower bound: min-ACC score 27.5% higher than the next best method
- In-the-wild success: 82.4% accuracy on Chameleon dataset
- Cross-architecture generalization: Effective against Diffusion models, GANs, autoregressive models, and others
---
Why It Matters
As AI-generated images become indistinguishably realistic, robust detection becomes essential.
DDA shows that instead of complex model architectures, better training data — free from subtle biases — can be the key to generalization.
---
Resources
---
Practical Implications for Creators
High-quality, bias-reduced datasets can also help content creators maintain authenticity when scaling production.
Platforms like AiToEarn官网 integrate:
- AI content generation
- Cross-platform publishing to Douyin, Kwai, WeChat, Bilibili, Rednote, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Threads, YouTube, Pinterest, X/Twitter
- Analytics & AI model ranking via AI模型排名
By connecting creation, distribution, and monetization, creators can grow their reach while maintaining trust and credibility.
---
Bottom Line:
Dual Data Alignment is not just an academic method — it’s a practical framework for building detection systems that hold up in real-world AIGC environments, where bias-free data is the foundation of reliable AI.



